Light consists of electromagnetic waves that have oscillating electric
... wavelength – a property called dispersion. The refractive index will also be wavelength dependent. One consequence is separation of different wavelengths of light by a prism because the different indices of refraction result in different deviations of the light from the incident direction as the lig ...
... wavelength – a property called dispersion. The refractive index will also be wavelength dependent. One consequence is separation of different wavelengths of light by a prism because the different indices of refraction result in different deviations of the light from the incident direction as the lig ...
Transmisi Optik Pertemuan 10
... Light Source • There are two fiber optic sources: light emitting diode (LED) or laser diode • LED are low cost and produce output that is nearly linear with the applied drive current, current greater than a very low threshold level must be applied to them before they begin to operate • LED has effi ...
... Light Source • There are two fiber optic sources: light emitting diode (LED) or laser diode • LED are low cost and produce output that is nearly linear with the applied drive current, current greater than a very low threshold level must be applied to them before they begin to operate • LED has effi ...
Suppression of optical damage at 532 nm in
... beam smearing whereas the beam propagating through Sample 4 experiences very little distortion. In fact for intensities greater than 3 kW/cm2 we could not obtain reliable data for Samples 1-3 because the smeared beam clipped on the active area of the CCD. Since the CCD measurements provide only a sn ...
... beam smearing whereas the beam propagating through Sample 4 experiences very little distortion. In fact for intensities greater than 3 kW/cm2 we could not obtain reliable data for Samples 1-3 because the smeared beam clipped on the active area of the CCD. Since the CCD measurements provide only a sn ...
Research on the Design of an Optical Information Storage Sensing
... beam focuses on the servo layer for focusing and tracking, while the first-order diffraction beams focuses on the recording layer. The two beams are controlled and focus on the corresponding layers independently when changing the positions of the objective lens and the DOE. Therefore, the zeroth-ord ...
... beam focuses on the servo layer for focusing and tracking, while the first-order diffraction beams focuses on the recording layer. The two beams are controlled and focus on the corresponding layers independently when changing the positions of the objective lens and the DOE. Therefore, the zeroth-ord ...
Tomographic Interference Microscopy of Living Cells
... ART algorithm, HG(n) is an operator in Fourier space, which changes the 3D Fourier transform according to the central slice theorem [14]; ⌽s and ⌽f are operators for a-priori information in spatial and frequency domain; and F is an operator for 3D Fourier transform. In our case the operator ⌽f has b ...
... ART algorithm, HG(n) is an operator in Fourier space, which changes the 3D Fourier transform according to the central slice theorem [14]; ⌽s and ⌽f are operators for a-priori information in spatial and frequency domain; and F is an operator for 3D Fourier transform. In our case the operator ⌽f has b ...
Measurement of radiation-pressure
... motion cannot be treated separately. A rich variety of physical phenomena resulting from radiation pressure effects include parametric instability 关2–5兴, optical tilt instability 关6兴, quantum radiation pressure noise 关1,8–11兴, and optomechanical rigidity 关7–11兴. In this paper, we report on the obser ...
... motion cannot be treated separately. A rich variety of physical phenomena resulting from radiation pressure effects include parametric instability 关2–5兴, optical tilt instability 关6兴, quantum radiation pressure noise 关1,8–11兴, and optomechanical rigidity 关7–11兴. In this paper, we report on the obser ...
Two-Photon Excited Fluorescence Microscopy - Spectra
... sections of the illuminating cone is largest at the focal plane and dies off rapidly in the regions in front and behind it. The confinement of excitation and thus signal production in a small volume within samples is certainly the key feature of TPM. It is demonstrated in Figure 2 by comparing the e ...
... sections of the illuminating cone is largest at the focal plane and dies off rapidly in the regions in front and behind it. The confinement of excitation and thus signal production in a small volume within samples is certainly the key feature of TPM. It is demonstrated in Figure 2 by comparing the e ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... A smaller pinhole gives a dimmer , but more detailed , image . however the smaller the pinhole , the more that diffraction reduces image quality . While a smaller blur circle preserves more detail, the only way to avoid any loss of detail is to produce a perfect point image of each object point . T ...
... A smaller pinhole gives a dimmer , but more detailed , image . however the smaller the pinhole , the more that diffraction reduces image quality . While a smaller blur circle preserves more detail, the only way to avoid any loss of detail is to produce a perfect point image of each object point . T ...
HOLOGRAPHY, 1948-1971
... suitable optics, and the other has then twice the aberration, which washes it out almost completely. Figure 7 shows that a perfectly sharp reconstruction, in which as good as nothing remains of the disturbance caused by the second image, can be obtained with a lens so bad that its definition is at l ...
... suitable optics, and the other has then twice the aberration, which washes it out almost completely. Figure 7 shows that a perfectly sharp reconstruction, in which as good as nothing remains of the disturbance caused by the second image, can be obtained with a lens so bad that its definition is at l ...
2 Theoretical Concepts
... We have already encountered evanescent fields in the previous subsection. Evanescent fields often play a crucial role in the field of nanooptics where the interaction on a length scale far below the wavelength of light is of interest. Evanescent fields are described as a plane wave of the form ...
... We have already encountered evanescent fields in the previous subsection. Evanescent fields often play a crucial role in the field of nanooptics where the interaction on a length scale far below the wavelength of light is of interest. Evanescent fields are described as a plane wave of the form ...
Observational Astronomy
... Light (high surface/weight ratio) Can be made in large sizes from temperature insensitive materials Can be made in large sizes Can be made segmented Shape can be adjusted (“flexible” mirrors) Difficult to combine Hard to make axial systems (vigneting) ...
... Light (high surface/weight ratio) Can be made in large sizes from temperature insensitive materials Can be made in large sizes Can be made segmented Shape can be adjusted (“flexible” mirrors) Difficult to combine Hard to make axial systems (vigneting) ...
Lecture 13-15
... Multi modes = different paths Refraction index is frequency (color) dependent High bandwidth ( > 1 GHz) Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) DWDM Data rate > TB/s in a single fiber ! ...
... Multi modes = different paths Refraction index is frequency (color) dependent High bandwidth ( > 1 GHz) Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) DWDM Data rate > TB/s in a single fiber ! ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... absorber of infrared light. 2. Far infrared—greater than 40,000 nm—can be detected from aircraft (e.g., the SOFIA project, NASA’s Airborne Observatory). 3. Infrared telescopes must be cooled so heat (IR radiation) from the surroundings does not mask the signals received from space. 4. Ozone is the c ...
... absorber of infrared light. 2. Far infrared—greater than 40,000 nm—can be detected from aircraft (e.g., the SOFIA project, NASA’s Airborne Observatory). 3. Infrared telescopes must be cooled so heat (IR radiation) from the surroundings does not mask the signals received from space. 4. Ozone is the c ...
Question 1 (a) ICSE X | PHYSICS Board Paper – 2016 ICSE Board
... (a) State two factors upon which the heat absorbed by a body depends. ...
... (a) State two factors upon which the heat absorbed by a body depends. ...
Three models of light
... A parallel bundle of rays could be a laser beam, or light from a distant object. ...
... A parallel bundle of rays could be a laser beam, or light from a distant object. ...
Temporal Integrated Detection and Applications of FS-Pulse Scattering S. Bakic
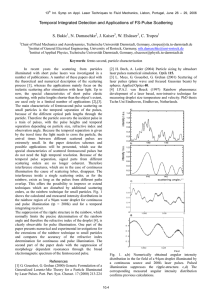
... small particles is the temporal separation of the pulses, because of the different optical path lengths through the particle. Therefore the particle converts the incident pulse in a train of pulses, with the pulse heights and temporal separation depending on particle size, refractive index and obser ...
... small particles is the temporal separation of the pulses, because of the different optical path lengths through the particle. Therefore the particle converts the incident pulse in a train of pulses, with the pulse heights and temporal separation depending on particle size, refractive index and obser ...