chapter 8
... D. Substitution Effect and Income Effect 1. For a normal good, a fall in price always increases the quantity consumed. We can prove this proposition by breaking the price effect in two different parts: a) The substitution effect is the effect of a change in price on the quantity bought when the cons ...
... D. Substitution Effect and Income Effect 1. For a normal good, a fall in price always increases the quantity consumed. We can prove this proposition by breaking the price effect in two different parts: a) The substitution effect is the effect of a change in price on the quantity bought when the cons ...
Economics
... numbers? What happens to the amount of dog food he sells and the price he charges? d. If Charlie is required to pay an excise tax of $6 per pound of dog food, what happens to his total cost numbers? What happens to the amount of dog food he sells and the price he charges? 2. Kites are manufactured b ...
... numbers? What happens to the amount of dog food he sells and the price he charges? d. If Charlie is required to pay an excise tax of $6 per pound of dog food, what happens to his total cost numbers? What happens to the amount of dog food he sells and the price he charges? 2. Kites are manufactured b ...
Answers to Questions in Chapter 3
... If one person gets a pay increase 5 per cent above the current rate of inflation, he or she will be 5 per cent better off (assuming no change in the rate of inflation). If everyone gets a pay increase 5 per cent above the current rate of inflation, then that will drive the rate of inflation up. Peop ...
... If one person gets a pay increase 5 per cent above the current rate of inflation, he or she will be 5 per cent better off (assuming no change in the rate of inflation). If everyone gets a pay increase 5 per cent above the current rate of inflation, then that will drive the rate of inflation up. Peop ...
Problem Set 10
... (E) The Fed charges when it lends reserves to banks. (Answer: (E)) 6. If households and firms find that their holdings of real money are less than desired, they will (A) Sell financial assets which will cause interest rates to rise. (B) Sell financial assets which will cause interest rates to fall. ...
... (E) The Fed charges when it lends reserves to banks. (Answer: (E)) 6. If households and firms find that their holdings of real money are less than desired, they will (A) Sell financial assets which will cause interest rates to rise. (B) Sell financial assets which will cause interest rates to fall. ...
1. Which of the following would necessarily cause a fall in the price
... A. an increase in population and a decrease in the price of an input B. an increase in population and a decrease in the number of firms producing the product C. an increase in average income and an improvement in production technology D. a decrease in the price of a substitute product and an improve ...
... A. an increase in population and a decrease in the price of an input B. an increase in population and a decrease in the number of firms producing the product C. an increase in average income and an improvement in production technology D. a decrease in the price of a substitute product and an improve ...
Today - People.vcu.edu
... At very low levels of income, meat is a luxury good and Y > 1. At moderate levels of income, meat is a necessity and Y < 1. At high levels of income, people don’t want more meat, and Y is near zero. Conclusion: The income elasticity of meat depends on the initial level of income. ...
... At very low levels of income, meat is a luxury good and Y > 1. At moderate levels of income, meat is a necessity and Y < 1. At high levels of income, people don’t want more meat, and Y is near zero. Conclusion: The income elasticity of meat depends on the initial level of income. ...
ppt
... • Theory of consumer choice analyses the responses of customers to income and price changes. • These responses are measured by elasticities, which can be estimated and are useful for policymakers and businesses. • The effect of a price rise on the demand for a good depends upon the balance between t ...
... • Theory of consumer choice analyses the responses of customers to income and price changes. • These responses are measured by elasticities, which can be estimated and are useful for policymakers and businesses. • The effect of a price rise on the demand for a good depends upon the balance between t ...
Answer Key
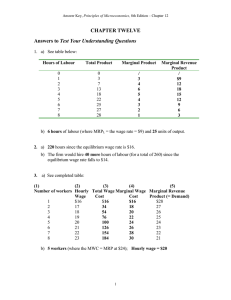
... d) 4 workers should be hired. (With the increase in the cost of labour to $140, the firm should reduce the number of to 4 since the marginal revenue product of the 4th worker is also $140. e) See Figure 12.21 (Completed) f) See Table 12.12 (Completed). g) 6 workers should be hired (With the increase ...
... d) 4 workers should be hired. (With the increase in the cost of labour to $140, the firm should reduce the number of to 4 since the marginal revenue product of the 4th worker is also $140. e) See Figure 12.21 (Completed) f) See Table 12.12 (Completed). g) 6 workers should be hired (With the increase ...
Top 10 AP Econ Mistakes
... Question: Assume that the government grants CableNow a lump-sum subsidy of $1 million. Will this policy change CableNow’s profit maximizing quantity of cable services? Explain. Answer: No (46% answered correctly—note that guessing would yield 50% correct), because the lump-sum tax will not affect ma ...
... Question: Assume that the government grants CableNow a lump-sum subsidy of $1 million. Will this policy change CableNow’s profit maximizing quantity of cable services? Explain. Answer: No (46% answered correctly—note that guessing would yield 50% correct), because the lump-sum tax will not affect ma ...
DEMAND - University of Miami
... • Raise Qs About Normative Use of Theory – Claims that results of comp. market always ...
... • Raise Qs About Normative Use of Theory – Claims that results of comp. market always ...
Middle-class squeeze

The middle-class squeeze is the situation where increases in wages fail to keep up with inflation for middle-income earners, while at the same time, the phenomenon fails to have a similar impact on the top wage earners. Persons belonging to the middle class find that inflation in consumer goods and the housing market prevent them from maintaining a middle-class lifestyle, making downward mobility a threat to aspirations of upward mobility. In the United States for example, middle-class income is declining while many goods and services are increasing in price, such as education, housing, child care and healthcare.