MAX15003 Triple-Output Buck Controller with Tracking/Sequencing General Description
... down to 0.6V and delivers up to 15A for each output with excellent load and line regulation. The MAX15003 is optimized for high-performance, small-size power management solutions. The options of coincident tracking, ratiometric tracking, and output sequencing allow the tailoring of the powerup/power ...
... down to 0.6V and delivers up to 15A for each output with excellent load and line regulation. The MAX15003 is optimized for high-performance, small-size power management solutions. The options of coincident tracking, ratiometric tracking, and output sequencing allow the tailoring of the powerup/power ...
MAX864 Dual-Output Charge Pump with Shutdown _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... second half cycle, switches S6 and S8 open, and switches S5 and S7 close, charging C2 from V+ (pumped up to 2VIN by the positive charge pump) to GND. In the first half of the clock cycle, switches S5 and S7 open, switches S6 and S8 close, and the charge on capacitor C2 transfers to C4, generating th ...
... second half cycle, switches S6 and S8 open, and switches S5 and S7 close, charging C2 from V+ (pumped up to 2VIN by the positive charge pump) to GND. In the first half of the clock cycle, switches S5 and S7 open, switches S6 and S8 close, and the charge on capacitor C2 transfers to C4, generating th ...
Minilyzer ML1 User Manual
... Please note that in certain selection modes, the measurement result will be updated with the new selection even before the enter key has been pressed for confirmation. For instance, if a new level unit is selected - but not yet confirmed - the display will instantly update to the newly selected unit ...
... Please note that in certain selection modes, the measurement result will be updated with the new selection even before the enter key has been pressed for confirmation. For instance, if a new level unit is selected - but not yet confirmed - the display will instantly update to the newly selected unit ...
0.8-V Input Synchronous Boost Converters with 100
... rectification to obtain maximum efficiency. At low load currents, the converter enters Power Save Mode to ensure high efficiency over a wide load current range. The TPS6126x is based on a current mode topology. The inductor current is regulated by a fast current regulator loop which is controlled by ...
... rectification to obtain maximum efficiency. At low load currents, the converter enters Power Save Mode to ensure high efficiency over a wide load current range. The TPS6126x is based on a current mode topology. The inductor current is regulated by a fast current regulator loop which is controlled by ...
AD5641: 英文产品数据手册下载
... High speed serial interface with clock speeds up to 30 MHz. Designed for very low power consumption. The interface powers up only during a write cycle. ...
... High speed serial interface with clock speeds up to 30 MHz. Designed for very low power consumption. The interface powers up only during a write cycle. ...
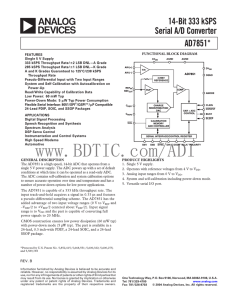
a 14-Bit 333 kSPS Serial A/D Converter AD7851
... The CONVST pulse width will only apply for normal operation. When the part is in power-down mode, a different CONVST pulse width will apply (see PowerDown section). ...
... The CONVST pulse width will only apply for normal operation. When the part is in power-down mode, a different CONVST pulse width will apply (see PowerDown section). ...
AND8256/D Control of the Output Voltage Range in NCP1653
... http://www.onsemi.com/pub/Collateral/NCP1653%20 ...
... http://www.onsemi.com/pub/Collateral/NCP1653%20 ...
AD9980 VGA Input CODEC
... reference and provides the frequency reference for pixel clock generation. The logic sense of this pin can be automatically determined by the chip or manually controlled by Serial Register 0x12, Bits [5:4] (Hsync polarity). Only the leading edge of Hsync is used by the PLL; the trailing edge is used ...
... reference and provides the frequency reference for pixel clock generation. The logic sense of this pin can be automatically determined by the chip or manually controlled by Serial Register 0x12, Bits [5:4] (Hsync polarity). Only the leading edge of Hsync is used by the PLL; the trailing edge is used ...
SN65LVDS3486 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The resistors present a total differential load of 100 Ω to match the characteristic impedance of the transmission line and to reduce the signal 10:1. The maximum 422 differential output signal, or 6 V, is reduced to 600 mV. The high input impedance of the LVDS receiver prevents input bias offsets a ...
... The resistors present a total differential load of 100 Ω to match the characteristic impedance of the transmission line and to reduce the signal 10:1. The maximum 422 differential output signal, or 6 V, is reduced to 600 mV. The high input impedance of the LVDS receiver prevents input bias offsets a ...
practical design techniques for sensor signal conditioning
... Both RTDs and strain gages are often placed in bridge circuits, and the conditioning circuits are therefore quite similar. In fact, bridges and their conditioning circuits deserve a detailed discussion. The full-scale outputs of most sensors (passive or active) are relatively small voltages, current ...
... Both RTDs and strain gages are often placed in bridge circuits, and the conditioning circuits are therefore quite similar. In fact, bridges and their conditioning circuits deserve a detailed discussion. The full-scale outputs of most sensors (passive or active) are relatively small voltages, current ...
Influence of Pin Setting on System Function and Performance
... The internal resistance of the keeper is much higher than the internal resistance of a standard output driver – see Table 5. This option is used to save power in applications that need a lot of energy when the logic value is changed, but little energy when it is needed to just keep the state; for ex ...
... The internal resistance of the keeper is much higher than the internal resistance of a standard output driver – see Table 5. This option is used to save power in applications that need a lot of energy when the logic value is changed, but little energy when it is needed to just keep the state; for ex ...
How to Select Little Logic (Rev. A)
... SN74LVC1G/2G/3G Little Logic components are designed with no clamp diodes to VCC on either inputs or outputs, making the interface voltage higher than applied VCC. This design allows the down translation from 5 V to a desired lower switch level, which refers to supply VCC of the chip. As its operati ...
... SN74LVC1G/2G/3G Little Logic components are designed with no clamp diodes to VCC on either inputs or outputs, making the interface voltage higher than applied VCC. This design allows the down translation from 5 V to a desired lower switch level, which refers to supply VCC of the chip. As its operati ...
SY89829U Oct05
... single 1:20 LVPECL Clock Driver. The part is designed for use in low voltage (2.5V/3.3V) applications which require a large number of outputs to drive precisely aligned, ultra low skew signals to their destination. The input is multiplexed from either LVDS or LVPECL by the CLK_SEL pin. The LVDS inpu ...
... single 1:20 LVPECL Clock Driver. The part is designed for use in low voltage (2.5V/3.3V) applications which require a large number of outputs to drive precisely aligned, ultra low skew signals to their destination. The input is multiplexed from either LVDS or LVPECL by the CLK_SEL pin. The LVDS inpu ...
AD9741 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... LMDS/MMDS, point-to-point Instrumentation: RF signal generators, arbitrary waveform generators ...
... LMDS/MMDS, point-to-point Instrumentation: RF signal generators, arbitrary waveform generators ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).