MicroEconomics
... commonly divided into four parts: allocation, distribution, stability, and growth. The study of allocation problems – what to produce and how much -, and the distribution problem – how real income is distributed among society’s members – are termed Microeconomic Theory. In microeconomics the major t ...
... commonly divided into four parts: allocation, distribution, stability, and growth. The study of allocation problems – what to produce and how much -, and the distribution problem – how real income is distributed among society’s members – are termed Microeconomic Theory. In microeconomics the major t ...
MEASURING PRODUCTION AND INCOME, Chapter 2
... In other words, C is the quantity of goods that the individual receives that is not related to hours worked. P C W L P C P C W L P C P C W L W L P C W L P C W (L L) P C W L P C W R P C W L Now we have combined the two constraints ...
... In other words, C is the quantity of goods that the individual receives that is not related to hours worked. P C W L P C P C W L P C P C W L W L P C W L P C W (L L) P C W L P C W R P C W L Now we have combined the two constraints ...
Chap 2 Microeconomic Tools for Health Economics
... • The PPF is a curve drawn in a graph to illustrate the trade-offs between two categories of goods=> no free lunch • Increasing opportunity cost (see Table 2-1) The slope of the PPF=opportunity cost Bowed-out shape of the PPF *An interior point in PPF means that it is inefficient. ...
... • The PPF is a curve drawn in a graph to illustrate the trade-offs between two categories of goods=> no free lunch • Increasing opportunity cost (see Table 2-1) The slope of the PPF=opportunity cost Bowed-out shape of the PPF *An interior point in PPF means that it is inefficient. ...
Inflation
... generally, the economic impact of an unanticipated moderate inflation is mainly on the distribution of income and wealth, and less on the efficiency of the system the mildest impact will be found when inflation is at a low rate – small, anticipated and balanced major social and economic imp ...
... generally, the economic impact of an unanticipated moderate inflation is mainly on the distribution of income and wealth, and less on the efficiency of the system the mildest impact will be found when inflation is at a low rate – small, anticipated and balanced major social and economic imp ...
Practice Quiz 5
... one another (e.g., coffee and cream for a coffee drinker who never varies the amount of cream used in each cup), then a. there is no substitution effect from a change in the price of coffee. b. there is no income effect from a change in the price of coffee. c. Giffen’s Paradox must occur if both cof ...
... one another (e.g., coffee and cream for a coffee drinker who never varies the amount of cream used in each cup), then a. there is no substitution effect from a change in the price of coffee. b. there is no income effect from a change in the price of coffee. c. Giffen’s Paradox must occur if both cof ...
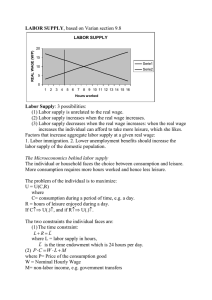
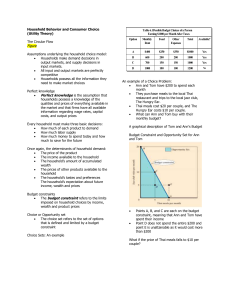
Household Behavior and Consumer Choice (Utility Theory) The
... The financial capital market refers to the complex set of institutions in which suppliers of capital (households that save) and the demanders of capital (business firms wanting to invest) interact. Saving and borrowing: Present vs. Future ...
... The financial capital market refers to the complex set of institutions in which suppliers of capital (households that save) and the demanders of capital (business firms wanting to invest) interact. Saving and borrowing: Present vs. Future ...
SOLUTION EXAM 08/07/04
... b) 100 more cars will cost 40 houses; 40/100 = 0.4 houses c) 100 more cars will cost 100 houses; 100/100 = 1 house d) Because in c we are using more resources in the production of cars than in d. If in c we want to produce more cars we will have to divert resources from other uses in which they are ...
... b) 100 more cars will cost 40 houses; 40/100 = 0.4 houses c) 100 more cars will cost 100 houses; 100/100 = 1 house d) Because in c we are using more resources in the production of cars than in d. If in c we want to produce more cars we will have to divert resources from other uses in which they are ...
Chapter 9: Introduction to Economic Fluctuations
... Firms track price changes of their own product more closely than changes of the general price level. Perceptions of an increase in the “relative” price level causes the labor demand, employment, and output to rise. Let PW = price of wheat and P = general price level. With inflation, farmers perceive ...
... Firms track price changes of their own product more closely than changes of the general price level. Perceptions of an increase in the “relative” price level causes the labor demand, employment, and output to rise. Let PW = price of wheat and P = general price level. With inflation, farmers perceive ...
8 National Income
... There is a redistribution effect due to unanticipated inflation. The empirical results of these redistribution effects are not clearly known. There is a resource misallocation effect due to greater uncertainty about the changes in price. Since information cost is positive, we have to spend resou ...
... There is a redistribution effect due to unanticipated inflation. The empirical results of these redistribution effects are not clearly known. There is a resource misallocation effect due to greater uncertainty about the changes in price. Since information cost is positive, we have to spend resou ...
Middle-class squeeze

The middle-class squeeze is the situation where increases in wages fail to keep up with inflation for middle-income earners, while at the same time, the phenomenon fails to have a similar impact on the top wage earners. Persons belonging to the middle class find that inflation in consumer goods and the housing market prevent them from maintaining a middle-class lifestyle, making downward mobility a threat to aspirations of upward mobility. In the United States for example, middle-class income is declining while many goods and services are increasing in price, such as education, housing, child care and healthcare.