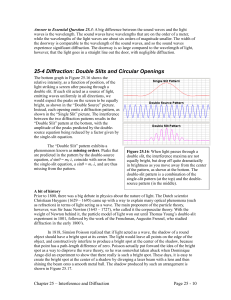
25-4 Diffraction: Double Slits and Circular Openings
... the narrower the width of the central peak in the diffraction pattern. This dependence on the diameter of the opening has implications for how close two objects can be before you cannot resolve them. For instance, when you look up at the sky at night, two stars that are very close together may appea ...
... the narrower the width of the central peak in the diffraction pattern. This dependence on the diameter of the opening has implications for how close two objects can be before you cannot resolve them. For instance, when you look up at the sky at night, two stars that are very close together may appea ...
Chapter 25: Interference and Diffraction
... All of these wavelengths will show constructive interference, but it is only this one that is in the visible portion of the spectrum. ...
... All of these wavelengths will show constructive interference, but it is only this one that is in the visible portion of the spectrum. ...
The Ring Nebula, NGC 6720
... that is a favorite of both amateur and professional astronomers alike. Located in the constellation Lyra (the lyre, or harp), the nebula is situated within the famous Summer Triangle of bright stars (Vega, Altair, and Deneb) for northern hemisphere observers. At a distance of 2,300 light-years, and ...
... that is a favorite of both amateur and professional astronomers alike. Located in the constellation Lyra (the lyre, or harp), the nebula is situated within the famous Summer Triangle of bright stars (Vega, Altair, and Deneb) for northern hemisphere observers. At a distance of 2,300 light-years, and ...
Dark Matter NS Warsaw
... ▸ Since the dark matter density near the Galactic center is significantly higher than regions near the solar position (where the oldest pulsars have been found) there is a parameter space where dark matter accumulation may solve the missing pulsar problem. ...
... ▸ Since the dark matter density near the Galactic center is significantly higher than regions near the solar position (where the oldest pulsars have been found) there is a parameter space where dark matter accumulation may solve the missing pulsar problem. ...
white dwarfs, neutron stars, black hole
... Electron degeneracy pressure is a quantum mechanical effect that comes into play at high densities. Just as electrons in an atom can only have specific energy levels, quantum mechanics places constraints on how closely together electrons can be packed in a gas. On the other hand, stars with masses 1 ...
... Electron degeneracy pressure is a quantum mechanical effect that comes into play at high densities. Just as electrons in an atom can only have specific energy levels, quantum mechanics places constraints on how closely together electrons can be packed in a gas. On the other hand, stars with masses 1 ...
Principles of Fourier Transform Optical Measurements
... • Move one mirror back 1/4 of a wavelength. The two beams will be 180° out of phase and they will destructively interfere, the field will ...
... • Move one mirror back 1/4 of a wavelength. The two beams will be 180° out of phase and they will destructively interfere, the field will ...
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... mass that gravitational forces cause the hydrogen nuclei to fuse and release energy (electromagnetic radiation). The Sun is luminescent. Eg: Protostars form within nebulae gas clouds under influence of gravity. • Brown dwarf has insufficient mass and therefore insufficient gravitational forces to be ...
... mass that gravitational forces cause the hydrogen nuclei to fuse and release energy (electromagnetic radiation). The Sun is luminescent. Eg: Protostars form within nebulae gas clouds under influence of gravity. • Brown dwarf has insufficient mass and therefore insufficient gravitational forces to be ...
Contents - Beck-Shop
... Why do astronomers want ever-larger telescopes? 226 What are the largest optical telescopes today? 227 How does the atmosphere degrade telescope images? 229 What is adaptive optics? 230 Are there any alternatives to traditional mirrors? 231 Where are the best astronomical sites? 232 What are the adv ...
... Why do astronomers want ever-larger telescopes? 226 What are the largest optical telescopes today? 227 How does the atmosphere degrade telescope images? 229 What is adaptive optics? 230 Are there any alternatives to traditional mirrors? 231 Where are the best astronomical sites? 232 What are the adv ...
Star Birth - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... and pressure – often called molecular clouds • A simple count shows that 2-3 new stars form each year in our part of the Milky Way ...
... and pressure – often called molecular clouds • A simple count shows that 2-3 new stars form each year in our part of the Milky Way ...
Hubble Science Briefing: The Real World: Black Hole Edition
... “from the black hole”. This is technically incorrect! It is still true that nothing escapes a black hole once it has fallen in. The extreme gravity of the black hole is essential to the whole system, but the outflows are not coming out of the black hole event horizon. It is more accurate to say thes ...
... “from the black hole”. This is technically incorrect! It is still true that nothing escapes a black hole once it has fallen in. The extreme gravity of the black hole is essential to the whole system, but the outflows are not coming out of the black hole event horizon. It is more accurate to say thes ...
Hubble Science Briefing: The Real World: Black Hole Edition
... from an AGN known as “M87”. It is one of the nearest jets to Earth. Using over 400 images taken of this jet over nearly 13 years, we were able to actually measure the motions of the plasma as it extends out into space. ...
... from an AGN known as “M87”. It is one of the nearest jets to Earth. Using over 400 images taken of this jet over nearly 13 years, we were able to actually measure the motions of the plasma as it extends out into space. ...
DTU_9e_ch13
... A burster emits X rays with a constant low intensity interspersed with occasional powerful bursts. This burst was recorded in September 1975 by an X-ray telescope that was pointed toward the globular cluster NGC 6624. ...
... A burster emits X rays with a constant low intensity interspersed with occasional powerful bursts. This burst was recorded in September 1975 by an X-ray telescope that was pointed toward the globular cluster NGC 6624. ...
Temperate Earth-sized planets transiting a nearby ultracool
... signals do not originate from eclipses of larger bodies in front of a background or a physically associated stellar-like object blended with the ultracool target star. These factors also establish that the light from the target is not diluted by an unresolved additional stellarlike object, confirmin ...
... signals do not originate from eclipses of larger bodies in front of a background or a physically associated stellar-like object blended with the ultracool target star. These factors also establish that the light from the target is not diluted by an unresolved additional stellarlike object, confirmin ...
31 October: Supernovae and Neutron Stars
... • An object having the mass of the Sun (or more) but in an object with the diameter of Iowa City! • An equivalent to the Chandrasekhar mass (largest possible mass of a neutron star) • Do they exist? ...
... • An object having the mass of the Sun (or more) but in an object with the diameter of Iowa City! • An equivalent to the Chandrasekhar mass (largest possible mass of a neutron star) • Do they exist? ...
Structure and optical properties of reconstructed Si and Ge surfaces
... as the forces on the bulk atoms are not similar to those on surface atoms. This is called surface reconstruction. When these systems are energetically relaxed, sometimes they form special ordered structures such as one dimensional atomic chains or rows of dimers etc. due to surface reconstruction. S ...
... as the forces on the bulk atoms are not similar to those on surface atoms. This is called surface reconstruction. When these systems are energetically relaxed, sometimes they form special ordered structures such as one dimensional atomic chains or rows of dimers etc. due to surface reconstruction. S ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.