Sound - Townley Grammar School
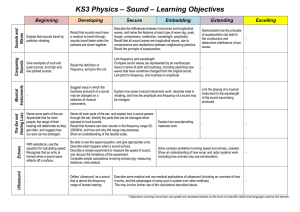
... Complete simple calculations involving echoes (eg. measuring distances, time delays). ...
... Complete simple calculations involving echoes (eg. measuring distances, time delays). ...
Waves transfer energy without transferring matter. There are two
... In transverse waves, the oscillation is at right-angles to the direction in which energy travels. Waves along a rope, light waves and waves on water are all examples of transverse waves. Wavelength ( λ) is the distance from the crest of a wave to the crest of the next wave (the length of each comple ...
... In transverse waves, the oscillation is at right-angles to the direction in which energy travels. Waves along a rope, light waves and waves on water are all examples of transverse waves. Wavelength ( λ) is the distance from the crest of a wave to the crest of the next wave (the length of each comple ...
CH 8-9 QUIZ
... Waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude in a process called _______. ...
... Waves combine to make a wave with a smaller amplitude in a process called _______. ...








