Higher-order Logic: Foundations
... element x for which f x is True, provided it exists. Otherwise, it yields an arbitrary value. • Note that in Isabelle, the provisos “for all types τ ” can be expressed by using polymorphic type variables α. (rev. 12275) ...
... element x for which f x is True, provided it exists. Otherwise, it yields an arbitrary value. • Note that in Isabelle, the provisos “for all types τ ” can be expressed by using polymorphic type variables α. (rev. 12275) ...
ppt
... We do not evaluate the last We need to evaluate the last argument in the above function argument yet, and figures out call, i.e., that we do not need it (add (inc 3) (dec 0)), Which becomes (add 4 -1) This then becomes infinite loop ...
... We do not evaluate the last We need to evaluate the last argument in the above function argument yet, and figures out call, i.e., that we do not need it (add (inc 3) (dec 0)), Which becomes (add 4 -1) This then becomes infinite loop ...
View raw file - aaa
... Idea: Allow abstraction over types. Then, we can write a single identity function for any type a: Λa.λx:a.x We extend our definition of types and terms: ...
... Idea: Allow abstraction over types. Then, we can write a single identity function for any type a: Λa.λx:a.x We extend our definition of types and terms: ...
Functional Programming in CLEAN
... Many centuries before the advent of digital computers, functions have been used to describe the relation between input and output of processes. Computer programs, too, are descriptions of the way a result can be computed, given some arguments. A natural way to write a computer program is therefore t ...
... Many centuries before the advent of digital computers, functions have been used to describe the relation between input and output of processes. Computer programs, too, are descriptions of the way a result can be computed, given some arguments. A natural way to write a computer program is therefore t ...
nil
... Definition From the "comp.lang.functional FAQ" Functional programming is a style of programming that emphasizes the evaluation of expressions, rather than execution of commands. The expressions in these ...
... Definition From the "comp.lang.functional FAQ" Functional programming is a style of programming that emphasizes the evaluation of expressions, rather than execution of commands. The expressions in these ...
Introduction to Imperative C Functional vs. imperative programming
... An expression with a side effect does more than produce a value: it also changes the state of the program (or “the world”). Functions (or programs) can also have side effects. We have already seen a C function with a side effect: printf. The side effect of printf is that it displays “output”. In oth ...
... An expression with a side effect does more than produce a value: it also changes the state of the program (or “the world”). Functions (or programs) can also have side effects. We have already seen a C function with a side effect: printf. The side effect of printf is that it displays “output”. In oth ...
X - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute: Computer Science
... • Embedding is when procedure values are put in data structures • Embedding has many uses: – Modules: a module is a record that groups together a set of related operations – Software components: a software component is a generic function that takes a set of modules as its arguments and returns a new ...
... • Embedding is when procedure values are put in data structures • Embedding has many uses: – Modules: a module is a record that groups together a set of related operations – Software components: a software component is a generic function that takes a set of modules as its arguments and returns a new ...
Introduction Into Functional Programming
... 2.2 If the searched word is “less” then the shown ones, then 2.2.1 continue search within the left half of the book; otherwise 2.2.2 continue search within with the right half of the book. ...
... 2.2 If the searched word is “less” then the shown ones, then 2.2.1 continue search within the left half of the book; otherwise 2.2.2 continue search within with the right half of the book. ...
Functional Programming Paradigm Learning Outcomes:
... • The objective of the design of a FPL is to mimic mathematical functions to the greatest extent possible • The basic process of computation is fundamentally different in a FPL than in an imperative language – In an imperative language, operations are done and the results are stored in variables for ...
... • The objective of the design of a FPL is to mimic mathematical functions to the greatest extent possible • The basic process of computation is fundamentally different in a FPL than in an imperative language – In an imperative language, operations are done and the results are stored in variables for ...
ppt
... 9. PDCS Exercise 2.11.10 (page 31). Test your representation of numbers in Haskell. 10. PDCS Exercise 2.11.11 (page 31). 11. Prove that your addition operation is correct using ...
... 9. PDCS Exercise 2.11.10 (page 31). Test your representation of numbers in Haskell. 10. PDCS Exercise 2.11.11 (page 31). 11. Prove that your addition operation is correct using ...
Boost.Lambda
... meaning of _2 in bind makes sense only in the context of the outer expression Warning: not always what one wants! ...
... meaning of _2 in bind makes sense only in the context of the outer expression Warning: not always what one wants! ...
Introduction to Functional Programming (1)
... 1960s Peter Landin develops ISWIM, the first pure functional language, based strongly on the lambda calculus, with no assignments. 1970s John Backus develops FP, a functional language that emphasizes higher-order functions and reasoning about programs. 1970s Robin Milner and others develop ML, the f ...
... 1960s Peter Landin develops ISWIM, the first pure functional language, based strongly on the lambda calculus, with no assignments. 1970s John Backus develops FP, a functional language that emphasizes higher-order functions and reasoning about programs. 1970s Robin Milner and others develop ML, the f ...
The Lambda Calculus: a minimal ML?
... β-reduction has some nice properties that enable a well-defined notion of computation over lambda terms. We reduce terms until no more reductions can be applied, in a manner that’s similar to evaluation of a functional language’s expressions. The lambda terms that have a reduced form— this is analog ...
... β-reduction has some nice properties that enable a well-defined notion of computation over lambda terms. We reduce terms until no more reductions can be applied, in a manner that’s similar to evaluation of a functional language’s expressions. The lambda terms that have a reduced form— this is analog ...
Functional Images
... We have explored this very simple notion of images as functions in a Haskell library–a “domain-specific embedded language” (DSEL) (Hudak, 1998)–that we call Pan. This paper presents the types and operations that make up Pan, and illustrates their use through a collection of examples. Some of the exa ...
... We have explored this very simple notion of images as functions in a Haskell library–a “domain-specific embedded language” (DSEL) (Hudak, 1998)–that we call Pan. This paper presents the types and operations that make up Pan, and illustrates their use through a collection of examples. Some of the exa ...
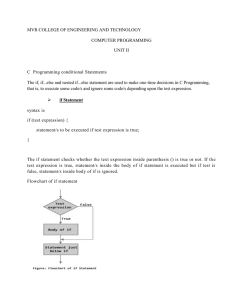
C Programming conditional Statements
... In this program, the user is asked to enter the value of n. Suppose you entered 19 then, count is initialized to 1 at first. Then, the test expression in the for loop,i.e., (count<= n) becomes true. So, the code in the body of for loop is executed which makes sum to 1. Then, the expression ++count i ...
... In this program, the user is asked to enter the value of n. Suppose you entered 19 then, count is initialized to 1 at first. Then, the test expression in the for loop,i.e., (count<= n) becomes true. So, the code in the body of for loop is executed which makes sum to 1. Then, the expression ++count i ...