Science Journals 4-18 to 5-5
... the current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across each resistor? If three resistors, 12 Ω , 24 Ω, and 6 Ω, are connected in parallel across a 24V battery, what is the current through each branch of the circuit? What is the total current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across e ...
... the current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across each resistor? If three resistors, 12 Ω , 24 Ω, and 6 Ω, are connected in parallel across a 24V battery, what is the current through each branch of the circuit? What is the total current in the circuit? What is the voltage drop across e ...
File: atrac
... Reverberation (second to higher order reflection) Sound waves that travel to the listener after reflection of first-order-reflection. Reverberation will decay with time as sound energy is absorbed by the enviroment. Reverberation time is the duration for the sound pressure to drop to 60dB of its in ...
... Reverberation (second to higher order reflection) Sound waves that travel to the listener after reflection of first-order-reflection. Reverberation will decay with time as sound energy is absorbed by the enviroment. Reverberation time is the duration for the sound pressure to drop to 60dB of its in ...
Electrical Safety
... d. Only on grounded equipment 2. When doing outside electrical work, what type of circuit needs to be used? a. 110 volt b. 220 volt c. A ground fault interrupter d. A buzz fuse 3. Which statement is true about a static charge? a. It’s developed by equipment statically standing there b. It’s develope ...
... d. Only on grounded equipment 2. When doing outside electrical work, what type of circuit needs to be used? a. 110 volt b. 220 volt c. A ground fault interrupter d. A buzz fuse 3. Which statement is true about a static charge? a. It’s developed by equipment statically standing there b. It’s develope ...
Electrical Circuits
... Electrical energy enters your home at the circuit breaker or fuse box and branches out to wall sockets, major appliances and ...
... Electrical energy enters your home at the circuit breaker or fuse box and branches out to wall sockets, major appliances and ...
Ch 16 Electricity test reivew
... 22. List two materials that are conductors and two materials that are insulators. 23. What happens to the current in a device if the resistance of the device increases and the voltage difference stays the same? 24. You install two batteries in a flashlight so that their positive ends are connected t ...
... 22. List two materials that are conductors and two materials that are insulators. 23. What happens to the current in a device if the resistance of the device increases and the voltage difference stays the same? 24. You install two batteries in a flashlight so that their positive ends are connected t ...
Analog Signal Conditioning
... no current drawn from the input circuits; I- = I+ • it has infinite gain, hence the difference between the input and output voltages is zero. This is denoted by short circuiting the two inputs; V- = V+ • it has zero output impedance, so that the output voltage is independent of the output current. ...
... no current drawn from the input circuits; I- = I+ • it has infinite gain, hence the difference between the input and output voltages is zero. This is denoted by short circuiting the two inputs; V- = V+ • it has zero output impedance, so that the output voltage is independent of the output current. ...
2.4 Circuits with Resistors and Capacitors
... • response of a series connected resistor and capacitor to a dc (steady) voltage • response of a series connected resistor and capacitor to an ac (varying) voltage • decibels and Bode plots • high-pass electronic filter • band-pass electronic filter • using a low-pass filter for signal-to-noise enha ...
... • response of a series connected resistor and capacitor to a dc (steady) voltage • response of a series connected resistor and capacitor to an ac (varying) voltage • decibels and Bode plots • high-pass electronic filter • band-pass electronic filter • using a low-pass filter for signal-to-noise enha ...
Effect of RF Noise on Position Accuracy
... approximately thirty minutes. This procedure was repeated three more times at different pseudolite attenuation levels. The second test removed an additional 18 dB of attenuation. This level was chosen because that was the level where the received signal to noise ratio of was seen to drop. The third ...
... approximately thirty minutes. This procedure was repeated three more times at different pseudolite attenuation levels. The second test removed an additional 18 dB of attenuation. This level was chosen because that was the level where the received signal to noise ratio of was seen to drop. The third ...
Pulse Code - s3.amazonaws.com
... * The signal is sampled at regular intervals such that each sample is proportional to the amplitude of the signal at that sampling instant. This technique is called “sampling”. * For minimum distortion, the sampling rate should be more than twice the signal frequency. ...
... * The signal is sampled at regular intervals such that each sample is proportional to the amplitude of the signal at that sampling instant. This technique is called “sampling”. * For minimum distortion, the sampling rate should be more than twice the signal frequency. ...
SGL0622Z 数据资料DataSheet下载
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
... Exceeding any one or a combination of the Absolute Maximum Rating conditions may cause permanent damage to the device. Extended application of Absolute Maximum Rating conditions to the device may reduce device reliability. Specified typical performance or functional operation of the device under Abs ...
Signals - theParticle.com
... Normally, when we think of signals or waves, we think of the familiar ‘time domain’ wave. Figure 2 illustrates a Sin wave at 4Hz. Notice that the horizontal axis is time, and is expressed in seconds. You can count the number of times the wave cycles, and you’ll see that it’s 4, ie: 4Hz. Given the fr ...
... Normally, when we think of signals or waves, we think of the familiar ‘time domain’ wave. Figure 2 illustrates a Sin wave at 4Hz. Notice that the horizontal axis is time, and is expressed in seconds. You can count the number of times the wave cycles, and you’ll see that it’s 4, ie: 4Hz. Given the fr ...
Tech License Study Guide PowerPoint
... the inductive reactance. • Theoretically, the resulting reactance is zero. – Leaving only resistance – meaning minimum impediment to the flow of the radio frequency currents flowing in the antenna and sending the radio wave into space. ...
... the inductive reactance. • Theoretically, the resulting reactance is zero. – Leaving only resistance – meaning minimum impediment to the flow of the radio frequency currents flowing in the antenna and sending the radio wave into space. ...
AtlasEng - pa0fri.com
... (SN76660) and is further converted back to audio for input to MIC. GAIN potentiometer. The resulting harmonics (of 6.4 MHz) are filtered out with simple RC filtering when it was demodulated back to audio. The result is a 'cleaner' clipped signal being finally transmitted. This increases the average ...
... (SN76660) and is further converted back to audio for input to MIC. GAIN potentiometer. The resulting harmonics (of 6.4 MHz) are filtered out with simple RC filtering when it was demodulated back to audio. The result is a 'cleaner' clipped signal being finally transmitted. This increases the average ...
QUESTION: what happens to light intensity of lamp in a series circuit
... QUESTION: what happens to light intensity of lamp in a series circuit when more lamps are added to the circuit SOLUTION: When lamps are added in a series circuit, the resistance of the circuit is R RL RL RL ... N RL Here N is quantity of lamps added to the circuit RL is the resistance of ...
... QUESTION: what happens to light intensity of lamp in a series circuit when more lamps are added to the circuit SOLUTION: When lamps are added in a series circuit, the resistance of the circuit is R RL RL RL ... N RL Here N is quantity of lamps added to the circuit RL is the resistance of ...
Section H5: High-Frequency Amplifier Response
... strategy will be to set all independent sources to zero (which, in this case, also sets the dependent source to zero) as shown in the figure to the right below. We can now calculate the individual time constants using the Method of Open Circuit Time Constants. Just as a sanity check – even if we had ...
... strategy will be to set all independent sources to zero (which, in this case, also sets the dependent source to zero) as shown in the figure to the right below. We can now calculate the individual time constants using the Method of Open Circuit Time Constants. Just as a sanity check – even if we had ...
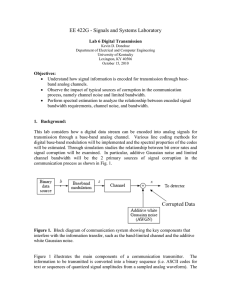
Lab6_EE422 - University of Kentucky College of Engineering
... 2. This next exercise examines the relationship between the line code PSD and the data rate Fd. For this part just consider the Manchester encoding and produce a PSD for different values of Fd, successively taken to be 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 b/s. Compute and plot the PSD (just record the dB plots ...
... 2. This next exercise examines the relationship between the line code PSD and the data rate Fd. For this part just consider the Manchester encoding and produce a PSD for different values of Fd, successively taken to be 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 b/s. Compute and plot the PSD (just record the dB plots ...
Ohms Law - Powerpoint Presentation
... The basic law concerning the flow of electricity is Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s law states that when electrical potential (voltage) creates a flow of electricity (current), the current and the electrical resistance of the circuit are proportional to the voltage. In mathematical terms, V = I x R where V is ...
... The basic law concerning the flow of electricity is Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s law states that when electrical potential (voltage) creates a flow of electricity (current), the current and the electrical resistance of the circuit are proportional to the voltage. In mathematical terms, V = I x R where V is ...