Annual Report 2012 - Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics
... quickly repaired by a complete exchange of the computer. In addition to the desktop systems, which, in large part are younger than 5 years and which (in 2012) amount to more than 170 fully equipped working places, users have access to central number crunchers (about 20 machines, all 64-bit architect ...
... quickly repaired by a complete exchange of the computer. In addition to the desktop systems, which, in large part are younger than 5 years and which (in 2012) amount to more than 170 fully equipped working places, users have access to central number crunchers (about 20 machines, all 64-bit architect ...
Astrobiological Stoichiometry
... and Fe in five different stars (the data sets are discussed and the research groups identified by Hinkel, 2012). The maximum abundance measurement minus the minimum for each element within a star is referred to as the ‘‘spread.’’ The observational spread in [Na/H] within HIP 79672, for example, is * ...
... and Fe in five different stars (the data sets are discussed and the research groups identified by Hinkel, 2012). The maximum abundance measurement minus the minimum for each element within a star is referred to as the ‘‘spread.’’ The observational spread in [Na/H] within HIP 79672, for example, is * ...
doc
... their autonomy and have become incorporated into larger political units, if we focus on their internal structure we find that they remained pretty much the same. They have proved to be remarkably stable units. Indeed, as tightly integrated social units, they have frequently outlasted the overarching ...
... their autonomy and have become incorporated into larger political units, if we focus on their internal structure we find that they remained pretty much the same. They have proved to be remarkably stable units. Indeed, as tightly integrated social units, they have frequently outlasted the overarching ...
Document
... distances from the galactic plane. We find Type A stars (perfectly normal main sequence type stars) moving at velocities even exceeding 400 kilometres per second. If they were gravitationally bound this observation would be seriously discrepant with estimates of the mass of the Milky Way Galaxy. Man ...
... distances from the galactic plane. We find Type A stars (perfectly normal main sequence type stars) moving at velocities even exceeding 400 kilometres per second. If they were gravitationally bound this observation would be seriously discrepant with estimates of the mass of the Milky Way Galaxy. Man ...
Galaxy Cosmological Mass Function
... estimate the redshift evolution of the average galactic mass and luminosity. These two pieces of information are crucial to our analysis because they cannot be obtained through cosmological principles, but have direct implications for a range of theoretical considerations and the determination of an ...
... estimate the redshift evolution of the average galactic mass and luminosity. These two pieces of information are crucial to our analysis because they cannot be obtained through cosmological principles, but have direct implications for a range of theoretical considerations and the determination of an ...
Jeopardy Atomic Physics
... When the intensity of light is increased in a photoelectric effect experiment, the energy of the emitted electrons stays the same. Back to Jeopardy ...
... When the intensity of light is increased in a photoelectric effect experiment, the energy of the emitted electrons stays the same. Back to Jeopardy ...
X-ray Emission Line Profiles from ... Confined Wind Shock Model
... field. Our analytic models produce simplified, steady-state velocity and density profiles of a structured wind, and our simulations provide time-dependent values for temperature, velocity, and density at points throughout the wind. The information from each of these methods allows us to determine wh ...
... field. Our analytic models produce simplified, steady-state velocity and density profiles of a structured wind, and our simulations provide time-dependent values for temperature, velocity, and density at points throughout the wind. The information from each of these methods allows us to determine wh ...
The Big Dipper Star Clock
... 2. Punch a hole in the middle of each circle. 3. Put a paper fastener through the two holes. The black circle with the notch and the words “THE TIME IS” should be on top. 4. Make sure the wheels can turn smoothly around the fastener. You may have to make your holes a little bigger if they don’t. ...
... 2. Punch a hole in the middle of each circle. 3. Put a paper fastener through the two holes. The black circle with the notch and the words “THE TIME IS” should be on top. 4. Make sure the wheels can turn smoothly around the fastener. You may have to make your holes a little bigger if they don’t. ...
A UV study of nearby luminous infrared galaxies: star formation
... The advent of the GALEX ultra-violet (UV) space telescope (Martin et al. 2005) is revolutionising our understanding of the local Universe in the UV wavelengths (shortward of ∼ 3000Å). The UV spectrum is overwhelmingly dominated by flux from young massive main sequence stars, making it an ideal prob ...
... The advent of the GALEX ultra-violet (UV) space telescope (Martin et al. 2005) is revolutionising our understanding of the local Universe in the UV wavelengths (shortward of ∼ 3000Å). The UV spectrum is overwhelmingly dominated by flux from young massive main sequence stars, making it an ideal prob ...
Lab 1
... Click and drag a graph to "Light Intensity." Click and drag the angular position to the x axis and release to create a graph with "Light Intensity" on the y-axis, and "angular position" on the x-axis. Now, you are ready to take data. The best data will be obtained if the light source, polarizers, an ...
... Click and drag a graph to "Light Intensity." Click and drag the angular position to the x axis and release to create a graph with "Light Intensity" on the y-axis, and "angular position" on the x-axis. Now, you are ready to take data. The best data will be obtained if the light source, polarizers, an ...
The Formation of High Mass Stars
... How do feedback mechanisms such as protostellar outflows and radiation affect protostellar evolution? These mechanisms can also have a dramatic effect on cluster formation ...
... How do feedback mechanisms such as protostellar outflows and radiation affect protostellar evolution? These mechanisms can also have a dramatic effect on cluster formation ...
The fourth catalogue of Population I Wolf
... emissions are observed, the WC sequence. In the scheme adopted by the IAU Commission 29 (Beals 1938), ranging from the highest to the lowest excitation, only the subtypes WN5 to WN8 and WC6 to WC8 were considered. Subsequent systematic investigations of the spectra of W − R stars in the Galaxy and t ...
... emissions are observed, the WC sequence. In the scheme adopted by the IAU Commission 29 (Beals 1938), ranging from the highest to the lowest excitation, only the subtypes WN5 to WN8 and WC6 to WC8 were considered. Subsequent systematic investigations of the spectra of W − R stars in the Galaxy and t ...
3-D Visualization of Cataclysmic Variables With IDL by:
... toward the white dwarf. In some systems, especially those where the magnetic field of the white dwarf is not very strong, the gas doesn’t actually fall directly into the white dwarf but encircles it and forms a disc. This disc, known as an accretion disc with the white dwarf serving as its center, ...
... toward the white dwarf. In some systems, especially those where the magnetic field of the white dwarf is not very strong, the gas doesn’t actually fall directly into the white dwarf but encircles it and forms a disc. This disc, known as an accretion disc with the white dwarf serving as its center, ...
Department of Physics, Technical University Ostrava 17. listopadu
... 80 µm. As an example, Fig. 2 shows by the dots the recorded spectral interferogram corresponding to the adjusted OPD between beams of the interferometer of approximately −10 µm. By processing the spectral interferogram using the FTM, the background spectrum a(λ), the envelope spectrum b(λ) and the u ...
... 80 µm. As an example, Fig. 2 shows by the dots the recorded spectral interferogram corresponding to the adjusted OPD between beams of the interferometer of approximately −10 µm. By processing the spectral interferogram using the FTM, the background spectrum a(λ), the envelope spectrum b(λ) and the u ...
Aalborg Universitet Slow-plasmon resonant-nanostrip antennas
... the scattering calculations considering scattered light in all directions 共Figs. 5 and 6兲 were similar to calculations including only scattered light in the limited angular range that the setup can collect. We notice that for the same strip width, the wavelength of spectral peaks are clearly differe ...
... the scattering calculations considering scattered light in all directions 共Figs. 5 and 6兲 were similar to calculations including only scattered light in the limited angular range that the setup can collect. We notice that for the same strip width, the wavelength of spectral peaks are clearly differe ...
12 Introduction to Cepheid Variable Stars Exercise
... If you know the distance to the bulb and measure its apparent brightness then you can calculate the wattage of the bulb. Likewise, if you know the wattage of the bulb and measure the observed brightness you can calculate the distance to the bulb. This can be applied to stars, if you determine the ap ...
... If you know the distance to the bulb and measure its apparent brightness then you can calculate the wattage of the bulb. Likewise, if you know the wattage of the bulb and measure the observed brightness you can calculate the distance to the bulb. This can be applied to stars, if you determine the ap ...
Table of Contents
... when people noticed a highly unusual source of radio emission in the southern constellation of Sagittarius (see Figure 2). This source was ...
... when people noticed a highly unusual source of radio emission in the southern constellation of Sagittarius (see Figure 2). This source was ...
a brief history of time
... Any physical theory is always provisional, in the sense that it is only a hypothesis: you can never prove it. No matter how many times the results of experiments agree with some theory, you can never be sure that the next time the result will not contradict the theory. On the other hand, you can dis ...
... Any physical theory is always provisional, in the sense that it is only a hypothesis: you can never prove it. No matter how many times the results of experiments agree with some theory, you can never be sure that the next time the result will not contradict the theory. On the other hand, you can dis ...
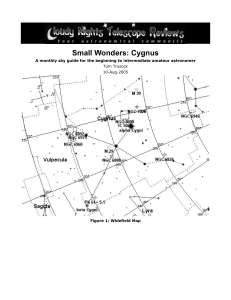
Small Wonders: Cygnus
... check out their website here: http://www.ceoptics.com/. Think night intensifier equipment mated to TeleVue optics. While it does not work equally well for all DSO’s, it does provide some very interesting views of planetary nebulae, usually makes nailing the central star a snap. ...
... check out their website here: http://www.ceoptics.com/. Think night intensifier equipment mated to TeleVue optics. While it does not work equally well for all DSO’s, it does provide some very interesting views of planetary nebulae, usually makes nailing the central star a snap. ...
AGN Science Collaboration - Active Galactic Nuclei Science
... AGN Dilution by Host Galaxy • Optical color selection of AGN is: - bias against AGN in SF galaxies - bias against low Eddington ratios • Selection bias can be partially overcome by: - variability (at least with nearby objects) - X-rays (not as deep as LSST) • LSST photometry / depth makes th ...
... AGN Dilution by Host Galaxy • Optical color selection of AGN is: - bias against AGN in SF galaxies - bias against low Eddington ratios • Selection bias can be partially overcome by: - variability (at least with nearby objects) - X-rays (not as deep as LSST) • LSST photometry / depth makes th ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.