AC Circuits
... Clock oscillator: Most digital circuits require a clock signal. This is simply a periodic digital waveform, which alternates between 0 and 1 states at some chosen frequency. (When a personal computer is advertised as having a 66 MHz CPU, for example, the 66 MHz refers to the clock frequency used in ...
... Clock oscillator: Most digital circuits require a clock signal. This is simply a periodic digital waveform, which alternates between 0 and 1 states at some chosen frequency. (When a personal computer is advertised as having a 66 MHz CPU, for example, the 66 MHz refers to the clock frequency used in ...
Low-Noise Amplifier
... – hold range: the frequency range over which phase tracking can be statically maintained – pull-in range: the frequency range over which PLL can become locked – pull-out range: dynamic limit of frequency range for stable operation – lock range: frequency range within which a PLL locks within one sin ...
... – hold range: the frequency range over which phase tracking can be statically maintained – pull-in range: the frequency range over which PLL can become locked – pull-out range: dynamic limit of frequency range for stable operation – lock range: frequency range within which a PLL locks within one sin ...
iC-RC1000 Sin/Cos Signal Safety Monitor IC - iC-Haus
... iC-RC1000 has intrinsic safety, enabling single errors to be securely identified through redundancy; two different diagnostic channels monitor the input signals and independently generate complementary messages: signal OK and signal ERROR. So that the external controller can safely detect an interru ...
... iC-RC1000 has intrinsic safety, enabling single errors to be securely identified through redundancy; two different diagnostic channels monitor the input signals and independently generate complementary messages: signal OK and signal ERROR. So that the external controller can safely detect an interru ...
The Input Offset
... However, note that this error is multiplied by one-half of the excess gate voltage VGS –Vt. The excess gate voltage is typically much larger than the BJT thermal voltage VT (a few volts versus 25 mV) ! As a result, the Input Offset Voltage for a MOSFET differential pair can be fairly large (e.g., >> ...
... However, note that this error is multiplied by one-half of the excess gate voltage VGS –Vt. The excess gate voltage is typically much larger than the BJT thermal voltage VT (a few volts versus 25 mV) ! As a result, the Input Offset Voltage for a MOSFET differential pair can be fairly large (e.g., >> ...
ICL7106/7107
... liquid crystal display (LCD) and includes a multiplexed backplane drive, the ICL7107 will directly drive an instrument size light emitting diode (LED) display. The ICL7106 and ICL7107 bring together a combination of high accuracy, versatility, and true economy. True differential inputs and reference ...
... liquid crystal display (LCD) and includes a multiplexed backplane drive, the ICL7107 will directly drive an instrument size light emitting diode (LED) display. The ICL7106 and ICL7107 bring together a combination of high accuracy, versatility, and true economy. True differential inputs and reference ...
AC Circuits - Oscilloscopes and Filter Circuits
... the CH1 input of the oscilloscope. In order to see the waveform on the screen, the two main things you’ll need to adjust are the TIME/DIV knob (the x-axis of the oscilloscope) and the VOLTS/DIV knob (the y-axis). You can also adjust the Trigger parameters (basically, the way the oscilloscope decides ...
... the CH1 input of the oscilloscope. In order to see the waveform on the screen, the two main things you’ll need to adjust are the TIME/DIV knob (the x-axis of the oscilloscope) and the VOLTS/DIV knob (the y-axis). You can also adjust the Trigger parameters (basically, the way the oscilloscope decides ...
Analog Filter Considerations
... Utilizing oversampling and a decimation filter, the SNR improvement can be derived from the theoretical SNR for an N-bit ADC: SNR = 6.02 × N + 1.76 dB + 10 × log10[OSR], OSR = f /(2 s ...
... Utilizing oversampling and a decimation filter, the SNR improvement can be derived from the theoretical SNR for an N-bit ADC: SNR = 6.02 × N + 1.76 dB + 10 × log10[OSR], OSR = f /(2 s ...
Circuit Note CN-0150
... 1 MHz to 6 GHz and provides useful operation to 8 GHz. The device provides a typical output voltage temperature stability of ±0.5 dB. ...
... 1 MHz to 6 GHz and provides useful operation to 8 GHz. The device provides a typical output voltage temperature stability of ±0.5 dB. ...
EECS 140/240A - Berkeley Robotics and Intelligent Machines Lab
... ADC – Analog to Digital Converter The ADC must use an 8 bit successive approximation charge-redistribution topology [1]. The digital output of the ADC taken as an integer between 0 and 255, times 1V/256, should be within 1 LSB of the analog input being sampled. In other words, each LSB should be jus ...
... ADC – Analog to Digital Converter The ADC must use an 8 bit successive approximation charge-redistribution topology [1]. The digital output of the ADC taken as an integer between 0 and 255, times 1V/256, should be within 1 LSB of the analog input being sampled. In other words, each LSB should be jus ...
Op Amps II, Page
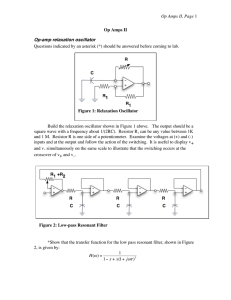
... Next, use what you know about RC filters to find v4 in terms of v1.] When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit n ...
... Next, use what you know about RC filters to find v4 in terms of v1.] When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit n ...
CN-0120
... use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other intellectual property by application or use of the "Circuits from the Lab". Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliabl ...
... use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other intellectual property by application or use of the "Circuits from the Lab". Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliabl ...
1073DPA and 1073DPD Mic Pre_Amplifier
... The 1073DPD has two sync inputs; AES3 on a female XLR and wordclock on a chassis BNC. If neither Sync Input is present the unit will synchronise to it's internal crystal clock. If one or other sync input is present at the correct sampling frequency selected on the front panel the LED (AES or WCLK) w ...
... The 1073DPD has two sync inputs; AES3 on a female XLR and wordclock on a chassis BNC. If neither Sync Input is present the unit will synchronise to it's internal crystal clock. If one or other sync input is present at the correct sampling frequency selected on the front panel the LED (AES or WCLK) w ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).