0.1 Chapter 2
... Fermi-Dirac. At high temperatures, both follow the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. 20. What is the planck function and what does it mean? Answer: The function for black bodies that describes how radiation depends on the frequenty. 21. Which equation becomes important by partial ionised matter? Answe ...
... Fermi-Dirac. At high temperatures, both follow the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. 20. What is the planck function and what does it mean? Answer: The function for black bodies that describes how radiation depends on the frequenty. 21. Which equation becomes important by partial ionised matter? Answe ...
Atomic Clocks
... frequency is in the microwave region. Its frequency is 9,192 megacycles. This puts it, very conveniently, in the range of three-centimeter microwaves, a region which has been intensively explOited for radar work. Thus the necessary equip ment and techniques are ready to hand. What can go on in the ...
... frequency is in the microwave region. Its frequency is 9,192 megacycles. This puts it, very conveniently, in the range of three-centimeter microwaves, a region which has been intensively explOited for radar work. Thus the necessary equip ment and techniques are ready to hand. What can go on in the ...
Dai, S - PulsarAstronomy.net
... Neutron Stars through Astrometric Microlensing Sahu, K. C.; Albrow, M.; Anderson, J.; Bond, H. E.; Bond, I.; Brown, T. M.; Casertano, S.; Dominik, M.; Ferguson, H. C.; Fryer, C.; Livio, M.; Mao, S.; Perrott, Y.; Udalski, A.; Yock, P. 2012, American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts, 220, #307.0 ...
... Neutron Stars through Astrometric Microlensing Sahu, K. C.; Albrow, M.; Anderson, J.; Bond, H. E.; Bond, I.; Brown, T. M.; Casertano, S.; Dominik, M.; Ferguson, H. C.; Fryer, C.; Livio, M.; Mao, S.; Perrott, Y.; Udalski, A.; Yock, P. 2012, American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts, 220, #307.0 ...
Observational studies of stellar rotation
... In fact, interferometry and spectroscopy can be combined, a technique called spectro-interferometry, to measure the position angle of the rotational axis of stars whose surface is not fully spatially resolved. The method consists in measuring the position of the star’s photocenter across a spectral ...
... In fact, interferometry and spectroscopy can be combined, a technique called spectro-interferometry, to measure the position angle of the rotational axis of stars whose surface is not fully spatially resolved. The method consists in measuring the position of the star’s photocenter across a spectral ...
PowerPoint
... If light emitted by #2 moves relative to #2 at speed c, Galileo says that #1 must see it move at c + v. But light emitted by #1 moves relative to #1 at speed c – or at speed c – v relative to #2! So the speed of light can’t be the same for everyone if Galileo – and our intuition – are right. But Max ...
... If light emitted by #2 moves relative to #2 at speed c, Galileo says that #1 must see it move at c + v. But light emitted by #1 moves relative to #1 at speed c – or at speed c – v relative to #2! So the speed of light can’t be the same for everyone if Galileo – and our intuition – are right. But Max ...
Beam manipulation: prisms vs. mirrors
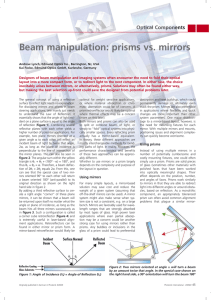
... number of potentially cumbersome and costly mounting fixtures, one could often simply use a prism. Prisms are solid pieces of glass (sometimes other materials) with polished faces that have been worked into optically meaningful shapes. Their effect depends on the position, number, and angles of face ...
... number of potentially cumbersome and costly mounting fixtures, one could often simply use a prism. Prisms are solid pieces of glass (sometimes other materials) with polished faces that have been worked into optically meaningful shapes. Their effect depends on the position, number, and angles of face ...
Optics - Frederiksen
... insulated holders with electrodes, where the lower holder is spring loaded parallel to the tube axis. The holder is provided with a power supply which can deliver 6 kV DC at max. 2 mA to the electrodes built into the base of the insulated holder. Can be used with spectral tubes 2850.00 – 2851.30 and ...
... insulated holders with electrodes, where the lower holder is spring loaded parallel to the tube axis. The holder is provided with a power supply which can deliver 6 kV DC at max. 2 mA to the electrodes built into the base of the insulated holder. Can be used with spectral tubes 2850.00 – 2851.30 and ...
02-01/02 Intro to Light and Electromagnetic waves Problem Set
... ____ 22. The primary purpose of polarized sunglasses is_____. a. to block ultraviolet rays. b. to block infrared rays. c. to block glare from reflections. d. to look cool. ____ 23. Light does not pass through what kind of materials? a. transparent b. opaque c. neither a nor b ____ 24. How far is a l ...
... ____ 22. The primary purpose of polarized sunglasses is_____. a. to block ultraviolet rays. b. to block infrared rays. c. to block glare from reflections. d. to look cool. ____ 23. Light does not pass through what kind of materials? a. transparent b. opaque c. neither a nor b ____ 24. How far is a l ...
Electrical properties of Nb-doped titanium dioxide TiO at room temperature A.
... study. Below doping level of 10 at. % of Nb, materials exhibit rutile structure and lattice parameters change with Nb concentration according to Vegard’s law. Above dopant concentration of 10 at. % of a second phase, TiNb2O7, was detected. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy within the frequency ...
... study. Below doping level of 10 at. % of Nb, materials exhibit rutile structure and lattice parameters change with Nb concentration according to Vegard’s law. Above dopant concentration of 10 at. % of a second phase, TiNb2O7, was detected. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy within the frequency ...
Comets and astrobiology
... ice to condense, embedding “dust” particles made of organic and/ or mineral material. The resulting “dirty snowball” is the nucleus of the comet, with typical sizes of 1 to 100 km: the nucleus of the famous comet 1P/Halley has an irregular shape, roughly 8 × 8 × 16 km. It was measured from pictures ...
... ice to condense, embedding “dust” particles made of organic and/ or mineral material. The resulting “dirty snowball” is the nucleus of the comet, with typical sizes of 1 to 100 km: the nucleus of the famous comet 1P/Halley has an irregular shape, roughly 8 × 8 × 16 km. It was measured from pictures ...
- Welcome to UC Santa Barbara
... Due to high intensity, fs pulses can not be amplified as is. Recipe for the amplification: Chirped pulse amplifier (CPA) • Stretch the pulse in time, thus reducing the peak power (I = J / tpulse !) (typically the pulse is stretched up to hundreds of ps) • Amplify the stretched pulse • Compress the p ...
... Due to high intensity, fs pulses can not be amplified as is. Recipe for the amplification: Chirped pulse amplifier (CPA) • Stretch the pulse in time, thus reducing the peak power (I = J / tpulse !) (typically the pulse is stretched up to hundreds of ps) • Amplify the stretched pulse • Compress the p ...
Introductory Astronomy
... at are its center • If “Nebulae” are other galaxies, must be far away, but “novae” in them are ~as bright as novae in our Galaxy • van Maanen: claimed to measure rotation of M31 • Nebulae “avoid” the Milky Way • Nebulae all appear to be moving away from us ...
... at are its center • If “Nebulae” are other galaxies, must be far away, but “novae” in them are ~as bright as novae in our Galaxy • van Maanen: claimed to measure rotation of M31 • Nebulae “avoid” the Milky Way • Nebulae all appear to be moving away from us ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.