Derivation of the Universal Force Law—Part 4
... The non-radial terms of the force law explain the experimentally observed curling of plasma currents, the tilting of the orbits of the planets with respect to the equatorial plane of the sun, and certain inertial gyroscope motions. The derived force law satisfies Newton’s third law, conservation of ...
... The non-radial terms of the force law explain the experimentally observed curling of plasma currents, the tilting of the orbits of the planets with respect to the equatorial plane of the sun, and certain inertial gyroscope motions. The derived force law satisfies Newton’s third law, conservation of ...
TIME ASYMMETRY IN ELECTRODYNAMICS AND COSMOLOGY
... of time are strongly related. A new feature into this argument was introduced by Hogarth4 many years later. He pointed out that the above argument ignores the cosmological time arrow. In an expanding universe the past and future light cones do not behave symmetrically where absorption is concerned. ...
... of time are strongly related. A new feature into this argument was introduced by Hogarth4 many years later. He pointed out that the above argument ignores the cosmological time arrow. In an expanding universe the past and future light cones do not behave symmetrically where absorption is concerned. ...
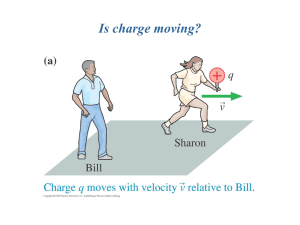
force on moving charge
... current-carrying wire. SHOW overhead view of B near currentcarrying wires. So now we have gotten completely away from permanent magnets, the historical and mysterious origin of the study of magnetism. From this point forward it became possible to create magnetic fields using coils of wire. A much cl ...
... current-carrying wire. SHOW overhead view of B near currentcarrying wires. So now we have gotten completely away from permanent magnets, the historical and mysterious origin of the study of magnetism. From this point forward it became possible to create magnetic fields using coils of wire. A much cl ...
em-gravit. waves - at www.arxiv.org.
... to eat it on the road before it melts. You take a carefree walk on a straight path, with constant pitch (thus, with constant velocity), without noticing a swarm of bees following you (or, rather, your ice cream)! When you suddenly notice them, you accelerate your motion in order to escape from them ...
... to eat it on the road before it melts. You take a carefree walk on a straight path, with constant pitch (thus, with constant velocity), without noticing a swarm of bees following you (or, rather, your ice cream)! When you suddenly notice them, you accelerate your motion in order to escape from them ...
Electroweak Physics (from an experimentalist!)
... this to observables that we can measure in experiments? ...
... this to observables that we can measure in experiments? ...
PHYSICS AM 26 SYLLABUS
... Progressive wave method for finding the wavelength of sound waves. Experiments to investigate reflection and refraction using visible light. Use of the spectrometer to measure wavelength using a diffraction grating. Experimental determination of the focal length of a thin converging lens by a graphi ...
... Progressive wave method for finding the wavelength of sound waves. Experiments to investigate reflection and refraction using visible light. Use of the spectrometer to measure wavelength using a diffraction grating. Experimental determination of the focal length of a thin converging lens by a graphi ...
D. Gravitational, Electric, and Magnetic Fields
... • use appropriate terminology related to fields, including, but not limited to: forces, potential energies, potential, and exchange particles • analyse, and solve problems relating to, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and circular motion (e.g., with respect to satellite orbits, black holes, d ...
... • use appropriate terminology related to fields, including, but not limited to: forces, potential energies, potential, and exchange particles • analyse, and solve problems relating to, Newton’s law of universal gravitation and circular motion (e.g., with respect to satellite orbits, black holes, d ...
Mass of an Electromagnetic Wave
... whilst also still having a maximum velocity equal to the speed of light. We find that their mass is inversely proportional to their velocity, such that they have no mass when travelling at the speed of light. This proportionality may also help explain the duality of light. ...
... whilst also still having a maximum velocity equal to the speed of light. We find that their mass is inversely proportional to their velocity, such that they have no mass when travelling at the speed of light. This proportionality may also help explain the duality of light. ...
Unit 8 Waves: Quantum Mechanical Waves
... of only about 10-10 m, about the same as the spacing between atoms in a solid, clearly showing that the wavelength of particles is important only on very small scales. While this is interesting, is it speculation or fact? Experimentation showed the basic factual nature of associating wave properties ...
... of only about 10-10 m, about the same as the spacing between atoms in a solid, clearly showing that the wavelength of particles is important only on very small scales. While this is interesting, is it speculation or fact? Experimentation showed the basic factual nature of associating wave properties ...
History of physics

Physics (from the Ancient Greek φύσις physis meaning ""nature"") is the fundamental branch of science that developed out of the study of nature and philosophy known, until around the end of the 19th century, as ""natural philosophy"". Today, physics is ultimately defined as the study of matter, energy and the relationships between them. Physics is, in some senses, the oldest and most basic pure science; its discoveries find applications throughout the natural sciences, since matter and energy are the basic constituents of the natural world. The other sciences are generally more limited in their scope and may be considered branches that have split off from physics to become sciences in their own right. Physics today may be divided loosely into classical physics and modern physics.