here. - SUNY Oswego
... Published data show PC relation at maximum light is flat which agrees with Galactic Cepheid observations. With an appropriate reddening/extinction error to make the PL linear, LMC Cepheids get hotter at maximum light as the period increases. But Galactic Cepheids have a flat PC relation at maximum l ...
... Published data show PC relation at maximum light is flat which agrees with Galactic Cepheid observations. With an appropriate reddening/extinction error to make the PL linear, LMC Cepheids get hotter at maximum light as the period increases. But Galactic Cepheids have a flat PC relation at maximum l ...
matter and dark energy Gravitational lensing: a unique probe of dark
... deflection (notwithstanding that his prediction doubled in value in the next 7 years!). He corresponded with George Ellery Hale at the Carnegie Observatories regarding the possibility of observing the much smaller deflection around the planet Jupiter, eventually concluding that photographs taken at ...
... deflection (notwithstanding that his prediction doubled in value in the next 7 years!). He corresponded with George Ellery Hale at the Carnegie Observatories regarding the possibility of observing the much smaller deflection around the planet Jupiter, eventually concluding that photographs taken at ...
NRO M33 All Disk Survey of Giant Molecular Clouds (NRO MAGiC
... Elmegreen (1993) introduced the molecular fraction fmol as a parameter to quantify the transition. It is the ratio of the molecular gas surface density to the total gas surface density including both atomic and molecular gases. fmol can be expressed as a function of metallicity, UV radiation field, a ...
... Elmegreen (1993) introduced the molecular fraction fmol as a parameter to quantify the transition. It is the ratio of the molecular gas surface density to the total gas surface density including both atomic and molecular gases. fmol can be expressed as a function of metallicity, UV radiation field, a ...
Imaging the dust sublimation front of a circumbinary disk
... excess in the spectral energy distribution (SED) of a post-AGB star correlates well with the central star being part of a ∼1-2 au wide binary system (e.g. van Winckel et al. 2009). Such evolved binaries are common in the Galaxy (de Ruyter et al. 2006) and recent studies show that about 30% of all op ...
... excess in the spectral energy distribution (SED) of a post-AGB star correlates well with the central star being part of a ∼1-2 au wide binary system (e.g. van Winckel et al. 2009). Such evolved binaries are common in the Galaxy (de Ruyter et al. 2006) and recent studies show that about 30% of all op ...
A historical perspective on the discovery of neutron stars
... the maximum mass of neutron stars Mmax ≃ 2M⊙ is much higher than that found by Oppenheimer and Volkoff neutron stars can thus be formed as proposed by Baade and Zwicky neutron star cores may contain various nuclear species such as hyperons. Formed in supernova explosions, neutron stars were thus exp ...
... the maximum mass of neutron stars Mmax ≃ 2M⊙ is much higher than that found by Oppenheimer and Volkoff neutron stars can thus be formed as proposed by Baade and Zwicky neutron star cores may contain various nuclear species such as hyperons. Formed in supernova explosions, neutron stars were thus exp ...
L173 HAT-P-5b: A JUPITER-LIKE HOT JUPITER TRANSITING A
... Over the past year the HATNet project11 (Bakos et al. 2002, 2004), a wide-angle photometric survey, has announced four TEPs. In this Letter we report on the detection of a new transiting exoplanet, which we label HAT-P-5b, and our determination of its parameters, such as mass, radius, density, and s ...
... Over the past year the HATNet project11 (Bakos et al. 2002, 2004), a wide-angle photometric survey, has announced four TEPs. In this Letter we report on the detection of a new transiting exoplanet, which we label HAT-P-5b, and our determination of its parameters, such as mass, radius, density, and s ...
Chapter 12
... • A brown dwarf emits infrared light because of heat left over from contraction. • Its luminosity gradually declines with time as it loses thermal energy. ...
... • A brown dwarf emits infrared light because of heat left over from contraction. • Its luminosity gradually declines with time as it loses thermal energy. ...
MidtermExam1-Sol-2011
... there is a path with an infinite sequence of zero-cost actions. b. Iterative Deepening. It is usually used in combination with what other method? State if it is optimal and complete and under what conditions. It is used in combination with depth-first search. It is complete if b and d are finite; it ...
... there is a path with an infinite sequence of zero-cost actions. b. Iterative Deepening. It is usually used in combination with what other method? State if it is optimal and complete and under what conditions. It is used in combination with depth-first search. It is complete if b and d are finite; it ...
THE KEPLER CLUSTER STUDY: STELLAR ROTATION IN NGC 6811
... evolution onto the slow branch, resulting in a unique relationship between P and M at ∼600 Myr (Radick et al. 1987; Collier Cameron et al. 2009; Delorme et al. 2011). The Hyades and Praesepe clusters constitute the oldest coeval stellar populations for which rotation periods have been measured. Olde ...
... evolution onto the slow branch, resulting in a unique relationship between P and M at ∼600 Myr (Radick et al. 1987; Collier Cameron et al. 2009; Delorme et al. 2011). The Hyades and Praesepe clusters constitute the oldest coeval stellar populations for which rotation periods have been measured. Olde ...
A Test of Pre-Main-Sequence Lithium Depletion Models
... lithium abundance of a star with theoretical evolutionary models, one might be able to derive an age of a PMS star whose distance is unknown, e.g. a young field star. In order to do this, we need to understand PMS lithium depletion very well. Most of the work comparing lithium depletion to HR diagra ...
... lithium abundance of a star with theoretical evolutionary models, one might be able to derive an age of a PMS star whose distance is unknown, e.g. a young field star. In order to do this, we need to understand PMS lithium depletion very well. Most of the work comparing lithium depletion to HR diagra ...
Wind Opacity Issues
... OFH2006 shows this plot of wind opacity for four stars (below), from “detailed” wind modeling using PoWR. It appears that the only K-shell edge is that of (a single ion state of) nitrogen. This seems pretty crude. And it makes me wonder what elements are included in the calculation of the overall op ...
... OFH2006 shows this plot of wind opacity for four stars (below), from “detailed” wind modeling using PoWR. It appears that the only K-shell edge is that of (a single ion state of) nitrogen. This seems pretty crude. And it makes me wonder what elements are included in the calculation of the overall op ...
High-Energy Emission from the PSR B1259
... for large mass outflow rates and high density of material near periastron. An example of direct accretion is the 69 ms X-ray pulsar A0538-66 in the LMC which occasionally accretes with an X-ray luminosity near the Eddington limit LE ∼ 1038 erg s−1 (Skinner et al. 1982). (2) Propeller effect emission ...
... for large mass outflow rates and high density of material near periastron. An example of direct accretion is the 69 ms X-ray pulsar A0538-66 in the LMC which occasionally accretes with an X-ray luminosity near the Eddington limit LE ∼ 1038 erg s−1 (Skinner et al. 1982). (2) Propeller effect emission ...
Document
... • State several ways in which high-mass stars differ from low-mass stars. • High-mass stars live much shorter lives than low-mass stars. High-mass stars have convective cores but no other convective layers, while low-mass stars have convection layers that can extend from their surface to large depth ...
... • State several ways in which high-mass stars differ from low-mass stars. • High-mass stars live much shorter lives than low-mass stars. High-mass stars have convective cores but no other convective layers, while low-mass stars have convection layers that can extend from their surface to large depth ...
Tasks - ESA Science
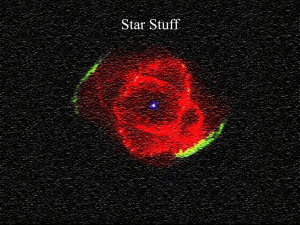
... the surface repeatedly during this late stage of a low-mass star’s life, thereby enriching the outer envelope with elements other than hydrogen, in a process called dredge-up. The envelope is finally ejected out into space, sometimes in a spherical shell, but often in an asymmetrical shape, creating ...
... the surface repeatedly during this late stage of a low-mass star’s life, thereby enriching the outer envelope with elements other than hydrogen, in a process called dredge-up. The envelope is finally ejected out into space, sometimes in a spherical shell, but often in an asymmetrical shape, creating ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... pass by the Sun only once or that repeatedly bring them through the solar system (as in the 76-year orbit of Halley’s Comet). A comet’s “signature” long, glowing tail Continued … ...
... pass by the Sun only once or that repeatedly bring them through the solar system (as in the 76-year orbit of Halley’s Comet). A comet’s “signature” long, glowing tail Continued … ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... • The axis ratio of the bar depends upon the degree o random motions in the original disks: the cooler the initial disk the narrower the resulting bar. • When the initial bar is short, it continues to interact with the outer disk through spiral activity: the trailing spirals remove angular momentum ...
... • The axis ratio of the bar depends upon the degree o random motions in the original disks: the cooler the initial disk the narrower the resulting bar. • When the initial bar is short, it continues to interact with the outer disk through spiral activity: the trailing spirals remove angular momentum ...
Slide 1
... Intensity in Single-Slit Diffraction, Qualitatively To obtain the locations of the minima, the slit was equally divided into N zones, each with width Dx. Each zone acts as a source of Huygens wavelets. Now these zones can be superimposed at the screen to obtain the intensity as function of q, the a ...
... Intensity in Single-Slit Diffraction, Qualitatively To obtain the locations of the minima, the slit was equally divided into N zones, each with width Dx. Each zone acts as a source of Huygens wavelets. Now these zones can be superimposed at the screen to obtain the intensity as function of q, the a ...
Star Formation in the Galaxy, An Observational Overview
... is again balanced by internal pressure. After this phase such stars will eject their outer atmospheres producing planetary nebula and leaving behind a white dwarf stellar remnant. More massive stars experience a more complex post-main sequence evolution during which they will fuse heavier elements i ...
... is again balanced by internal pressure. After this phase such stars will eject their outer atmospheres producing planetary nebula and leaving behind a white dwarf stellar remnant. More massive stars experience a more complex post-main sequence evolution during which they will fuse heavier elements i ...
White dwarfs, black holes, dark matter
... a heavy mass is strongly attracted by gravity, e.g. from Earth; a low mass less so it takes more effort to bring a heavy mass into motion than a light mass: the inert mass of a heavy object is bigger as a result a low-mass object falls equally fast as a heavy one: heavy mass = inert mass. Accidental ...
... a heavy mass is strongly attracted by gravity, e.g. from Earth; a low mass less so it takes more effort to bring a heavy mass into motion than a light mass: the inert mass of a heavy object is bigger as a result a low-mass object falls equally fast as a heavy one: heavy mass = inert mass. Accidental ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.