Power Quality Improvement through Unified power quality
... (Synchronous reference frame) theory combined of extended p-q theory is used to get reference signals for the series and shunt APFs. One of advantages of a d-q domain derivation of reference signals lies in easier signal filtration, since the 50Hz components are transferred into DC. Reference voltag ...
... (Synchronous reference frame) theory combined of extended p-q theory is used to get reference signals for the series and shunt APFs. One of advantages of a d-q domain derivation of reference signals lies in easier signal filtration, since the 50Hz components are transferred into DC. Reference voltag ...
UPS Operating Modes: A Global Standard
... discusses the capabilities and limitations of the various classifications. ...
... discusses the capabilities and limitations of the various classifications. ...
AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER`S GUIDE
... BNC Connector: Used to connect the customer’s coaxial cable. Conversion Gain: The relative level of the optical input power that is amplified and converted into a voltage output. Dark Current: When a termination is present, a dark current (nA range) will flow if the photodiode is biased. Disconnecti ...
... BNC Connector: Used to connect the customer’s coaxial cable. Conversion Gain: The relative level of the optical input power that is amplified and converted into a voltage output. Dark Current: When a termination is present, a dark current (nA range) will flow if the photodiode is biased. Disconnecti ...
MS Word version
... Cardinal, Paul 2010-PSEC-557 Influence of Reactors on Input Harmonics of Variable Frequency Drives Liang, Xiaodong, Ilochonwu, Obinna, Lim, Jeffrey. ...
... Cardinal, Paul 2010-PSEC-557 Influence of Reactors on Input Harmonics of Variable Frequency Drives Liang, Xiaodong, Ilochonwu, Obinna, Lim, Jeffrey. ...
The Effect of Power Factor On An Electrical System
... P.F. as shown in vector diagram (see diagram two) is the ratio of true power (shown as watts (W) amps x volts) to the apparent power (shown as VA amps x volts) flowing to the load in an alternating current (AC) system. Watts and VA are more commonly quoted in thousands as kW and kVA. kW and kVA in a ...
... P.F. as shown in vector diagram (see diagram two) is the ratio of true power (shown as watts (W) amps x volts) to the apparent power (shown as VA amps x volts) flowing to the load in an alternating current (AC) system. Watts and VA are more commonly quoted in thousands as kW and kVA. kW and kVA in a ...
Code - SVNIT
... Alternating voltages and currents and their vector and time domain representations, average and rms values, form factor, phase difference, power and power factor, purely resistive inductive and capacitive circuits, R-L, R-C and R-L-C series circuits, impedance and admittance, circuits in parallel, s ...
... Alternating voltages and currents and their vector and time domain representations, average and rms values, form factor, phase difference, power and power factor, purely resistive inductive and capacitive circuits, R-L, R-C and R-L-C series circuits, impedance and admittance, circuits in parallel, s ...
Syllabus for Physics
... infinitely long current carrying straight wire and circular coil – Tangent galvanometer – Construction and working – Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid – magnetic field lines. Ampere’s circuital law and its application. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic field and electric field – cyclot ...
... infinitely long current carrying straight wire and circular coil – Tangent galvanometer – Construction and working – Bar magnet as an equivalent solenoid – magnetic field lines. Ampere’s circuital law and its application. Force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic field and electric field – cyclot ...
H5P2 Source Follower Large Signal
... Here the source labeled VDD is the power supply. Although the source follower has no voltage gain (actually a small loss) it has power gain: it presents a very high resistance to the signal source so it takes no power from the source, but it can drive a low resistance load. Also, because of feedback ...
... Here the source labeled VDD is the power supply. Although the source follower has no voltage gain (actually a small loss) it has power gain: it presents a very high resistance to the signal source so it takes no power from the source, but it can drive a low resistance load. Also, because of feedback ...
BJTAMP-fre1q-lab
... The common emitter amplifier is one of the most widely used amplifier configurations due to its high gain. Other configurations are the common collector and common base amplifiers which respectively have the collector and base of the transistor grounded, or common to the input and output AC signals. ...
... The common emitter amplifier is one of the most widely used amplifier configurations due to its high gain. Other configurations are the common collector and common base amplifiers which respectively have the collector and base of the transistor grounded, or common to the input and output AC signals. ...
Supporting_Information
... alkaline niobate has high Curie temperature and large electromechanical coupling factor d33. KNN-LTS has the electric dipoles that can be aligned along the electric field direction by high electric field. When the poled device in original state (without tapping), as shown in the cross-sectional stru ...
... alkaline niobate has high Curie temperature and large electromechanical coupling factor d33. KNN-LTS has the electric dipoles that can be aligned along the electric field direction by high electric field. When the poled device in original state (without tapping), as shown in the cross-sectional stru ...
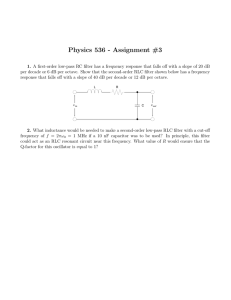
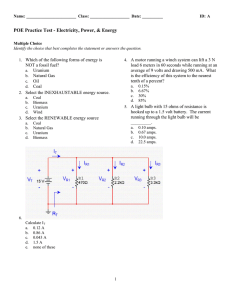
ExamView - POE Practice Test
... a. 9 volts b. 12 volts c. 3 volts d. 6 volts 20. Two resistors with 15 ohms of resistance each are connected in series to a 1.5-volt battery. The current running through the system will be ___________. a. 0.50 amps b. 0.05 amps c. 1.0 amps d. 0.2 amps e. none of these 21. In a series circuit, increa ...
... a. 9 volts b. 12 volts c. 3 volts d. 6 volts 20. Two resistors with 15 ohms of resistance each are connected in series to a 1.5-volt battery. The current running through the system will be ___________. a. 0.50 amps b. 0.05 amps c. 1.0 amps d. 0.2 amps e. none of these 21. In a series circuit, increa ...
Electricity - SFSU Physics & Astronomy
... – Conduct/insulate depending on circumstances – Applications: Computer chips, solar cells, ... ...
... – Conduct/insulate depending on circumstances – Applications: Computer chips, solar cells, ... ...
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING EA5210: POWER ELECTRONICS DIT UNIVERSITY, DEHRA DUN
... 4. To study single phase (i) fully controlled (ii) half controlled bridge rectifiers with resistive and inductive loads. 5. To study three-phase fully/half controlled bridge rectifier with resistive and inductive loads. 6. To study single-phase ac voltage regulator with resistive and inductive loads ...
... 4. To study single phase (i) fully controlled (ii) half controlled bridge rectifiers with resistive and inductive loads. 5. To study three-phase fully/half controlled bridge rectifier with resistive and inductive loads. 6. To study single-phase ac voltage regulator with resistive and inductive loads ...
Name - OnCourse
... Batteries contain only a limited amount of the chemicals needed to create this electric field. A battery is “dead” when ______________________________________________ ,_________________________________________________________________ ...
... Batteries contain only a limited amount of the chemicals needed to create this electric field. A battery is “dead” when ______________________________________________ ,_________________________________________________________________ ...
SP Valves and Coil Operating Parameters
... In order to maintain maximum flow at high temperatures, it is important to know the actual applied voltage to the coil including any voltage drop across the controller. Generally, on engine-driven equipment where alternator voltage is several volts above battery voltage, a coil rated at nominal volt ...
... In order to maintain maximum flow at high temperatures, it is important to know the actual applied voltage to the coil including any voltage drop across the controller. Generally, on engine-driven equipment where alternator voltage is several volts above battery voltage, a coil rated at nominal volt ...
OPERATION/MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS FOR DLM-50-20-100
... input becomes positive with respect to the non-inverting input. This causes U1b output to limit the drive to shunt transistors by restricting the base drive of Q1 via CR1, thus limiting the current though the load. As the source voltage is increased, VR6 conducts which allows current to flow through ...
... input becomes positive with respect to the non-inverting input. This causes U1b output to limit the drive to shunt transistors by restricting the base drive of Q1 via CR1, thus limiting the current though the load. As the source voltage is increased, VR6 conducts which allows current to flow through ...
TT2140LS
... semiconductor products fail with some probability. It is possible that these probabilistic failures could give rise to accidents or events that could endanger human lives, that could give rise to smoke or fire, or that could cause damage to other property. When designing equipment, adopt safety meas ...
... semiconductor products fail with some probability. It is possible that these probabilistic failures could give rise to accidents or events that could endanger human lives, that could give rise to smoke or fire, or that could cause damage to other property. When designing equipment, adopt safety meas ...
RPI-246
... t r : Rise time (time for output current to rise from 10% to 90% of peak current) t f : Fall time (time for output current to fall from 90% to 10% of peak current) ...
... t r : Rise time (time for output current to rise from 10% to 90% of peak current) t f : Fall time (time for output current to fall from 90% to 10% of peak current) ...
Alternating current
Alternating current (AC), is an electric current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction, whereas in direct current (DC, also dc), the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.AC is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave. In certain applications, different waveforms are used, such as triangular or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information encoded (or modulated) onto the AC signal, such as sound (audio) or images (video).