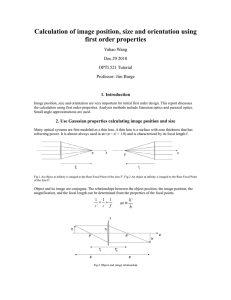
Evidence of the accelerated expansion of the Universe from weak
... new constituent named dark energy, which counteracts the attractive force of gravity on the largest scales and contributes ∼70% to the total energy budget today. There have been various attempts to explain dark energy, ranging from Einstein’s cosmological constant, via a dynamic fluid named quintess ...
... new constituent named dark energy, which counteracts the attractive force of gravity on the largest scales and contributes ∼70% to the total energy budget today. There have been various attempts to explain dark energy, ranging from Einstein’s cosmological constant, via a dynamic fluid named quintess ...
Penumbral thermal structure below the visible surface
... optical depth offers the possibility of observing slightly deeper or higher layers of the solar atmosphere by observing different wavelengths (Chandrasekhar & Breen 1946). The observed surface of the Sun (see Figure 9 in Borrero et al. 2016) is located about 70 − 80 km deeper at 1565 nm (near-infrar ...
... optical depth offers the possibility of observing slightly deeper or higher layers of the solar atmosphere by observing different wavelengths (Chandrasekhar & Breen 1946). The observed surface of the Sun (see Figure 9 in Borrero et al. 2016) is located about 70 − 80 km deeper at 1565 nm (near-infrar ...
Cooling and Trapping Neutral Atoms W. Ketterle, D. E. Pritchard
... to generate a coherent sample of atoms all occupying the same quantum state (this was subsequently used to realize an atom laser, a device which generates coherent matter waves); and (3) to create a quantum fluid with properties quite different from the quantum liquids He-3 and He-4. This provides a ...
... to generate a coherent sample of atoms all occupying the same quantum state (this was subsequently used to realize an atom laser, a device which generates coherent matter waves); and (3) to create a quantum fluid with properties quite different from the quantum liquids He-3 and He-4. This provides a ...
Further VLBA Observations of SiO Masers toward Mira
... Abstract. We present the results of continued monitoring of the SiO masers at 7 mm wavelength in several of the Mira variable stars reported in Cotton et al. (2004) (o Ceti=Mira, U Orionis=U Ori, R Aquarii=R Aqr) over a period of 16 months, extending the observations to several pulsation cycles. The ...
... Abstract. We present the results of continued monitoring of the SiO masers at 7 mm wavelength in several of the Mira variable stars reported in Cotton et al. (2004) (o Ceti=Mira, U Orionis=U Ori, R Aquarii=R Aqr) over a period of 16 months, extending the observations to several pulsation cycles. The ...
stellar rotation in m35: mass–period relations, spin
... problem. The fastest spinning stars in the youngest clusters cannot be explained from Skumanich-style spin-down (Skumanich 1972) of the fastest spinning T Tauri stars. The rapid rotators can be explained only by introducing “magnetic saturation” ...
... problem. The fastest spinning stars in the youngest clusters cannot be explained from Skumanich-style spin-down (Skumanich 1972) of the fastest spinning T Tauri stars. The rapid rotators can be explained only by introducing “magnetic saturation” ...
Beta Pictoris and Other Solar Systems
... initially to β Pic (cf. Artymowicz, 1997). However, the effects of radiation are quite similar in different systems (e. g., Artymowicz and Clampin, 1997). For instance, the luminosity differences between the stars will simply shift the ‘blow-out grain radius’ but will not change the characteristic s ...
... initially to β Pic (cf. Artymowicz, 1997). However, the effects of radiation are quite similar in different systems (e. g., Artymowicz and Clampin, 1997). For instance, the luminosity differences between the stars will simply shift the ‘blow-out grain radius’ but will not change the characteristic s ...
Millisecond Pulsars in X-Ray Binaries - CIERA
... NS/LMXBs is 1 per cent or less, raising the question of what is different about this group of 5 pulsars: why is it so difficult to find persistent millisecond pulsations in most NS/LMXBs? It should be noted that none of the millisecond X-ray pulsars has been detected as a radio pulsar. While both kH ...
... NS/LMXBs is 1 per cent or less, raising the question of what is different about this group of 5 pulsars: why is it so difficult to find persistent millisecond pulsations in most NS/LMXBs? It should be noted that none of the millisecond X-ray pulsars has been detected as a radio pulsar. While both kH ...
Bose-Einstein condensation in dilute atomic gases
... Fritz London who connected it with a real phenomenon when he suggested in 1938 that the recently discovered superfluidity of liquid helium was related to Bose-Einstein condensation [1,2]. BEC in dilute atomic gases is a new subfield which is interdisciplinary between atomic and condensed matter physic ...
... Fritz London who connected it with a real phenomenon when he suggested in 1938 that the recently discovered superfluidity of liquid helium was related to Bose-Einstein condensation [1,2]. BEC in dilute atomic gases is a new subfield which is interdisciplinary between atomic and condensed matter physic ...
Michell, Laplace and the Origin of the Black Hole Concept
... proportion to its vis inertiae, with other bodies, all light emitted from such a body would be made to return towards it, by its own proper gravity. (Michell, 1784: ...
... proportion to its vis inertiae, with other bodies, all light emitted from such a body would be made to return towards it, by its own proper gravity. (Michell, 1784: ...
11.6 Protoplanetary disks
... - Disk sizes between 200 and 2000AU. - Most disks are in Keplerian rotation. - Temperature structure consistent with flared disk models and T at CO disk surface (t=1) goes like T(r) ~ r-0.6. - Vertical temperature gradients with cooler disk mid-plane. ...
... - Disk sizes between 200 and 2000AU. - Most disks are in Keplerian rotation. - Temperature structure consistent with flared disk models and T at CO disk surface (t=1) goes like T(r) ~ r-0.6. - Vertical temperature gradients with cooler disk mid-plane. ...
The impact of surface temperature inhomogeneities on quiescent
... magnetized (B ≪ 109 G), therefore the effects of the magnetic field on the opacity and equation of state of the atmosphere can be neglected. The opacity within the atmosphere is due to a combination of thermal free-free absorption and Thomson scattering. Light-element neutron star atmosphere models ...
... magnetized (B ≪ 109 G), therefore the effects of the magnetic field on the opacity and equation of state of the atmosphere can be neglected. The opacity within the atmosphere is due to a combination of thermal free-free absorption and Thomson scattering. Light-element neutron star atmosphere models ...
The solar silicon abundance based on 3D non
... their collisional coupling with Si i levels is minute. The excited states are also sparsely populated in the solar photosphere (e.g. Wedemeyer 2001), implying that any non-LTE behaviour in the Si ii ion will have only a minute effect on the ground state of Si ii. Consequently, the excited states of ...
... their collisional coupling with Si i levels is minute. The excited states are also sparsely populated in the solar photosphere (e.g. Wedemeyer 2001), implying that any non-LTE behaviour in the Si ii ion will have only a minute effect on the ground state of Si ii. Consequently, the excited states of ...
Slide 1
... But what if we have an even bigger core? With enough pressure, we can FORCE atoms to let their electrons overlap. This happens for stars with cores up to 3 times heavier than the sun. This is the case with neutron stars. When a big core dies, gravity crushes down, but it crushes even harder than ele ...
... But what if we have an even bigger core? With enough pressure, we can FORCE atoms to let their electrons overlap. This happens for stars with cores up to 3 times heavier than the sun. This is the case with neutron stars. When a big core dies, gravity crushes down, but it crushes even harder than ele ...
Hydrogen Bonding and Vibrational Energy Relaxation in Water
... between water molecules can be controlled in a simple way. A great deal of information about the structure and properties has already been obtained using experimental methods of thermodynamics, optical spectroscopy, and electrochemistry, as well as computer simulations.51 In light of these studies i ...
... between water molecules can be controlled in a simple way. A great deal of information about the structure and properties has already been obtained using experimental methods of thermodynamics, optical spectroscopy, and electrochemistry, as well as computer simulations.51 In light of these studies i ...
- ANU Repository
... of planets around M dwarfs, the distribution with radii, and the number of planets within a ‘habitable zone’ (HZ) bounded by minimum and maximum irradiance levels. Both Dressing & Charbonneau (2013, hereafter, DC13) and Gaidos (2013, hereafter, G13) carried out Bayesian estimations of properties of ...
... of planets around M dwarfs, the distribution with radii, and the number of planets within a ‘habitable zone’ (HZ) bounded by minimum and maximum irradiance levels. Both Dressing & Charbonneau (2013, hereafter, DC13) and Gaidos (2013, hereafter, G13) carried out Bayesian estimations of properties of ...
Kepler-21b: A Rocky Planet Around a V = 8.25 Mag Star
... such as the planet’s phase curve or stellar variations due to rotation or pulsation, are removed. This is due mainly to the harmonic filter and median detrender, which are selected to preserve features with timescales in the order of the transits. Detailed inspection of the light curves also shows th ...
... such as the planet’s phase curve or stellar variations due to rotation or pulsation, are removed. This is due mainly to the harmonic filter and median detrender, which are selected to preserve features with timescales in the order of the transits. Detailed inspection of the light curves also shows th ...
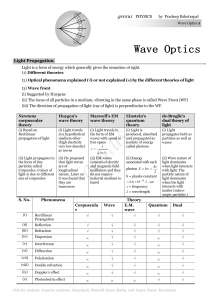
genius PHYSICS by Pradeep Kshetrapal Newtons corpuscular
... Central maxima means the maxima formed with zero optical path difference. It may be formed anywhere on the screen. ...
... Central maxima means the maxima formed with zero optical path difference. It may be formed anywhere on the screen. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.