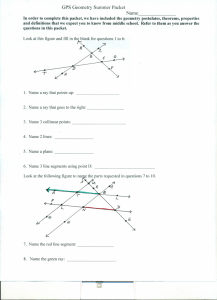
GPS Geometry Summer Packet Name
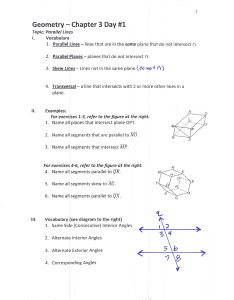
... Corresponding Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and correspond to the same position at the points of intersection. Alternate Interior Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and are between the lines, on opposite sides of the transversal and at ...
... Corresponding Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and correspond to the same position at the points of intersection. Alternate Interior Angles - the angles formed when 2 lines are cut by a transversal and are between the lines, on opposite sides of the transversal and at ...
ExamView - Geometry Midterm 2012 Draft.tst
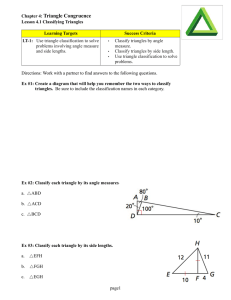
... 41. Two angles with measures (2x 2 + 3x − 5)° and (x 2 + 11x − 7)° are supplementary. Find the value of x and the measure of each angle. 42. Two lines intersect to form two pairs of vertical angles. ∠1 with measure (20x + 7)º and ∠3 with measure (5x + 7y + 49)º are vertical angles. ∠2 with measure ( ...
... 41. Two angles with measures (2x 2 + 3x − 5)° and (x 2 + 11x − 7)° are supplementary. Find the value of x and the measure of each angle. 42. Two lines intersect to form two pairs of vertical angles. ∠1 with measure (20x + 7)º and ∠3 with measure (5x + 7y + 49)º are vertical angles. ∠2 with measure ( ...
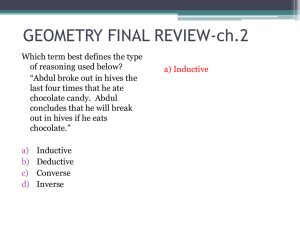
9 Neutral Triangle Geometry
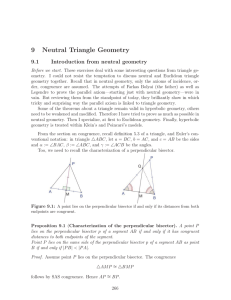
... triangle, not the extensions—as follows from the exterior angle theorem. Hence the Crossbar Theorem implies that any two altitude do intersect. The remaining details are left as an exercise. Here is stated what we have gathered up to this point. It is little, but more than nothing! ...
... triangle, not the extensions—as follows from the exterior angle theorem. Hence the Crossbar Theorem implies that any two altitude do intersect. The remaining details are left as an exercise. Here is stated what we have gathered up to this point. It is little, but more than nothing! ...
Geometry Module 1, Topic G, Overview
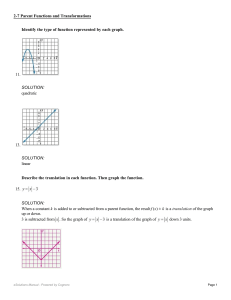
... geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). ...
... geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). ...
Geometry Module 1, Topic G, Overview
... geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). ...
... geometry software; describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. Compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). ...
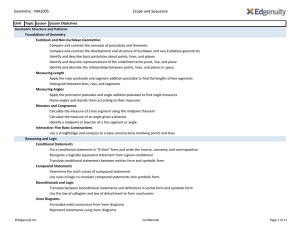
Geometry - MA2005 Scope and Sequence
... Cross Sections of Solid Figures Apply Cavalieri's principle to calculate the volume of solid figures Identify cross sections of solid figures Similar Solids Calculate the surface areas and volumes of similar solids Identify the relationships between the surface areas and volumes of similar solids An ...
... Cross Sections of Solid Figures Apply Cavalieri's principle to calculate the volume of solid figures Identify cross sections of solid figures Similar Solids Calculate the surface areas and volumes of similar solids Identify the relationships between the surface areas and volumes of similar solids An ...
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference line is called a coordinate axis or just axis of the system, and the point where they meet is its origin, usually at ordered pair (0, 0). The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin.One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, n Cartesian coordinates (an element of real n-space) specify the point in an n-dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension n. These coordinates are equal, up to sign, to distances from the point to n mutually perpendicular hyperplanes.The invention of Cartesian coordinates in the 17th century by René Descartes (Latinized name: Cartesius) revolutionized mathematics by providing the first systematic link between Euclidean geometry and algebra. Using the Cartesian coordinate system, geometric shapes (such as curves) can be described by Cartesian equations: algebraic equations involving the coordinates of the points lying on the shape. For example, a circle of radius 2 in a plane may be described as the set of all points whose coordinates x and y satisfy the equation x2 + y2 = 4.Cartesian coordinates are the foundation of analytic geometry, and provide enlightening geometric interpretations for many other branches of mathematics, such as linear algebra, complex analysis, differential geometry, multivariate calculus, group theory and more. A familiar example is the concept of the graph of a function. Cartesian coordinates are also essential tools for most applied disciplines that deal with geometry, including astronomy, physics, engineering and many more. They are the most common coordinate system used in computer graphics, computer-aided geometric design and other geometry-related data processing.