ly Searching the Sky: The Swift Mission and High Energy Physics Connections
... • LIGO analyzes a candidate trigger by dividing the sky into 0.4°× 0.4° pixels and assigning a likelihood to each pixel. A combined LIGO/Virgo trigger will produce a region of ~50 pixels, localizing the candidate gravitational wave source • Currently, LIGO/Virgo is sensitive out to ~100 Mpc. A real- ...
... • LIGO analyzes a candidate trigger by dividing the sky into 0.4°× 0.4° pixels and assigning a likelihood to each pixel. A combined LIGO/Virgo trigger will produce a region of ~50 pixels, localizing the candidate gravitational wave source • Currently, LIGO/Virgo is sensitive out to ~100 Mpc. A real- ...
From: BXSVR0::OWOCKI 12-JAN-2001 10:16:41.12 To: DCOHEN
... a toy model. Sure enough, I got profiles that are reasonably symmetric, with slight blueshifts of the peak line emission. There is still some asymmetry between red and blue wings, as there must, but optical depth effects do introduce a new 'knob', and the lines being shown in papers are presumably t ...
... a toy model. Sure enough, I got profiles that are reasonably symmetric, with slight blueshifts of the peak line emission. There is still some asymmetry between red and blue wings, as there must, but optical depth effects do introduce a new 'knob', and the lines being shown in papers are presumably t ...
Michelson interferometer
... All source points on plate M seen under the same angle θn radiate with the same phase, the reason being that the actual light source behind the plate M radiates coherently, approximately from a single point. The same interference condition therefore applies on a conical surface with top angle 2θ wit ...
... All source points on plate M seen under the same angle θn radiate with the same phase, the reason being that the actual light source behind the plate M radiates coherently, approximately from a single point. The same interference condition therefore applies on a conical surface with top angle 2θ wit ...
Electron-impact broadening parameters for Be II, Sr II, and Ba II
... relies on the Be II resonance doublet at 3130 Å, which emphasizes the importance of these lines in our present work (Barklem & O’Mara 2000). Moreover, Be II line profiles are of interest for opacity calculations (Dimitrijević & Sahal-Bréchot 1992). The Sr II resonance lines (4077.7 Å, 4215.5 Å) an ...
... relies on the Be II resonance doublet at 3130 Å, which emphasizes the importance of these lines in our present work (Barklem & O’Mara 2000). Moreover, Be II line profiles are of interest for opacity calculations (Dimitrijević & Sahal-Bréchot 1992). The Sr II resonance lines (4077.7 Å, 4215.5 Å) an ...
Mirrors form images by reflecting light.
... Mirrors, lenses, and other optical inventions are called optical tools. By combining optical tools, inventors have developed powerful instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine opt ...
... Mirrors, lenses, and other optical inventions are called optical tools. By combining optical tools, inventors have developed powerful instruments to extend human vision. For example, the microscope uses a combination of mirrors and lenses to make very small structures visible. Telescopes combine opt ...
Here - Osservatorio di Arcetri
... Understanding the chemical evolution of interstellar clouds and star-forming regions is a central problem in astrophysics and astrochemistry. The starting point is the identification of the chemical species through their spectroscopic signatures: the frequency information in fact provides the unequi ...
... Understanding the chemical evolution of interstellar clouds and star-forming regions is a central problem in astrophysics and astrochemistry. The starting point is the identification of the chemical species through their spectroscopic signatures: the frequency information in fact provides the unequi ...
Rocky planetesimals as the origin of metals in DZ stars
... in sufficient density a few to several times per Galactic orbit (on average) for the solar neighbourhood (Dupuis et al. 1992, 1993a; Dupuis, Fontaine & Wesemael 1993b). Several factors have continually challenged the ISM pollution scenario. First, the typical dearth of hydrogen relative to calcium i ...
... in sufficient density a few to several times per Galactic orbit (on average) for the solar neighbourhood (Dupuis et al. 1992, 1993a; Dupuis, Fontaine & Wesemael 1993b). Several factors have continually challenged the ISM pollution scenario. First, the typical dearth of hydrogen relative to calcium i ...
chemical compositions of rv tauri stars and related objects
... abundances to the uncertainties of atmospheric parameters Teff , log g and ξ is presented in Table 3. For three stars representing the full temperature range of our sample, we present changes in [X/Fe] caused by varying atmospheric parameters by 200 K, 0.25 cm s−2 and 0.5 km s−1 (average accuracies ...
... abundances to the uncertainties of atmospheric parameters Teff , log g and ξ is presented in Table 3. For three stars representing the full temperature range of our sample, we present changes in [X/Fe] caused by varying atmospheric parameters by 200 K, 0.25 cm s−2 and 0.5 km s−1 (average accuracies ...
ATACAMA LARGE MILLIMETER / SUBMILLIMETER ARRAY
... in both continuum and the emission lines of interstellar molecules. It will image stars and planets being formed in gas clouds near the Sun, and it will observe galaxies in their formative stages at the edge of the Universe, which we see as they were roughly ten billion years ago. ALMA will provide ...
... in both continuum and the emission lines of interstellar molecules. It will image stars and planets being formed in gas clouds near the Sun, and it will observe galaxies in their formative stages at the edge of the Universe, which we see as they were roughly ten billion years ago. ALMA will provide ...
Lesson 1-0 Slides The Cosmic Landscape
... How can we measure huge distances? A clue—the common flashlight Speed of light—a way to measure distances in space ...
... How can we measure huge distances? A clue—the common flashlight Speed of light—a way to measure distances in space ...
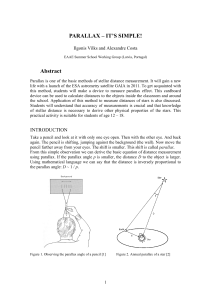
PARALLAX – IT`S SIMPLE! Abstract
... The first stellar parallax was measured by German astronomer F.W. Bessel in 1838. The parallax angle of star Cygnus 61 was very small, some tenths of arcsecond and hard to measure. Even for the nearest star, Alpha Centauri the annual parallax is less than 1 arcsecond (less than 1/3600 of one arc deg ...
... The first stellar parallax was measured by German astronomer F.W. Bessel in 1838. The parallax angle of star Cygnus 61 was very small, some tenths of arcsecond and hard to measure. Even for the nearest star, Alpha Centauri the annual parallax is less than 1 arcsecond (less than 1/3600 of one arc deg ...
BLAST: Study of the Earliest Stages of Galactic Star Formation
... D are at a distance of 700 ± 200 pc while Cloud B is ∼ 2 kpc away [10]. The VMR is an actively low- and intermediate-mass star forming region. It has been searched for young stellar objects (YSO) by different authors, usually through the IRAS and/or MSX Point Source Catalogues (PSC). NIR observation ...
... D are at a distance of 700 ± 200 pc while Cloud B is ∼ 2 kpc away [10]. The VMR is an actively low- and intermediate-mass star forming region. It has been searched for young stellar objects (YSO) by different authors, usually through the IRAS and/or MSX Point Source Catalogues (PSC). NIR observation ...
Observations of binary systems with pulsating components
... Binary systems parameters: summary We can derive masses of binary system’s components in following cases: • Visual binary with absolute orbit and parallax. • Visual binary with relative orbit + SB2: • we have 7 elements of relative orbit (we know the orbital inclination) • from spectroscopic soluti ...
... Binary systems parameters: summary We can derive masses of binary system’s components in following cases: • Visual binary with absolute orbit and parallax. • Visual binary with relative orbit + SB2: • we have 7 elements of relative orbit (we know the orbital inclination) • from spectroscopic soluti ...
Galactic astroarchaeology: reconstructing the bulge history by
... ratios in stars in Baade’s window and concluded that [Mg/Fe] was indeed high for a wide range of [Fe/H]. For other elements, such as oxygen, the situation was not very clear. These data were derived from low-resolution spectra. Minniti (1996) concluded from kinematics and metallicities of red giant ...
... ratios in stars in Baade’s window and concluded that [Mg/Fe] was indeed high for a wide range of [Fe/H]. For other elements, such as oxygen, the situation was not very clear. These data were derived from low-resolution spectra. Minniti (1996) concluded from kinematics and metallicities of red giant ...
An asymmetry detected in the disk of κ CMa⋆ with the AMBER/VLTI
... and from the measurements shown in Fig. 2, are given in Table 3. Using a uniform disk model for the envelope contribution, for each measurement, we also estimate in Table 3 the corresponding angular diameters in the continuum and in the Brγ line. Since the envelope is marginally resolved in the cont ...
... and from the measurements shown in Fig. 2, are given in Table 3. Using a uniform disk model for the envelope contribution, for each measurement, we also estimate in Table 3 the corresponding angular diameters in the continuum and in the Brγ line. Since the envelope is marginally resolved in the cont ...
Star formation in quasar hosts and the origin of radio emission in
... 2007; Mullaney et al. 2011; Chen et al. 2015) attempt to decompose emission from AGNs into a component powered by the black hole and a component powered by star formation in the host galaxy, and to use these measurements to determine the power of both processes. At the heart of these methods is the ...
... 2007; Mullaney et al. 2011; Chen et al. 2015) attempt to decompose emission from AGNs into a component powered by the black hole and a component powered by star formation in the host galaxy, and to use these measurements to determine the power of both processes. At the heart of these methods is the ...
Document
... R = nN Where n is the diffraction order and N is the number of illuminated blazes. Therefore, better resolving powers can be obtained for: a. Longer gratings. b. higher blaze density. c. Higher order of diffraction. ...
... R = nN Where n is the diffraction order and N is the number of illuminated blazes. Therefore, better resolving powers can be obtained for: a. Longer gratings. b. higher blaze density. c. Higher order of diffraction. ...
document
... A photodiode converts photons that hit its surface into a current. We place a photodiode such that the light from the atoms hit it, and measure the electric current. Using this value, we can calculate the steady-state atom number in the trap as well as the loading time. We found that 5.6 million ato ...
... A photodiode converts photons that hit its surface into a current. We place a photodiode such that the light from the atoms hit it, and measure the electric current. Using this value, we can calculate the steady-state atom number in the trap as well as the loading time. We found that 5.6 million ato ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.