LTC5542 - 1.6GHz to 2.7GHz High Dynamic Range Downconverting Mixer.
... The LTC®5542 is part of a family of high dynamic range, high gain, passive downconverting mixers covering the 600MHz to 4GHz frequency range. The LTC5542 is optimized for 1.6GHz to 2.7GHz RF applications. The LO frequency must fall within the 1.7GHz to 2.5GHz range for optimum performance. A typical ...
... The LTC®5542 is part of a family of high dynamic range, high gain, passive downconverting mixers covering the 600MHz to 4GHz frequency range. The LTC5542 is optimized for 1.6GHz to 2.7GHz RF applications. The LO frequency must fall within the 1.7GHz to 2.5GHz range for optimum performance. A typical ...
AD8339 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... are available for each channel. For example, if Channel 1 is used as a reference and Channel 2 has an I/Q phase lead of 45°, then the user can phase align Channel 2 with Channel 1 by choosing the correct code. ...
... are available for each channel. For example, if Channel 1 is used as a reference and Channel 2 has an I/Q phase lead of 45°, then the user can phase align Channel 2 with Channel 1 by choosing the correct code. ...
service manual
... The circuit board KLM-6023 PEAK LED is lit by the comparator circuit formed by IC24 (2901). After the signal passes through the TRIG detection circuit formed by IC24 (2901), part of it is input to the key matrix by transistor Q2 (2SA1175), and the re mainder lights the circuit board KLM-6023 TRIG LE ...
... The circuit board KLM-6023 PEAK LED is lit by the comparator circuit formed by IC24 (2901). After the signal passes through the TRIG detection circuit formed by IC24 (2901), part of it is input to the key matrix by transistor Q2 (2SA1175), and the re mainder lights the circuit board KLM-6023 TRIG LE ...
607 Lect 12 LDO
... Line regulation; This the variation in output voltage as supply voltage is varied from minimum to maximum. PSR; Power Supply Rejection ( or ripple rejection) is a measure of the ac coupling between the input supply voltage on the output voltage. Load/Line transient regulation; This is a measure of t ...
... Line regulation; This the variation in output voltage as supply voltage is varied from minimum to maximum. PSR; Power Supply Rejection ( or ripple rejection) is a measure of the ac coupling between the input supply voltage on the output voltage. Load/Line transient regulation; This is a measure of t ...
LTC5541 - 1.3GHz to 2.3GHz High Dynamic Range Downconverting Mixer.
... The LTC®5541 is part of a family of high dynamic range passive, high gain downconverting mixers covering the 600MHz to 4GHz frequency range. The LTC5541 is optimized for 1.3GHz to 2.3GHz RF applications. The LO frequency must fall within the 1.4GHz to 2.0GHz range for optimum performance. A typical ...
... The LTC®5541 is part of a family of high dynamic range passive, high gain downconverting mixers covering the 600MHz to 4GHz frequency range. The LTC5541 is optimized for 1.3GHz to 2.3GHz RF applications. The LO frequency must fall within the 1.4GHz to 2.0GHz range for optimum performance. A typical ...
AD8065
... Low noise 7 nV/√Hz (f = 10 kHz) 0.6 fA/√Hz (f = 10 kHz) Wide supply voltage range: 5 V to 24 V Single-supply and rail-to-rail output Low offset voltage 1.5 mV maximum High common-mode rejection ratio: −100 dB ...
... Low noise 7 nV/√Hz (f = 10 kHz) 0.6 fA/√Hz (f = 10 kHz) Wide supply voltage range: 5 V to 24 V Single-supply and rail-to-rail output Low offset voltage 1.5 mV maximum High common-mode rejection ratio: −100 dB ...
Evaluates: MAX1748/MAX1779 MAX1748 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... must be installed and jumper JU2 modified to utilize the tripler circuit. Capacitors C10 and C11 should be 0.1µF (Taiyo Yuden, UMK212BJ104MG recommended) with a voltage rating equal to or greater than the expected output voltage at VPA. Lower cost diodes with higher forward voltage drops can be used ...
... must be installed and jumper JU2 modified to utilize the tripler circuit. Capacitors C10 and C11 should be 0.1µF (Taiyo Yuden, UMK212BJ104MG recommended) with a voltage rating equal to or greater than the expected output voltage at VPA. Lower cost diodes with higher forward voltage drops can be used ...
PDF
... Fig (1) Block Diagram A further application of the rectifier is driving a DC motor. Speed control in DC motor is an important issue. With time the need of flexible speed control for motor is becoming essential. One way to control the speed of the motor is by varying its input voltage. Thus this proj ...
... Fig (1) Block Diagram A further application of the rectifier is driving a DC motor. Speed control in DC motor is an important issue. With time the need of flexible speed control for motor is becoming essential. One way to control the speed of the motor is by varying its input voltage. Thus this proj ...
HMC747LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
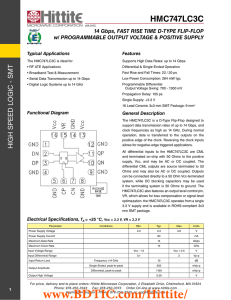
... All differential inputs to the HMC747LC3C are CML and terminated on-chip with 50 Ohms to the positive supply, Vcc, and may be AC or DC coupled. The differential CML outputs are source terminated to 50 Ohms and may also be AC or DC coupled. Outputs can be connected directly to a 50 Ohm Vcc-terminated ...
... All differential inputs to the HMC747LC3C are CML and terminated on-chip with 50 Ohms to the positive supply, Vcc, and may be AC or DC coupled. The differential CML outputs are source terminated to 50 Ohms and may also be AC or DC coupled. Outputs can be connected directly to a 50 Ohm Vcc-terminated ...
Laboratory 3 Strain Gage Sensors
... where ∆f is the frequency spacing between tick marks, fS is the sampling frequency, and N is the number of samples. Until now, you have used the AI Sample Channel VI to sample external voltages. This VI provides a non-buffered input, which means the software reads one value from an input channel and ...
... where ∆f is the frequency spacing between tick marks, fS is the sampling frequency, and N is the number of samples. Until now, you have used the AI Sample Channel VI to sample external voltages. This VI provides a non-buffered input, which means the software reads one value from an input channel and ...
LT1014D-EP
... includes ground, and the output swings within a few millivolts of ground. Furthermore, the LT1014D has specific circuitry that addresses the difficulties of single-supply operation, both at the input and at the output. At the input, the driving signal can fall below 0 V, either inadvertently or on a ...
... includes ground, and the output swings within a few millivolts of ground. Furthermore, the LT1014D has specific circuitry that addresses the difficulties of single-supply operation, both at the input and at the output. At the input, the driving signal can fall below 0 V, either inadvertently or on a ...
High Sensitivity Photoreceiver Design
... signal-to-noise ratio (S N) in direct detection systems and advanced IR methods. The main purpose was to analyse the input stages of IR receivers (photodetector plus low noise preamplifier and biasing circuit of the detector) to optimise them providing maximal value of signal-to-noise ratio. Preampl ...
... signal-to-noise ratio (S N) in direct detection systems and advanced IR methods. The main purpose was to analyse the input stages of IR receivers (photodetector plus low noise preamplifier and biasing circuit of the detector) to optimise them providing maximal value of signal-to-noise ratio. Preampl ...
been investigated [7] - [9]. ... extremely low coupling capacitance require ultra-high input Abstract
... been investigated [7] - [9]. Insulated electrodes having extremely low coupling capacitance require ultra-high input impedance amplifiers, which are highly susceptible to external electrostatic and electromagnetic interference even when shielding is used around the electrodes. Their reported lack of ...
... been investigated [7] - [9]. Insulated electrodes having extremely low coupling capacitance require ultra-high input impedance amplifiers, which are highly susceptible to external electrostatic and electromagnetic interference even when shielding is used around the electrodes. Their reported lack of ...
AN3424
... includes a special circuit, able to reduce AC input current distortion, that allows wide-rangemains operation with an extremely low THD, even over a large load range. The TSM101 compares the DC voltage and current level of a switching power supply to an internal reference. It provides a feedback thr ...
... includes a special circuit, able to reduce AC input current distortion, that allows wide-rangemains operation with an extremely low THD, even over a large load range. The TSM101 compares the DC voltage and current level of a switching power supply to an internal reference. It provides a feedback thr ...
DAC5662A 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Operating with update rates of up to 275 MSPS, the DAC5662A offers exceptional dynamic performance and tight-gain and offset matching, characteristics that make it suitable in either I/Q baseband or direct IF communication applications. Each DAC has a high-impedance differential current output, suit ...
... Operating with update rates of up to 275 MSPS, the DAC5662A offers exceptional dynamic performance and tight-gain and offset matching, characteristics that make it suitable in either I/Q baseband or direct IF communication applications. Each DAC has a high-impedance differential current output, suit ...
STM32F050C4
... I2C, one SPI, one I2S, and one USART), one 12-bit ADC, up to five general-purpose 16-bit timers, a 32-bit timer and an advanced-control PWM timer. The STM32F050xx family operates in the -40 to +85 °C and -40 to +105 °C temperature ranges, from a 2.0 to 3.6 V power supply. A comprehensive set of powe ...
... I2C, one SPI, one I2S, and one USART), one 12-bit ADC, up to five general-purpose 16-bit timers, a 32-bit timer and an advanced-control PWM timer. The STM32F050xx family operates in the -40 to +85 °C and -40 to +105 °C temperature ranges, from a 2.0 to 3.6 V power supply. A comprehensive set of powe ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).














![been investigated [7] - [9]. ... extremely low coupling capacitance require ultra-high input Abstract](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008415826_1-b2d6ab6bf6b67f7918778c5674407c67-300x300.png)