paper
... The goal of this experiment was to measure the delay of a long optical path in order to predict the influence of the fibre thermal dilatation on changes of the link asymmetry. 1PPS from a local clock was transmitted in both directions and using two time interval counters, the delays δAB and δBA (Fig ...
... The goal of this experiment was to measure the delay of a long optical path in order to predict the influence of the fibre thermal dilatation on changes of the link asymmetry. 1PPS from a local clock was transmitted in both directions and using two time interval counters, the delays δAB and δBA (Fig ...
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
... The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In a uniform medium (where the refractive index is the same everywhere) the rays are straight lines, tho ...
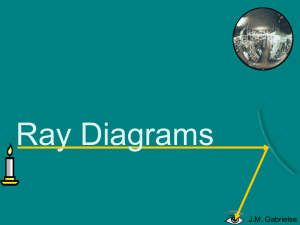
Ray Diagrams
... Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Download PDF
... field. For clarity, the values of normalized backscattered intensities have been scaled as indicated. To account for instrumentation effects we use a twofold fitting procedure. First, the trail of the distribution is fitted with 25y2 dependence to yield an amplitude normalization constant and, secon ...
... field. For clarity, the values of normalized backscattered intensities have been scaled as indicated. To account for instrumentation effects we use a twofold fitting procedure. First, the trail of the distribution is fitted with 25y2 dependence to yield an amplitude normalization constant and, secon ...
1 - Capanina
... Radio Frequency vs. Optical Communication – some considerations (Shlomi) 1.5p It will be clear from the preceding sections that optical communications can provide the very large data-rates required for broadband communications, by virtue of both the high frequency of the optical carrier and the vast ...
... Radio Frequency vs. Optical Communication – some considerations (Shlomi) 1.5p It will be clear from the preceding sections that optical communications can provide the very large data-rates required for broadband communications, by virtue of both the high frequency of the optical carrier and the vast ...
Glossary (PDF file)
... reflect To bounce back from a surface. We can see things because light reflects off of them and travels to our eyes. Some objects reflect light better than others. refraction The bending of light when it moves from one material to another. Light travels at different speeds through different materials. ...
... reflect To bounce back from a surface. We can see things because light reflects off of them and travels to our eyes. Some objects reflect light better than others. refraction The bending of light when it moves from one material to another. Light travels at different speeds through different materials. ...
Integration of a semiconductor laser source on silicon
... t is expected that in year 2020, there will be six devices connected to the Internet for each person on the planet! The era of “Internet of Things” has the potential to optimize our way of living but doing so it will generate enormous amounts of data which has to be processed and analyzed in real ti ...
... t is expected that in year 2020, there will be six devices connected to the Internet for each person on the planet! The era of “Internet of Things” has the potential to optimize our way of living but doing so it will generate enormous amounts of data which has to be processed and analyzed in real ti ...
TEM - UiO
... A diffraction pattern is always formed at the back focal plane of the objective (even in OM). To view this diffraction pattern one has to change the excitation of the intermediate lens. A higher strength projects the specimen image on the screen, a lower strength project the DP. The optical system o ...
... A diffraction pattern is always formed at the back focal plane of the objective (even in OM). To view this diffraction pattern one has to change the excitation of the intermediate lens. A higher strength projects the specimen image on the screen, a lower strength project the DP. The optical system o ...
Youngs Double Slit
... The double slit slide has several sets of slits. Use black tape to leave one set of slits only. Set up the white light or white LED source on the optical bench. Bring the slit up close to the eye and view the light source. What do you see? The interference pattern can only occur when the light diffr ...
... The double slit slide has several sets of slits. Use black tape to leave one set of slits only. Set up the white light or white LED source on the optical bench. Bring the slit up close to the eye and view the light source. What do you see? The interference pattern can only occur when the light diffr ...
2nd Semester Review
... If your answer to that question is No, ASK someone how to use it. It will help you on the final exam! ...
... If your answer to that question is No, ASK someone how to use it. It will help you on the final exam! ...
Telescopes for CCD Imaging
... your primary interest is planetary imaging. There is a certain optimum distance that must be maintained between the secondary and primary mirrors. If this spacing is allowed to deviate much more than a few millimeters, significant deterioration of performance will result due to spherical aberratio ...
... your primary interest is planetary imaging. There is a certain optimum distance that must be maintained between the secondary and primary mirrors. If this spacing is allowed to deviate much more than a few millimeters, significant deterioration of performance will result due to spherical aberratio ...
Practical Calculations for Designing a Newtonian Telescope
... A Newtonian reflecting telescope can be designed to perform more efficiently than any other type of optical system, if one is careful to follow the laws of nature. One must have optics made from precision Pyrex or a similar material and figured to a high quality. The mounting hardware must be well p ...
... A Newtonian reflecting telescope can be designed to perform more efficiently than any other type of optical system, if one is careful to follow the laws of nature. One must have optics made from precision Pyrex or a similar material and figured to a high quality. The mounting hardware must be well p ...
1. INTRODUCTION
... seen on the viewing screen to be in a steady state of drift when the optical beat frequency f is less than 10 Hz. The radio transceivers have a frequency stability of better than 0. 1 Hz per 10 5, 50 that it is easy to adjust their frequencies to maintain a steady drifting of the interference fringe ...
... seen on the viewing screen to be in a steady state of drift when the optical beat frequency f is less than 10 Hz. The radio transceivers have a frequency stability of better than 0. 1 Hz per 10 5, 50 that it is easy to adjust their frequencies to maintain a steady drifting of the interference fringe ...
Motion and Optical Flow
... – Matching algorithms – Based on correlation or features – Sparse correspondence estimates – Most common with multiple cameras / stereo ...
... – Matching algorithms – Based on correlation or features – Sparse correspondence estimates – Most common with multiple cameras / stereo ...
Behavior Of Waves
... – The angle of incidence: the angle between the incident ray and a line normal (perpendicular) to the surface at the point where the light ...
... – The angle of incidence: the angle between the incident ray and a line normal (perpendicular) to the surface at the point where the light ...
FA15Lec16 Optical Trap
... Twisters (like F1Fo-ATPases) RNA & DNA Polymerases Viruses Optical Tweezers is an ultrasensitive technique ...
... Twisters (like F1Fo-ATPases) RNA & DNA Polymerases Viruses Optical Tweezers is an ultrasensitive technique ...
Overview of various methods for measuring a lens focal length
... This technique uses the Talbot effect: the image of a coherent wave with 2D periodic amplitude distribution, incident upon a diffraction grating, is regularly repeated. The distance between each self-image is the Talbot length ∆. If the wave interferes with another wave diffracted by a grating with ...
... This technique uses the Talbot effect: the image of a coherent wave with 2D periodic amplitude distribution, incident upon a diffraction grating, is regularly repeated. The distance between each self-image is the Talbot length ∆. If the wave interferes with another wave diffracted by a grating with ...
Atchison Eye Models For Correction
... Early Greek descriptions of the eye were based more on philosophy than on observation Democritus described the eye as three concentric spheres containing the various humours required by the visual sense The innermost sphere (the crystalline humour) produces the visual impression when it receives vis ...
... Early Greek descriptions of the eye were based more on philosophy than on observation Democritus described the eye as three concentric spheres containing the various humours required by the visual sense The innermost sphere (the crystalline humour) produces the visual impression when it receives vis ...
ICSE | PHYSICS Board Paper ˗ 2014 ICSE Board Class X Physics
... having an identical box walks the same distance on a levelled road. Who does more work against the force of gravity and why? (ii) Two forces each of 5N act vertically upwards and downwards respectively on the two ends of a uniform metre rule which is placed at its mid-point as shown in the diagram. ...
... having an identical box walks the same distance on a levelled road. Who does more work against the force of gravity and why? (ii) Two forces each of 5N act vertically upwards and downwards respectively on the two ends of a uniform metre rule which is placed at its mid-point as shown in the diagram. ...
explanation
... How do we “see” things? It works like this. We need to expose an object to a source of light. If we are outside in the daylight, the light source is provided by the sun for free. When light hits the atoms the object is made of, various things can happen. The light can be absorbed, reflected or trans ...
... How do we “see” things? It works like this. We need to expose an object to a source of light. If we are outside in the daylight, the light source is provided by the sun for free. When light hits the atoms the object is made of, various things can happen. The light can be absorbed, reflected or trans ...