DC Electrical Characteristics of MM74HC High-Speed CMOS Logic
... These diodes are larger than those used in metal-gate CMOS to enable greater current shunting and make them less susceptible to damage. The input network is ringed by VCC and ground diffusions, which prevent substrate currents caused by these transients from affecting other circuitry. ...
... These diodes are larger than those used in metal-gate CMOS to enable greater current shunting and make them less susceptible to damage. The input network is ringed by VCC and ground diffusions, which prevent substrate currents caused by these transients from affecting other circuitry. ...
ADA4412-3 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... feature. Output voltage offset is continuously adjustable over an input-referred range of ±500 mV by applying a differential voltage to an independent offset control input. ...
... feature. Output voltage offset is continuously adjustable over an input-referred range of ±500 mV by applying a differential voltage to an independent offset control input. ...
Voltage Dividers File
... What this means is that selecting a value for Rtop close to 58.2 kΩ will make the voltage divider for the ice alert most sensitive at 4°C. The nearest E12/E24 value is 56 kΩ. This matters because large changes in Vout make it easier to design the other subsystems in the ice alert, so that temperatur ...
... What this means is that selecting a value for Rtop close to 58.2 kΩ will make the voltage divider for the ice alert most sensitive at 4°C. The nearest E12/E24 value is 56 kΩ. This matters because large changes in Vout make it easier to design the other subsystems in the ice alert, so that temperatur ...
LTC490 - Linear Technology
... cable is lightly loaded (470Ω), the signal reflects in phase and increases the amplitude at the driver output. An input frequency of 30kHz is adequate for tests out to 4000 feet of cable. AC Cable Termination Cable termination resistors are necessary to prevent unwanted reflections, but they consume ...
... cable is lightly loaded (470Ω), the signal reflects in phase and increases the amplitude at the driver output. An input frequency of 30kHz is adequate for tests out to 4000 feet of cable. AC Cable Termination Cable termination resistors are necessary to prevent unwanted reflections, but they consume ...
CS1611-FSZ Datasheet
... An external, high-voltage source-follower circuit is used to deliver startup current to the IC. During steady-state operation, an auxiliary winding on the boost inductor biases this circuit to an off state to improve system efficiency, and all IC supply current is generated from the auxiliary windin ...
... An external, high-voltage source-follower circuit is used to deliver startup current to the IC. During steady-state operation, an auxiliary winding on the boost inductor biases this circuit to an off state to improve system efficiency, and all IC supply current is generated from the auxiliary windin ...
AD8099
... (–92 dBc @10 MHz) voltage feedback op amp, the combination of which make it ideal for 16- and 18-bit systems. The AD8099 features a new, highly linear, low noise input stage that increases the full power bandwidth (FPBW) at low gains with high slew rates. ADI’s proprietary next generation XFCB proce ...
... (–92 dBc @10 MHz) voltage feedback op amp, the combination of which make it ideal for 16- and 18-bit systems. The AD8099 features a new, highly linear, low noise input stage that increases the full power bandwidth (FPBW) at low gains with high slew rates. ADI’s proprietary next generation XFCB proce ...
AN-404 - SMD Technology Kft.
... frequency response and an overall reduction in gain. The gain loss can be as much as –30 dB at 20 Hz. ...
... frequency response and an overall reduction in gain. The gain loss can be as much as –30 dB at 20 Hz. ...
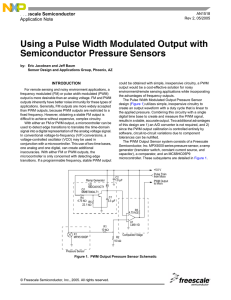
AN1518 Using a Pulse Width Modulated Output with Semiconductor
... There are four clock cycles per timer count. This results in 2 µs per timer count. Thus, to obtain 256 timer counts (or 8-bit resolution), the difference between the zero pressure and full scale pressure PWM output pulse widths must be at least 512 µs (2 µs x 256). But since an additional 60 µs is n ...
... There are four clock cycles per timer count. This results in 2 µs per timer count. Thus, to obtain 256 timer counts (or 8-bit resolution), the difference between the zero pressure and full scale pressure PWM output pulse widths must be at least 512 µs (2 µs x 256). But since an additional 60 µs is n ...
MAX17595/MAX17596/MAX17597 Peak-Current-Mode Controllers for Flyback and Boost Regulators General Description
... Note 3: The MAX17595 is intended for use in universal input power supplies. The internal clamp circuit at VIN is used to prevent the bootstrap capacitor from charging to a voltage beyond the absolute maximum rating of the device when EN is low (shutdown mode). Externally limit the maximum current t ...
... Note 3: The MAX17595 is intended for use in universal input power supplies. The internal clamp circuit at VIN is used to prevent the bootstrap capacitor from charging to a voltage beyond the absolute maximum rating of the device when EN is low (shutdown mode). Externally limit the maximum current t ...
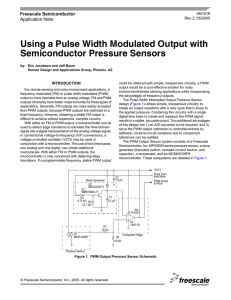
AN1518 Using a Pulse Width Modulated Output
... There are four clock cycles per timer count. This results in 2 µs per timer count. Thus, to obtain 256 timer counts (or 8-bit resolution), the difference between the zero pressure and full scale pressure PWM output pulse widths must be at least 512 µs (2 µs x 256). But since an additional 60 µs is n ...
... There are four clock cycles per timer count. This results in 2 µs per timer count. Thus, to obtain 256 timer counts (or 8-bit resolution), the difference between the zero pressure and full scale pressure PWM output pulse widths must be at least 512 µs (2 µs x 256). But since an additional 60 µs is n ...
Monolithic Active Pixel Detectors
... What do we want from one module? A large high resolution “picture” as fast and easy as possible! few 10 cm2 ...
... What do we want from one module? A large high resolution “picture” as fast and easy as possible! few 10 cm2 ...
ADA4932-1 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... between the supply pins (VS) times the quiescent current (IS). The power dissipated due to the load drive depends upon the particular application. The power due to load drive is calculated by multiplying the load current by the associated voltage drop across the device. RMS voltages and currents mus ...
... between the supply pins (VS) times the quiescent current (IS). The power dissipated due to the load drive depends upon the particular application. The power due to load drive is calculated by multiplying the load current by the associated voltage drop across the device. RMS voltages and currents mus ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Wireless Components ASK Single Conversion Receiver
... bandwidths between 60kHz and 280kHz. The user is free to select other IFs and/or filters that are compatible with the 3MHz - 25MHz bandwidth provided by the 90dB limiting IF. The IF provides over 80dB of received signal strength indication (RSSI). The RSSI output is used as the demodulator for the A ...
... bandwidths between 60kHz and 280kHz. The user is free to select other IFs and/or filters that are compatible with the 3MHz - 25MHz bandwidth provided by the 90dB limiting IF. The IF provides over 80dB of received signal strength indication (RSSI). The RSSI output is used as the demodulator for the A ...
OPA4684 Quad, Low-Power, Current-Feedback Operational Amplifier FEATURES
... The OPA4684 provides a new level of performance in lowpower, wideband, current-feedback (CFB) amplifiers. This CFBPLUS amplifier is among the first to use an internally closed-loop input buffer stage that enhances performance significantly over earlier low-power CFB amplifiers. This new architecture ...
... The OPA4684 provides a new level of performance in lowpower, wideband, current-feedback (CFB) amplifiers. This CFBPLUS amplifier is among the first to use an internally closed-loop input buffer stage that enhances performance significantly over earlier low-power CFB amplifiers. This new architecture ...
MAX9129 Quad Bus LVDS Driver with Flow-Through Pinout General Description
... Note 2: Current into the device is defined as positive, and current out of the device is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VOD and ∆VOD. Note 3: AC parameters are guaranteed by design and characterization. Note 4: CL includes probe and jig capacitance. Note 5: Signal ...
... Note 2: Current into the device is defined as positive, and current out of the device is defined as negative. All voltages are referenced to ground except VOD and ∆VOD. Note 3: AC parameters are guaranteed by design and characterization. Note 4: CL includes probe and jig capacitance. Note 5: Signal ...
R.C.N. Pilawa-Podgurski, D. Giuliano, and D.J. Perreault, “Merged Two-Stage Power Converter Architecture with Soft Charging Switched-Capacitor Energy Transfer,” 2008 IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference , June 2008, pp. 4008 – 4015
... stage with a high-frequency, low-voltage regulation stage. This strategy makes use of on-die device characteristics available in CMOS processes. As examined in the appendix, lowvoltage submicron CMOS processes inherently provide far higher achievable switching frequencies than higher-voltage process ...
... stage with a high-frequency, low-voltage regulation stage. This strategy makes use of on-die device characteristics available in CMOS processes. As examined in the appendix, lowvoltage submicron CMOS processes inherently provide far higher achievable switching frequencies than higher-voltage process ...
Document
... A process of converting analog data into digital data, which process is known as digitization. The device used for converting analog data into digital form for transmission, and subsequently recovering the original data from the digital is known as a codec (coder-decoder) ...
... A process of converting analog data into digital data, which process is known as digitization. The device used for converting analog data into digital form for transmission, and subsequently recovering the original data from the digital is known as a codec (coder-decoder) ...
AD7190 数据手册DataSheet下载
... GENERAL DESCRIPTION The AD7190 is a low noise, complete analog front end for high precision measurement applications. It contains a low noise, 24-bit sigma-delta (∑-Δ) analog to digital converter (ADC). The on-chip low noise gain stage means that signals of small amplitude can be interfaced directly ...
... GENERAL DESCRIPTION The AD7190 is a low noise, complete analog front end for high precision measurement applications. It contains a low noise, 24-bit sigma-delta (∑-Δ) analog to digital converter (ADC). The on-chip low noise gain stage means that signals of small amplitude can be interfaced directly ...
a AN-402 APPLICATION NOTE •
... Various clamp amps can be used in these systems to restrict signal excursions at their outputs to protect downstream devices. So far most of the clamping amplifiers have relied upon an output clamping architecture and are called output clamp amps (OCAs). A new architecture called an input clamp amp ...
... Various clamp amps can be used in these systems to restrict signal excursions at their outputs to protect downstream devices. So far most of the clamping amplifiers have relied upon an output clamping architecture and are called output clamp amps (OCAs). A new architecture called an input clamp amp ...
0-1A, Single-Supply, Low-Side Current Sensing
... Figure 13. Uncalibrated DC Transfer Function (VOUT vs. IIN) A plot of full-scale error vs. input current is shown in Figure 14. As shown, the gain error and offset error are linear across the input range which allows them to be removed with a 2-point calibration. ...
... Figure 13. Uncalibrated DC Transfer Function (VOUT vs. IIN) A plot of full-scale error vs. input current is shown in Figure 14. As shown, the gain error and offset error are linear across the input range which allows them to be removed with a 2-point calibration. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).