Experimental Competition
... frequency ranges over which the properties of the “image” are drastically different. To describe these observations complete the table on the answer form by adding a row to this table for each such frequency range and fill it in by using the appropriate notations explained on that page. ...
... frequency ranges over which the properties of the “image” are drastically different. To describe these observations complete the table on the answer form by adding a row to this table for each such frequency range and fill it in by using the appropriate notations explained on that page. ...
WDM Concepts and Components
... of 2x2 MZI multiplexer • The lengths of adjacent waveguides differ by a constant L • Different wavelengths get multiplexed (multi-inputs one output) or de-multiplexed (one input multi output) • For wavelength routing applications multiinput multi-output routers are available ...
... of 2x2 MZI multiplexer • The lengths of adjacent waveguides differ by a constant L • Different wavelengths get multiplexed (multi-inputs one output) or de-multiplexed (one input multi output) • For wavelength routing applications multiinput multi-output routers are available ...
Daedalon EO-85 Computerized Spectrophotometer
... screen. Adjust the exposure so that all three peaks are about the same height. You may have to change the exposure time to get them all about the same size on the graph. You can also change height by changing the distance from the LED to the entrance port. Note that you can erase one or more spectra ...
... screen. Adjust the exposure so that all three peaks are about the same height. You may have to change the exposure time to get them all about the same size on the graph. You can also change height by changing the distance from the LED to the entrance port. Note that you can erase one or more spectra ...
student spectrometer
... year from the date of shipment to the customer. PASCO will repair or replace, at its option, any part of the product which is deemed to be defective in material or workmanship. This warranty does not cover damage to the product caused by abuse or improper use. Determination of whether a product fail ...
... year from the date of shipment to the customer. PASCO will repair or replace, at its option, any part of the product which is deemed to be defective in material or workmanship. This warranty does not cover damage to the product caused by abuse or improper use. Determination of whether a product fail ...
Effect of group-delay ripples on dispersion
... with the predictions of the reduced models. If the input pulse’s energies are sufficiently large that the bandwidths of the resultant solitons are much larger than the ripple period, the relative phase between the center frequency of the soliton and the ripples does not affect the results. However, ...
... with the predictions of the reduced models. If the input pulse’s energies are sufficiently large that the bandwidths of the resultant solitons are much larger than the ripple period, the relative phase between the center frequency of the soliton and the ripples does not affect the results. However, ...
Multiple wavelength diffractive imaging - X
... diffraction #8,9$ are not well matched to the phase space of the light delivered by tabletop sources. A better match between the phase space of the incident light and the image formation method will provide corresponding efficiencies in the utilization of the source. In this paper we demonstrate coh ...
... diffraction #8,9$ are not well matched to the phase space of the light delivered by tabletop sources. A better match between the phase space of the incident light and the image formation method will provide corresponding efficiencies in the utilization of the source. In this paper we demonstrate coh ...
4.3 Wave characteristics
... When two waves of the same frequency superimpose, we can get constructive interference or destructive interference. ...
... When two waves of the same frequency superimpose, we can get constructive interference or destructive interference. ...
Practical Laboratory #2: Emission Spectra 2
... • measure the emission spectrum of a heated gas using the digital spectrometer. • record a number of the bright lines in the spectrum. • compare the measured spectrum with the known spectra for specific gases • identify the unknown gas. ...
... • measure the emission spectrum of a heated gas using the digital spectrometer. • record a number of the bright lines in the spectrum. • compare the measured spectrum with the known spectra for specific gases • identify the unknown gas. ...
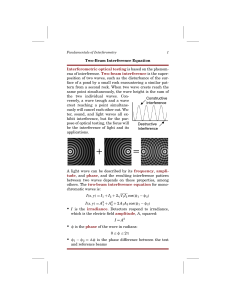
Two-Beam Interference Equation Interferometric optical testing is
... Most laboratory interferometers create two beams using division of amplitude beamsplitters, where the irradiance is divided across the entire wavefront such that the diameter of the beam is unchanged. This can be done using cube beamsplitters, plate beamsplitters, pellicles, and diffraction gratings ...
... Most laboratory interferometers create two beams using division of amplitude beamsplitters, where the irradiance is divided across the entire wavefront such that the diameter of the beam is unchanged. This can be done using cube beamsplitters, plate beamsplitters, pellicles, and diffraction gratings ...
Fresnel`s Theory of wave propagation
... Figure 2: Huygens' wavelets. Originating along the fronts of (A) circular waves and (B) plane waves, wavelets recombine to produce the propagating wave front. (C) The diffraction of sound around a corner arising from Huygens' wavelets. ...
... Figure 2: Huygens' wavelets. Originating along the fronts of (A) circular waves and (B) plane waves, wavelets recombine to produce the propagating wave front. (C) The diffraction of sound around a corner arising from Huygens' wavelets. ...
VCE UNIT 4 SAC
... image produced is on the attached sheet. This image resulted from green light of wavelength 520 nm passing through two slits that were separated by 1 mm and then travelled a distance of 80 cm to a screen. There are various points marked on the image produced where A is the centre of the pattern. (a) ...
... image produced is on the attached sheet. This image resulted from green light of wavelength 520 nm passing through two slits that were separated by 1 mm and then travelled a distance of 80 cm to a screen. There are various points marked on the image produced where A is the centre of the pattern. (a) ...
Tutor 4
... resolution is possible. Consider the simple case of a mask pattern of equal lines and spaces. As we have seen, the resulting diffraction pattern is a series of discrete diffraction orders. In order to produce an image which even remotely resembles the original mask pattern it is necessary for the ob ...
... resolution is possible. Consider the simple case of a mask pattern of equal lines and spaces. As we have seen, the resulting diffraction pattern is a series of discrete diffraction orders. In order to produce an image which even remotely resembles the original mask pattern it is necessary for the ob ...
Application of Digital Phase-shift Shadow Moiré to Micro
... categories: projection Moiré and shadow Moiré, according to the optical arrangement used. In the case of a standard projection Moiré system, a precisely matching pair of gratings is typically used. The projection grating is placed in front of the light source and the reference grating or camera grat ...
... categories: projection Moiré and shadow Moiré, according to the optical arrangement used. In the case of a standard projection Moiré system, a precisely matching pair of gratings is typically used. The projection grating is placed in front of the light source and the reference grating or camera grat ...
Observation of sagittal X-ray diffraction by surface acoustic waves in
... In the present work we concentrate on surface acoustic waves (SAWs). SAWs propagate on the surface of a solid, parallel to it, and their amplitude shows an exponential decay in the bulk. SAWs modulate the surface of a crystal or a multilayer and can be used as a diffraction grating for X-ray radiati ...
... In the present work we concentrate on surface acoustic waves (SAWs). SAWs propagate on the surface of a solid, parallel to it, and their amplitude shows an exponential decay in the bulk. SAWs modulate the surface of a crystal or a multilayer and can be used as a diffraction grating for X-ray radiati ...
revision_foundation_..
... • If a radio wave is transmitted from a vertical aerial then the wave will have vertical polarisation and any receiving aerial must also be positioned vertically. • The main transmitters in the U.K. send out signals which are horizontally polarised. • Many areas of the country are now served by mixe ...
... • If a radio wave is transmitted from a vertical aerial then the wave will have vertical polarisation and any receiving aerial must also be positioned vertically. • The main transmitters in the U.K. send out signals which are horizontally polarised. • Many areas of the country are now served by mixe ...
The Refraction of Light
... • When light travels from one medium into another, some of the light is reflected and some is refracted. • Recall: Light bends away from the normal when it speeds up at the boundary of two media (example: as light travels from water to air) • As angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction ...
... • When light travels from one medium into another, some of the light is reflected and some is refracted. • Recall: Light bends away from the normal when it speeds up at the boundary of two media (example: as light travels from water to air) • As angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction ...
Refraction - Snell`s Law, Internal Reflection, Dispersion (PowerPoint)
... The fact that rainbows are semicircular tells you that the light from one has to come from the water drops at the right angle angle*. When white light enters a water drop light is refracted and disperses into its component colors. Violet is bent the most and red the least. When the rays reach the op ...
... The fact that rainbows are semicircular tells you that the light from one has to come from the water drops at the right angle angle*. When white light enters a water drop light is refracted and disperses into its component colors. Violet is bent the most and red the least. When the rays reach the op ...
Planck`s “quantum of action” from the photoelectric effect (line
... As can be seen on the graph in Fig.2, when the value of V is high and positive, the current i is a constant. This occurs because all the photoelectrons formed at the cathode are reaching the anode. By increasing the intensity I, a higher constant value and current is obtained, because more electrons ...
... As can be seen on the graph in Fig.2, when the value of V is high and positive, the current i is a constant. This occurs because all the photoelectrons formed at the cathode are reaching the anode. By increasing the intensity I, a higher constant value and current is obtained, because more electrons ...
refraction ppt_2010
... • A ray of light is traveling through air (n = 1.00) towards a lucite block (n = 1.40) in the shape of a 30-60-90 triangle. Trace the path of the light ray through the lucite block shown in the diagram below. ...
... • A ray of light is traveling through air (n = 1.00) towards a lucite block (n = 1.40) in the shape of a 30-60-90 triangle. Trace the path of the light ray through the lucite block shown in the diagram below. ...
Reflection of Light
... • Because the surface is not smooth, the light rays are scattered in many directions. This is called diffuse reflection. • The laws of reflection still apply to rough surfaces! ...
... • Because the surface is not smooth, the light rays are scattered in many directions. This is called diffuse reflection. • The laws of reflection still apply to rough surfaces! ...
Efficient output coupling of intracavity high harmonic generation
... revolutionized optical frequency metrology [1, 2]. However these techniques have in general been limited to the visible and near IR spectral regions. Meanwhile, progress in short-wavelength light sources has been rapid, achieving unprecedented temporal resolution, spectral coverage, and brightness [ ...
... revolutionized optical frequency metrology [1, 2]. However these techniques have in general been limited to the visible and near IR spectral regions. Meanwhile, progress in short-wavelength light sources has been rapid, achieving unprecedented temporal resolution, spectral coverage, and brightness [ ...
Anisotropic Minerals
... The two waves are OUT OF PHASE they destructively interfere, cancelling each other out, producing the resultant wave (R), which has no amplitude or wavelength. ...
... The two waves are OUT OF PHASE they destructively interfere, cancelling each other out, producing the resultant wave (R), which has no amplitude or wavelength. ...
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves – Radiant Energy II
... e) Explain the different effects when red and blue photons strike the fluorescent board. (Hint: How can the visible light given off by fluorescing materials be explained in terms of the energy of photons?) A photon of blue light has a shorter wavelength and more energy than a photon of red light. Th ...
... e) Explain the different effects when red and blue photons strike the fluorescent board. (Hint: How can the visible light given off by fluorescing materials be explained in terms of the energy of photons?) A photon of blue light has a shorter wavelength and more energy than a photon of red light. Th ...
Diffraction grating

In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The emerging coloration is a form of structural coloration. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as the dispersive element. Because of this, gratings are commonly used in monochromators and spectrometers.For practical applications, gratings generally have ridges or rulings on their surface rather than dark lines. Such gratings can be either transmissive or reflective. Gratings which modulate the phase rather than the amplitude of the incident light are also produced, frequently using holography.The principles of diffraction gratings were discovered by James Gregory, about a year after Newton's prism experiments, initially with items such as bird feathers. The first man-made diffraction grating was made around 1785 by Philadelphia inventor David Rittenhouse, who strung hairs between two finely threaded screws. This was similar to notable German physicist Joseph von Fraunhofer's wire diffraction grating in 1821.Diffraction can create ""rainbow"" colors when illuminated by a wide spectrum (e.g., continuous) light source. The sparkling effects from the closely spaced narrow tracks on optical storage disks such as CD's or DVDs are an example, while the similar rainbow effects caused by thin layers of oil (or gasoline, etc.) on water are not caused by a grating, but rather by interference effects in reflections from the closely spaced transmissive layers (see Examples, below). A grating has parallel lines, while a CD has a spiral of finely-spaced data tracks. Diffraction colors also appear when one looks at a bright point source through a translucent fine-pitch umbrella-fabric covering. Decorative patterned plastic films based on reflective grating patches are very inexpensive, and are commonplace.