Document
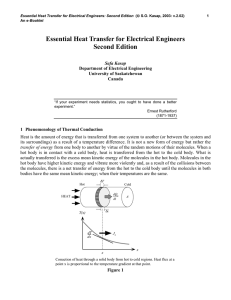
... According to the first law of thermodynamics, heat and work are related through the “internal energy” of a system and generally cannot be interconverted. However, we can ask the question: How many times does a person need to lift a 500 N barbell a height of 2 m to correspond to 2000 Calories (1 Calo ...
... According to the first law of thermodynamics, heat and work are related through the “internal energy” of a system and generally cannot be interconverted. However, we can ask the question: How many times does a person need to lift a 500 N barbell a height of 2 m to correspond to 2000 Calories (1 Calo ...
Thermal Simulation for a Room with Solid and One
... (slab, walls, columns and plaster) was conducted with two types of slab (solid slab and one-way-ribbed slab) using finite element model (FEM) with ABAQUS software to investigate the effect of slab type and plastering on the overall inner surface temperature of the room. Plastering with thickness of ...
... (slab, walls, columns and plaster) was conducted with two types of slab (solid slab and one-way-ribbed slab) using finite element model (FEM) with ABAQUS software to investigate the effect of slab type and plastering on the overall inner surface temperature of the room. Plastering with thickness of ...
Dufour and Soret effects on MHD flow of Williamson fluid over
... The resemblance of this model of non-Newtonian fluid to the blood flow has captivated the attention of researchers as it essentially exhibits the behavior of blood flow. Many valuable works have constantly been added to this field in recent years. Nadeem, et al. [2] presented a study on the two dime ...
... The resemblance of this model of non-Newtonian fluid to the blood flow has captivated the attention of researchers as it essentially exhibits the behavior of blood flow. Many valuable works have constantly been added to this field in recent years. Nadeem, et al. [2] presented a study on the two dime ...
Full-Text PDF
... (3) The mat area is calculated as: 0.1 m × 0.1 m = 0.01 m2; (4) Therefore, the PCM cells can be assumed to be a continuous layer with a thickness of 0.0064 m (=0.000064 m3/0.01 m2). Dynamic energy simulations have been performed by EnergyPlus 6.0. The basic algorithm used in EnergyPlus for calculati ...
... (3) The mat area is calculated as: 0.1 m × 0.1 m = 0.01 m2; (4) Therefore, the PCM cells can be assumed to be a continuous layer with a thickness of 0.0064 m (=0.000064 m3/0.01 m2). Dynamic energy simulations have been performed by EnergyPlus 6.0. The basic algorithm used in EnergyPlus for calculati ...
REVIEW ARTICLES AAEM
... between a surface and a gas or liquid. In addition to simple temperature gradient, the rate of motion of the gas (air movement) or liquid (water) and its relative heat storage capacity will affect the rate of energy transfer. However, the compensatory mechanisms remain essentially the same as for co ...
... between a surface and a gas or liquid. In addition to simple temperature gradient, the rate of motion of the gas (air movement) or liquid (water) and its relative heat storage capacity will affect the rate of energy transfer. However, the compensatory mechanisms remain essentially the same as for co ...
REFRACTORY ENGINEERING STRUCTURES
... In specific calculations we will not consider them with physical properties as with constants, but if we have available their dependence on temperature, we can calculate them according to regressive equations. In most solution cases we do not directly know surface temperatures, but only the temperat ...
... In specific calculations we will not consider them with physical properties as with constants, but if we have available their dependence on temperature, we can calculate them according to regressive equations. In most solution cases we do not directly know surface temperatures, but only the temperat ...
Three-dimensional analysis of heat transfer in a micro
... material compatibility, high surface area per unit volume ratios, and large potential heat transfer performance, with highly sophisticated and economic fabrication processes. These advantages make these silicon based microchannel heat sinks extremely attractive for a wide variety of commercial appli ...
... material compatibility, high surface area per unit volume ratios, and large potential heat transfer performance, with highly sophisticated and economic fabrication processes. These advantages make these silicon based microchannel heat sinks extremely attractive for a wide variety of commercial appli ...
Unit B Ch 6 TR
... • compare the speed at which different substances warm; and • learn more about how water affects climate. Science Background Specific heat capacity is the amount of energy, in joules, needed to warm 1 g of a substance by 1ºC. For instance, it takes 4.19 J to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by ...
... • compare the speed at which different substances warm; and • learn more about how water affects climate. Science Background Specific heat capacity is the amount of energy, in joules, needed to warm 1 g of a substance by 1ºC. For instance, it takes 4.19 J to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by ...
C121
... Utilizing MCHX leads to size reductions and performance improvements in air-conditioning systems. Kim and Bullard [14] compared the performance of two different types of MCHX with the baseline case of finned round-tube condenser and found that for the same Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER), the MCHX des ...
... Utilizing MCHX leads to size reductions and performance improvements in air-conditioning systems. Kim and Bullard [14] compared the performance of two different types of MCHX with the baseline case of finned round-tube condenser and found that for the same Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER), the MCHX des ...
Two-dimensional simulations of magma ascent in volcanic conduits
... During volcanic eruptions, hot magma traverses a conduit from the magmatic source to the surface through cold crustal rocks. As a consequence, the magma may solidify. Similarly, in many industrial processes, such as injection moulding and continuous casting, hot fluid is forced to flow between cold ...
... During volcanic eruptions, hot magma traverses a conduit from the magmatic source to the surface through cold crustal rocks. As a consequence, the magma may solidify. Similarly, in many industrial processes, such as injection moulding and continuous casting, hot fluid is forced to flow between cold ...
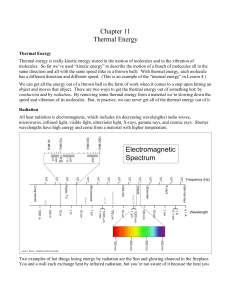
Chapter 11 - Wolaver.org
... effectively shines for only 8 hours a day (this accounts for times when it isn’t shining straight in the skylight). Problem 2 The log in Example 2 is deprived of air, and it stops burning. After a while it cools to 70°F. Find its net radiation now. Problem 3 In Example 3 the stove must produce 24,00 ...
... effectively shines for only 8 hours a day (this accounts for times when it isn’t shining straight in the skylight). Problem 2 The log in Example 2 is deprived of air, and it stops burning. After a while it cools to 70°F. Find its net radiation now. Problem 3 In Example 3 the stove must produce 24,00 ...
as PDF
... isothermal processes, respectively, with T1 < TH and TL < T2. There is also a heat loss Q from the hot reservoir to the cold reservoir and there are other internal irreversibilities (such as dissipative processes inside the working fluid). This Carnot-like model was chosen because of its simplicity ...
... isothermal processes, respectively, with T1 < TH and TL < T2. There is also a heat loss Q from the hot reservoir to the cold reservoir and there are other internal irreversibilities (such as dissipative processes inside the working fluid). This Carnot-like model was chosen because of its simplicity ...
Dynamic insulation

Dynamic insulation is a form of insulation where cool outside air flowing through the thermal insulation in the envelope of a building will pick up heat from the insulation fibres. Buildings can be designed to exploit this to reduce the transmission heat loss (U-value) and to provide pre-warmed, draft free air to interior spaces. This is known as dynamic insulation since the U-value is no longer constant for a given wall or roof construction but varies with the speed of the air flowing through the insulation (climate adaptive building shell). Dynamic insulation is different from breathing walls. The positive aspects of dynamic insulation need to be weighed against the more conventional approach to building design which is to create an airtight envelope and provide appropriate ventilation using either natural ventilation or mechanical ventilation with heat recovery. The air-tight approach to building envelope design, unlike dynamic insulation, results in a building envelope that provides a consistent performance in terms of heat loss and risk of interstitial condensation that is independent of wind speed and direction. Under certain wind conditions a dynamically insulated building can have a higher heat transmission loss than an air-tight building with the same thickness of insulation.