PHY 1150 - Concepts of Physics
... 1) List the 4 equations for ‘uniformly accelerated motion’. 2) Solve the sample problems dealing with uniformly accelerated motion as introduced in class. e) the ‘acceleration due to gravity’ – “free fall” 1) Explain how the ‘acceleration due to gravity’ is dependant upon the size, mass, ‘density’ a ...
... 1) List the 4 equations for ‘uniformly accelerated motion’. 2) Solve the sample problems dealing with uniformly accelerated motion as introduced in class. e) the ‘acceleration due to gravity’ – “free fall” 1) Explain how the ‘acceleration due to gravity’ is dependant upon the size, mass, ‘density’ a ...
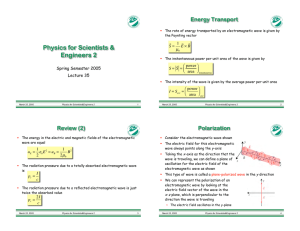
The Unification of Electricity and Magnetism
... (1) Dropping his molecular vortex concept simply because he couldn’t accurately visualize how the electrical particles interacted with the vortices. (2) Interpreting displacement current in electromagnetic radiation as a linear polarization effect. This had the long term effect of causing the scient ...
... (1) Dropping his molecular vortex concept simply because he couldn’t accurately visualize how the electrical particles interacted with the vortices. (2) Interpreting displacement current in electromagnetic radiation as a linear polarization effect. This had the long term effect of causing the scient ...
Thermo-charged capacitors and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... us take into account the Brownian motion or every fluctuation phenomena, for example. About Brownian motion, Poincaré wrote [1]: “[...] we see under our eyes now motion transformed into heat by friction, now heat changed inversely into motion, and that without loss since the movement lasts forever. ...
... us take into account the Brownian motion or every fluctuation phenomena, for example. About Brownian motion, Poincaré wrote [1]: “[...] we see under our eyes now motion transformed into heat by friction, now heat changed inversely into motion, and that without loss since the movement lasts forever. ...
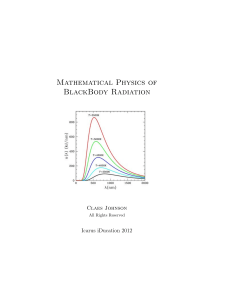
A Model for the Universe (5) Quanta and the Atom
... are the underlying basis for them and that this Universal Physics unifies and extends them. Now, however, the development has come to a point where there are mere hypotheses of various qualities and validities rather than "established physical laws". The presentation can no longer be in terms of cor ...
... are the underlying basis for them and that this Universal Physics unifies and extends them. Now, however, the development has come to a point where there are mere hypotheses of various qualities and validities rather than "established physical laws". The presentation can no longer be in terms of cor ...
ARE THERE REALLY ELECTRONS? EXPERIMENT AND REALITY
... do with the cathode rays build—and often enough sucAllan Franklin than a rifle-ball has with the ceed in building—new kinds flash when a rifle is fired."3 of device that use various Thomson repeated the experiment in 1897, but in a well-understood causal properties of electrons to interfere form tha ...
... do with the cathode rays build—and often enough sucAllan Franklin than a rifle-ball has with the ceed in building—new kinds flash when a rifle is fired."3 of device that use various Thomson repeated the experiment in 1897, but in a well-understood causal properties of electrons to interfere form tha ...
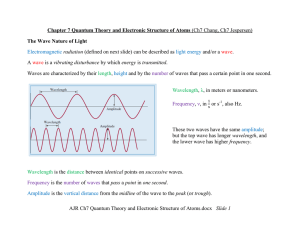
Faraday`s Law
... To oppose the change in flux, which is what Lenz’s law requires, the loop itself needs to generate an downward-pointing magnetic field. The induced current ceases as soon as the magnet stops moving. ...
... To oppose the change in flux, which is what Lenz’s law requires, the loop itself needs to generate an downward-pointing magnetic field. The induced current ceases as soon as the magnet stops moving. ...
paper
... 3. The luminosity of the Sun is 3·9 × 10 W and the mean radius of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is 1 astronomical unit (AU). (a) Calculate the Sun’s apparent brightness at the surface of the Earth. ...
... 3. The luminosity of the Sun is 3·9 × 10 W and the mean radius of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun is 1 astronomical unit (AU). (a) Calculate the Sun’s apparent brightness at the surface of the Earth. ...
Transport Theory Breakdown of Onsager Symmetry in Neoclassical PFC/JA-82-31
... asymmetry in the explicit processes can be brought out by small modifications of the boundary layer particle dynamics. This can cause a breakdown of the symmetry when turbulence is present. Whereas neoclassical theory can be viewed as a collisional scattering from one global collisionless orbit to a ...
... asymmetry in the explicit processes can be brought out by small modifications of the boundary layer particle dynamics. This can cause a breakdown of the symmetry when turbulence is present. Whereas neoclassical theory can be viewed as a collisional scattering from one global collisionless orbit to a ...
History of physics

Physics (from the Ancient Greek φύσις physis meaning ""nature"") is the fundamental branch of science that developed out of the study of nature and philosophy known, until around the end of the 19th century, as ""natural philosophy"". Today, physics is ultimately defined as the study of matter, energy and the relationships between them. Physics is, in some senses, the oldest and most basic pure science; its discoveries find applications throughout the natural sciences, since matter and energy are the basic constituents of the natural world. The other sciences are generally more limited in their scope and may be considered branches that have split off from physics to become sciences in their own right. Physics today may be divided loosely into classical physics and modern physics.