74LCX652 Low Voltage Transceiver/Register with 5V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... bus-management functions that can be performed with the Octal bus transceiver and receiver. ...
... bus-management functions that can be performed with the Octal bus transceiver and receiver. ...
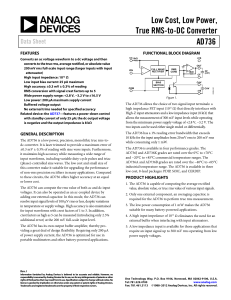
AD736 - Analog Devices
... The AD736 is a low power, precision, monolithic true rms-todc converter. It is laser trimmed to provide a maximum error of ±0.3 mV ± 0.3% of reading with sine wave inputs. Furthermore, it maintains high accuracy while measuring a wide range of input waveforms, including variable duty-cycle pulses an ...
... The AD736 is a low power, precision, monolithic true rms-todc converter. It is laser trimmed to provide a maximum error of ±0.3 mV ± 0.3% of reading with sine wave inputs. Furthermore, it maintains high accuracy while measuring a wide range of input waveforms, including variable duty-cycle pulses an ...
High-Side Voltage-to-Current (VI) Converter
... The first and second stages both require compensation components to ensure proper design stability. A thorough stability analysis is outside of the scope of this document and can be reviewed using the first reference in Section 9. The compensation components in the first stage are R2, R3, and C6, an ...
... The first and second stages both require compensation components to ensure proper design stability. A thorough stability analysis is outside of the scope of this document and can be reviewed using the first reference in Section 9. The compensation components in the first stage are R2, R3, and C6, an ...
a LC MOS 16-Bit Voltage Output DAC
... while the 12 LSBs control DAC3. Using DAC1 and DAC2, the MSBs select a pair of adjacent nodes on the resistor string and present that voltage to the positive and negative inputs of DAC3. This DAC interpolates between these two voltages to produce the analog output voltage. ...
... while the 12 LSBs control DAC3. Using DAC1 and DAC2, the MSBs select a pair of adjacent nodes on the resistor string and present that voltage to the positive and negative inputs of DAC3. This DAC interpolates between these two voltages to produce the analog output voltage. ...
AD9862
... The AD9860 and AD9862 (AD9860/AD9862) are versatile integrated mixed-signal front-ends (MxFE) that are optimized for broadband communication markets. The AD9860/AD9862 are cost effective, mixed signal solutions for wireless or wireline standards based or proprietary broadband modem systems where dyn ...
... The AD9860 and AD9862 (AD9860/AD9862) are versatile integrated mixed-signal front-ends (MxFE) that are optimized for broadband communication markets. The AD9860/AD9862 are cost effective, mixed signal solutions for wireless or wireline standards based or proprietary broadband modem systems where dyn ...
LT5524
... bandwidth extending from low frequency (LF) to 540MHz. It consists of a digitally controlled variable attenuator, followed by a high linearity amplifier. Four parallel digital inputs control the gain over a 22.5dB range with 1.5dB step resolution. An on-chip power supply regulator/filter helps isola ...
... bandwidth extending from low frequency (LF) to 540MHz. It consists of a digitally controlled variable attenuator, followed by a high linearity amplifier. Four parallel digital inputs control the gain over a 22.5dB range with 1.5dB step resolution. An on-chip power supply regulator/filter helps isola ...
DM74LS181 4-Bit Arithmetic Logic Unit
... When the Mode Control input (M) is HIGH, all internal carries are inhibited and the device performs logic operations on the individual bits as listed. When the Mode Control input is LOW, the carries are enabled and the device performs arithmetic operations on the two 4-bit words. The device incorpor ...
... When the Mode Control input (M) is HIGH, all internal carries are inhibited and the device performs logic operations on the individual bits as listed. When the Mode Control input is LOW, the carries are enabled and the device performs arithmetic operations on the two 4-bit words. The device incorpor ...
Laboratory Exercise 1 – Voltage Dividers
... Circuit Exercise 2 – Construct a variable voltage supply circuit using a MΩ range variable resistor (pot) and observe how the voltage output changes as you turn the knob on the potentiometer. Diagram your circuit below. What is the measured voltage range of your variable power supply? How small of ...
... Circuit Exercise 2 – Construct a variable voltage supply circuit using a MΩ range variable resistor (pot) and observe how the voltage output changes as you turn the knob on the potentiometer. Diagram your circuit below. What is the measured voltage range of your variable power supply? How small of ...
NB4N507A 3.3V/5V, 50 MHz to 200 MHz PECL Clock Synthesizer
... ECLinPS is a trademark of Semiconductor Components INdustries, LLC (SCILLC). ON Semiconductor and are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, represe ...
... ECLinPS is a trademark of Semiconductor Components INdustries, LLC (SCILLC). ON Semiconductor and are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC). SCILLC reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. SCILLC makes no warranty, represe ...
DM74LS181 4-Bit Arithmetic Logic Unit
... When the Mode Control input (M) is HIGH, all internal carries are inhibited and the device performs logic operations on the individual bits as listed. When the Mode Control input is LOW, the carries are enabled and the device performs arithmetic operations on the two 4-bit words. The device incorpor ...
... When the Mode Control input (M) is HIGH, all internal carries are inhibited and the device performs logic operations on the individual bits as listed. When the Mode Control input is LOW, the carries are enabled and the device performs arithmetic operations on the two 4-bit words. The device incorpor ...
Compact 600 mA, 3 MHz, Step-Down Converter with Output Discharge ADP2109
... The total solution requires only three tiny external components. It uses a proprietary high speed current mode and constant frequency pulse-width modulation (PWM) control scheme for excellent stability, and transient response. To ensure the longest battery life in portable applications, the ADP2109 ...
... The total solution requires only three tiny external components. It uses a proprietary high speed current mode and constant frequency pulse-width modulation (PWM) control scheme for excellent stability, and transient response. To ensure the longest battery life in portable applications, the ADP2109 ...
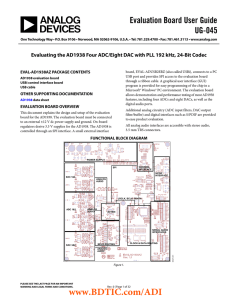
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-045
... In this mode, the AD1938 ADC port generates BCLK and LRCLK when given a valid MCLK. For full flexibility of the AD1938, the part can be put in SPI control mode and programmed with the Automated Register Window Builder application (see Figure 4 for the appropriate jumper settings). Changing the regi ...
... In this mode, the AD1938 ADC port generates BCLK and LRCLK when given a valid MCLK. For full flexibility of the AD1938, the part can be put in SPI control mode and programmed with the Automated Register Window Builder application (see Figure 4 for the appropriate jumper settings). Changing the regi ...
Phase-locked-loop with lock detector
... the SIGIN frequency is lower than the COMPIN frequency, then it is the n-type driver that is held “ON” for most of the cycle. Subsequently, the voltage at the capacitor (C2) of the low-pass filter connected to PC2OUT varies until the signal and comparator inputs are equal in both phase and frequency ...
... the SIGIN frequency is lower than the COMPIN frequency, then it is the n-type driver that is held “ON” for most of the cycle. Subsequently, the voltage at the capacitor (C2) of the low-pass filter connected to PC2OUT varies until the signal and comparator inputs are equal in both phase and frequency ...
MAX16976 28V, 600mA Automotive Step-Down Converter with Low Operating Current General Description
... with Low Operating Current Detailed Description The MAX16976 is a constant-frequency, current-mode automotive buck converter with an integrated high-side switch. The device operates with input voltages from 3.5V to 28V and tolerates input transients up to 42V. During undervoltage events, such as col ...
... with Low Operating Current Detailed Description The MAX16976 is a constant-frequency, current-mode automotive buck converter with an integrated high-side switch. The device operates with input voltages from 3.5V to 28V and tolerates input transients up to 42V. During undervoltage events, such as col ...
MAX7031 Low-Cost, 308MHz, 315MHz, and 433.92MHz FSK Transceiver with Fractional-N PLL General Description
... 10.7MHz above the receive LO. Retaining the fixed-N PLL for the receiver avoids the higher current-drain requirements of a fractional-N PLL and keeps the receiver current drain as low as possible. The fractional-N architecture of the MAX7031 transmit PLL allows the transmit FSK signal to be preset f ...
... 10.7MHz above the receive LO. Retaining the fixed-N PLL for the receiver avoids the higher current-drain requirements of a fractional-N PLL and keeps the receiver current drain as low as possible. The fractional-N architecture of the MAX7031 transmit PLL allows the transmit FSK signal to be preset f ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).