n 3.5.1 Noise Figure
... where Pn is the extra noise power at the output introduced by the component. As a convention, we assume that the input noise corresponds to room temperature, so that Ni = kB T0 B with T0 = 290 K. Since noise figure is a dimensionless quantity, it is often expressed in dB. ...
... where Pn is the extra noise power at the output introduced by the component. As a convention, we assume that the input noise corresponds to room temperature, so that Ni = kB T0 B with T0 = 290 K. Since noise figure is a dimensionless quantity, it is often expressed in dB. ...
RT9368 - Richtek
... 250 times greater than the current of RSET. The white LED can be estimated by following equation : V ILED = ( SET ) × 250 R SET Where VSET = 1.2V, and RSET is the resistor connected from ISET to GND. If the LED is not used, the LEDs pin should be connected to GND. Figure 4 shows the connection for 3 ...
... 250 times greater than the current of RSET. The white LED can be estimated by following equation : V ILED = ( SET ) × 250 R SET Where VSET = 1.2V, and RSET is the resistor connected from ISET to GND. If the LED is not used, the LEDs pin should be connected to GND. Figure 4 shows the connection for 3 ...
PSC18
... the delivered module. Familiarity with the contents of this manual is required for installing and operating the specified module. The function description in this manual corresponds to the stage of technology at the date of publishing. Technical changes and changes in form and content can be made at ...
... the delivered module. Familiarity with the contents of this manual is required for installing and operating the specified module. The function description in this manual corresponds to the stage of technology at the date of publishing. Technical changes and changes in form and content can be made at ...
AD7942 数据手册DataSheet下载
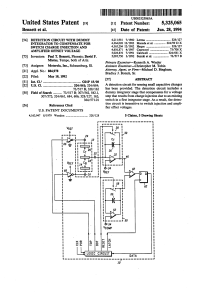
... The AD7942 is a 14-bit, charge redistribution, successive approximation PulSAR® ADC that operates from a single power supply, VDD, between 2.3 V to 5.5 V. It contains a low power, high speed, 14-bit sampling ADC with no missing codes, an internal conversion clock, and a versatile serial interface po ...
... The AD7942 is a 14-bit, charge redistribution, successive approximation PulSAR® ADC that operates from a single power supply, VDD, between 2.3 V to 5.5 V. It contains a low power, high speed, 14-bit sampling ADC with no missing codes, an internal conversion clock, and a versatile serial interface po ...
AN4076
... After each of the signals on the shunt resistors have been filtered, amplification is required for each of them in order to adapt the signals to the range of voltage that can be read by the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) peripheral embedded in the microcontroller unit (MCU). The non-inverting con ...
... After each of the signals on the shunt resistors have been filtered, amplification is required for each of them in order to adapt the signals to the range of voltage that can be read by the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) peripheral embedded in the microcontroller unit (MCU). The non-inverting con ...
AD9866
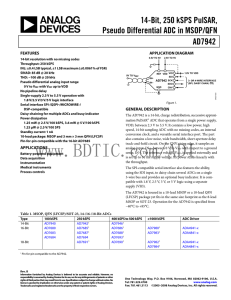
... −12 dB to +48 dB in 1 dB steps. Its input referred noise is less than 3.3 nV/rtHz for gain settings beyond 30 dB. The receive path LPF cutoff frequency can be set over a 15 MHz to 35 MHz range or simply bypassed. The 12-bit ADC achieves excellent dynamic performance over a 5 MSPS to 80 MSPS span. Bo ...
... −12 dB to +48 dB in 1 dB steps. Its input referred noise is less than 3.3 nV/rtHz for gain settings beyond 30 dB. The receive path LPF cutoff frequency can be set over a 15 MHz to 35 MHz range or simply bypassed. The 12-bit ADC achieves excellent dynamic performance over a 5 MSPS to 80 MSPS span. Bo ...
Charge pump: adaptive hysteretic control with modular switches
... switches, so that for lower output currents only 1/3 of the switching strength is used, and for higher currents or during transients, full switching strength is used. This way, driver capacitance is reduced for most of the output current range of the charge pump. To further increase efficiency, a br ...
... switches, so that for lower output currents only 1/3 of the switching strength is used, and for higher currents or during transients, full switching strength is used. This way, driver capacitance is reduced for most of the output current range of the charge pump. To further increase efficiency, a br ...
AD9865
... −12 dB to +48 dB in 1 dB steps. Its input referred noise is less than 3 nV/rtHz for gain settings beyond 36 dB. The receive path LPF cutoff frequency can be set over a 15 MHz to 35 MHz range or simply bypassed. The 10-bit ADC achieves excellent dynamic performance over a 5 MSPS to 80 MSPS span. Both ...
... −12 dB to +48 dB in 1 dB steps. Its input referred noise is less than 3 nV/rtHz for gain settings beyond 36 dB. The receive path LPF cutoff frequency can be set over a 15 MHz to 35 MHz range or simply bypassed. The 10-bit ADC achieves excellent dynamic performance over a 5 MSPS to 80 MSPS span. Both ...
PAK MKII - PAK | Mueller
... All Modules have been designed to be readily interchangeable. This allows each measurement test to be perfectly configured. Many users own more Modules than can fit into their Mainframes so that the perfect combination for every test is always achieved. To reduce power consumption, Modules which are ...
... All Modules have been designed to be readily interchangeable. This allows each measurement test to be perfectly configured. Many users own more Modules than can fit into their Mainframes so that the perfect combination for every test is always achieved. To reduce power consumption, Modules which are ...
Data Sheet Features
... 5.1 The VIN quiescent current loss comprises two parts: the DC bias current as given in the electrical characteristics and the internal MOSFET switch gate charge currents. The gate charge current results from switching the gate capacitance of the internal power MOSFET switches. Each cycle the gate i ...
... 5.1 The VIN quiescent current loss comprises two parts: the DC bias current as given in the electrical characteristics and the internal MOSFET switch gate charge currents. The gate charge current results from switching the gate capacitance of the internal power MOSFET switches. Each cycle the gate i ...
An Op Amp Tutorial - W. Marshall Leach, Jr.
... (0.325 − VT ln 19) /0.9IQ = 5.53 kΩ, where we have assumed that VT = 0.0259 V. Square-Wave Input Signal The transient examples that we have looked at so far assume that the op amp input voltage is a step and that the initial value of the output voltage is zero. Transient response measurements on op ...
... (0.325 − VT ln 19) /0.9IQ = 5.53 kΩ, where we have assumed that VT = 0.0259 V. Square-Wave Input Signal The transient examples that we have looked at so far assume that the op amp input voltage is a step and that the initial value of the output voltage is zero. Transient response measurements on op ...
Minimizing Distortion in Operational Transconductance Amplifiers
... The Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) is perhaps one of the most indispensable circuits in analog music synthesis. It can be used to make VCOs, VCFs, VCAs, and a myriad other sound modifying devices. The reason for this, is that it is the simplest way to implement the mathematical functio ...
... The Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA) is perhaps one of the most indispensable circuits in analog music synthesis. It can be used to make VCOs, VCFs, VCAs, and a myriad other sound modifying devices. The reason for this, is that it is the simplest way to implement the mathematical functio ...
Si4063/60 - Silicon Labs
... and Fractional-N PLL synthesizer. The synthesizer is designed to support configurable data rates from 100 bps to 1 Mbps. The Si4063/60 operate in the frequency bands of 142–175, 283–350, 420–525, and 850–1050 MHz with a maximum frequency accuracy step size of 28.6 Hz. The transmit FSK data is mod ...
... and Fractional-N PLL synthesizer. The synthesizer is designed to support configurable data rates from 100 bps to 1 Mbps. The Si4063/60 operate in the frequency bands of 142–175, 283–350, 420–525, and 850–1050 MHz with a maximum frequency accuracy step size of 28.6 Hz. The transmit FSK data is mod ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).