Analysing the potential for application of the phase shift method in
... of the interference fringes from the diffraction grating is securing a monochromatic and coherent light source5). The light waves emitted by the LED diodes are monochromatic, which means that they have the same wave length λ, but they are not coherent, i.e. the sinusoidal waves of the light beam do ...
... of the interference fringes from the diffraction grating is securing a monochromatic and coherent light source5). The light waves emitted by the LED diodes are monochromatic, which means that they have the same wave length λ, but they are not coherent, i.e. the sinusoidal waves of the light beam do ...
MICROWAVE OPTICS – THE MEASUREMENTS OF THE
... (what corresponds to the frequencies of 109-1011Hz). These waves are used in radars and other communication systems, as well as in the analyses of very fine details of atomic and molecular structure, and are also generated by electronic devices. As everybody knows interference is one of the phenomen ...
... (what corresponds to the frequencies of 109-1011Hz). These waves are used in radars and other communication systems, as well as in the analyses of very fine details of atomic and molecular structure, and are also generated by electronic devices. As everybody knows interference is one of the phenomen ...
Wavelength measurements using prism spectroscopy (Spk)
... lines, one shall determine one of the fundamental constants of nuclear physics, the so-called Rydberg constant R. The decomposition of light into its spectral colors inside of a prism is caused by dispersion. Dispersion occurs, when light is being diffracted at the boundary layers between air and gl ...
... lines, one shall determine one of the fundamental constants of nuclear physics, the so-called Rydberg constant R. The decomposition of light into its spectral colors inside of a prism is caused by dispersion. Dispersion occurs, when light is being diffracted at the boundary layers between air and gl ...
PDF Format
... experience two different indices of refraction. Consequently, one polarization of light travels faster in the wave plate compared to the other. The birefringent material of the wave plate are asymmetric in that they have a different index of refraction in one polarization direction compared to the o ...
... experience two different indices of refraction. Consequently, one polarization of light travels faster in the wave plate compared to the other. The birefringent material of the wave plate are asymmetric in that they have a different index of refraction in one polarization direction compared to the o ...
High refractive index Fresnel lens on a fiber fabricated by
... Fresnel lens [10] fabricated directly on top of an optical fiber via Ultra Violet Nanoimprint Lithography (UV-NIL). NIL represents not only a low-cost, high-throughput nanopatterning technique with single-digit nanoscale resolution [11], but it also enables patterning of functional high refractive i ...
... Fresnel lens [10] fabricated directly on top of an optical fiber via Ultra Violet Nanoimprint Lithography (UV-NIL). NIL represents not only a low-cost, high-throughput nanopatterning technique with single-digit nanoscale resolution [11], but it also enables patterning of functional high refractive i ...
Tutorial for Chapter 8
... A Gaussian beam of Rayleigh range z0 = 50 cm and wavelength = 488 nm is converted into another Gaussian beam with using a lens of focal length f = 5 cm at a distance z = 75 cm. Find the beam waist and location (from the lens) for the new Gaussian beam. ...
... A Gaussian beam of Rayleigh range z0 = 50 cm and wavelength = 488 nm is converted into another Gaussian beam with using a lens of focal length f = 5 cm at a distance z = 75 cm. Find the beam waist and location (from the lens) for the new Gaussian beam. ...
Introduction to Nonlinear Optics
... Second Harmonic Generation and Nonlinear Microscopy Nonlinear Optical Microscopy An important application of harmonic generation is nonlinear microscopy. . . Microscopy based on second-harmonic generation in the configuration of a confocal microscope and excited by femtosecond laser pulses was intr ...
... Second Harmonic Generation and Nonlinear Microscopy Nonlinear Optical Microscopy An important application of harmonic generation is nonlinear microscopy. . . Microscopy based on second-harmonic generation in the configuration of a confocal microscope and excited by femtosecond laser pulses was intr ...
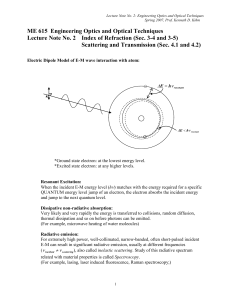
ME 615 Engineering Optics and Optical Techniques
... Both molecules, a distance of / 2 apart at the same lateral line, re-radiate at the same time as they are bombarded by the incident radiation simultaneously. Then the both wavelets cancel in the transverse direction, because of the symmetry, and negate the lateral irradiance each other. Similarly, ...
... Both molecules, a distance of / 2 apart at the same lateral line, re-radiate at the same time as they are bombarded by the incident radiation simultaneously. Then the both wavelets cancel in the transverse direction, because of the symmetry, and negate the lateral irradiance each other. Similarly, ...
Stellar Activity with SONG
... by the amount of relative phase that it imparts on the two components ...
... by the amount of relative phase that it imparts on the two components ...
Optical Prescriptions Spectacle Lenses
... energy transmitted through the lens to the amount incident on the front surface. It is expressed as a percentage. Luminous transmittance- describes the visual characteristics of tinted lens Optical density- another descriptor, usually for occupational tint (welders) ...
... energy transmitted through the lens to the amount incident on the front surface. It is expressed as a percentage. Luminous transmittance- describes the visual characteristics of tinted lens Optical density- another descriptor, usually for occupational tint (welders) ...
Halogen Lamp Ultraviolet Output
... Tungsten halogen incandescent lamps emit a small amount of ultraviolet energy (UV). There have been studies that suggest a possible small risk associated with exposure to this UV. For example, a letter in the 16 April 1992 issue of Nature (DeFlora & D’Agnostini, 356:569) reported an experiment in wh ...
... Tungsten halogen incandescent lamps emit a small amount of ultraviolet energy (UV). There have been studies that suggest a possible small risk associated with exposure to this UV. For example, a letter in the 16 April 1992 issue of Nature (DeFlora & D’Agnostini, 356:569) reported an experiment in wh ...
Prism Design
... diagram similar to Fig. 6.4(b), he noted that the proportion of face width Ai to reduced thickness was Ai: (2Ai /ni ) or ni /2. He then redrew the diagram in the form shown in Fig. 6.5 to facilitate calculating the minimum value for A1 and A2. The dashed lines drawn from the top front prism corners ...
... diagram similar to Fig. 6.4(b), he noted that the proportion of face width Ai to reduced thickness was Ai: (2Ai /ni ) or ni /2. He then redrew the diagram in the form shown in Fig. 6.5 to facilitate calculating the minimum value for A1 and A2. The dashed lines drawn from the top front prism corners ...
Chapter 6. Light Source and Detectors
... release more electrons but their energies, and their velocities, will remain the same. The energy of the photoelectrons depends on the frequency of the light: blue light produces more energetic photo-electrons than red light. The response of a quantum detector is all but instantaneous: there is no ...
... release more electrons but their energies, and their velocities, will remain the same. The energy of the photoelectrons depends on the frequency of the light: blue light produces more energetic photo-electrons than red light. The response of a quantum detector is all but instantaneous: there is no ...
Optical metamaterials at near and mid-IR range fabricated by nanoimprint lithography
... wavelength 1.064 µm, 20-Hz repetition rate, and 20-ps pulse duration was used to supply the third-harmonic radiation, which is a pump for the OPG/OPA system. The OPG/OPA output could be tuned over the range of signal wavelength from 450 nm to 2500 nm. The OPG/OPA output was used for characterizing t ...
... wavelength 1.064 µm, 20-Hz repetition rate, and 20-ps pulse duration was used to supply the third-harmonic radiation, which is a pump for the OPG/OPA system. The OPG/OPA output could be tuned over the range of signal wavelength from 450 nm to 2500 nm. The OPG/OPA output was used for characterizing t ...
Optical metamaterials at near and mid-IR range fabricated by nanoimprint lithography
... wavelength 1.064 µm, 20-Hz repetition rate, and 20-ps pulse duration was used to supply the third-harmonic radiation, which is a pump for the OPG/OPA system. The OPG/OPA output could be tuned over the range of signal wavelength from 450 nm to 2500 nm. The OPG/OPA output was used for characterizing t ...
... wavelength 1.064 µm, 20-Hz repetition rate, and 20-ps pulse duration was used to supply the third-harmonic radiation, which is a pump for the OPG/OPA system. The OPG/OPA output could be tuned over the range of signal wavelength from 450 nm to 2500 nm. The OPG/OPA output was used for characterizing t ...
Click To
... Background: A high-average-power solid-state laser is typically pumped by injecting light from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays. The laser arrays are frequently fitted with lenses that separately collimate the output of the bars so that the pump light is collimated well enough f ...
... Background: A high-average-power solid-state laser is typically pumped by injecting light from high-power two-dimensional semiconductor laser arrays. The laser arrays are frequently fitted with lenses that separately collimate the output of the bars so that the pump light is collimated well enough f ...
Lecture Notes
... the speed of light in that medium. Higher RI means lower speed of light in that medium. If light travels from a higher RI isotropic medium to lower RI isotropic medium same laws apply, but in this case refracted ray moves away from the normal to the interface. At a certain critical angle of incidenc ...
... the speed of light in that medium. Higher RI means lower speed of light in that medium. If light travels from a higher RI isotropic medium to lower RI isotropic medium same laws apply, but in this case refracted ray moves away from the normal to the interface. At a certain critical angle of incidenc ...
Coating Materials - Umicore Thin Film Products
... to materials of a different origin. Even minute concentrations of transition elements can have a marked effect on the transmission properties of dielectric layers. Unfortunately, there are only few publications that address this topic. Nowhere is there a description, for instance, of the relationshi ...
... to materials of a different origin. Even minute concentrations of transition elements can have a marked effect on the transmission properties of dielectric layers. Unfortunately, there are only few publications that address this topic. Nowhere is there a description, for instance, of the relationshi ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.