Chapter 20 Notes
... Ohm’s Law: the voltage (V) in a circuit equals the product of the current (I) and the resistance (R). V = I x R or I = V/R Increasing the voltage increases the current. Keeping the same voltage and increasing the resistance decreases the current. ...
... Ohm’s Law: the voltage (V) in a circuit equals the product of the current (I) and the resistance (R). V = I x R or I = V/R Increasing the voltage increases the current. Keeping the same voltage and increasing the resistance decreases the current. ...
TIGER ELECTRONIC CO.,LTD
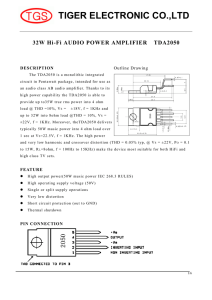
... typically 50W music power into 4 ohm load over 1 sec at V S =22.5V, f = 1KHz. The high power and very low harmonic and crossover distortion (THD = 0.05% typ, @ V S = ±22V, P O = 0.1 to 15W, R L =8ohm, f = 100Hz to 15KHz) make the device most suitable for both HiFi and high class TV sets. ...
... typically 50W music power into 4 ohm load over 1 sec at V S =22.5V, f = 1KHz. The high power and very low harmonic and crossover distortion (THD = 0.05% typ, @ V S = ±22V, P O = 0.1 to 15W, R L =8ohm, f = 100Hz to 15KHz) make the device most suitable for both HiFi and high class TV sets. ...
Challenger Early College High School
... Challenger Early College High School High School Course Unit Syllabus Teacher: Mrs. Donna Americo Course: Physical Science Unit 5: Electricity and Magnetism Unit Objectives: Static Electricity ...
... Challenger Early College High School High School Course Unit Syllabus Teacher: Mrs. Donna Americo Course: Physical Science Unit 5: Electricity and Magnetism Unit Objectives: Static Electricity ...
PH4705/ET4305:Instrumentation Amp
... the input. It will have zero output impedance, so as to drive any following circuit with ease. It will have infinite gain so that any required gain can be set easily with a couple of resistors. It will have zero offset, so that a zero input signal results in a zero output. It will have an infinite f ...
... the input. It will have zero output impedance, so as to drive any following circuit with ease. It will have infinite gain so that any required gain can be set easily with a couple of resistors. It will have zero offset, so that a zero input signal results in a zero output. It will have an infinite f ...
Chapter 15 Lesson 2: Physical Science
... People use circuit diagrams to help build circuits and the lines on a circuit diagram show how electricity moves through the circuit. -The symbols on a circuit diagram show different parts of the circuit. -For example, the symbol for a wire looks like a line and the symbol for a resistor is an uneve ...
... People use circuit diagrams to help build circuits and the lines on a circuit diagram show how electricity moves through the circuit. -The symbols on a circuit diagram show different parts of the circuit. -For example, the symbol for a wire looks like a line and the symbol for a resistor is an uneve ...
Hearing Science
... • When you have two (or more) sinusoids as inputs, the output will be the difference of these tones. ...
... • When you have two (or more) sinusoids as inputs, the output will be the difference of these tones. ...
Electron Shuffle
... Electricity can be explained using a basic illustration known as the electron shuffle. The electron shuffle is used to exemplify what happens during electron flow (ie. electricity). Though not perfectly complete, it does help to give one an idea of what is transpiring. To begin with, we’ll start wit ...
... Electricity can be explained using a basic illustration known as the electron shuffle. The electron shuffle is used to exemplify what happens during electron flow (ie. electricity). Though not perfectly complete, it does help to give one an idea of what is transpiring. To begin with, we’ll start wit ...
Activity 1.2.4 Circuit Calculation
... to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experience applying Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s voltage and current laws to circuits in order to gain understanding of circuit requirements and r ...
... to apply basic electrical theories to circuits in order to verify safe operation and troubleshoot unexpected circuit failure. In this activity you will gain experience applying Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s voltage and current laws to circuits in order to gain understanding of circuit requirements and r ...
amplitude modulation
... the Frequency Domain Frequency-Domain Representation of AM – Observing an AM signal on an oscilloscope, you see only amplitude variations of the carrier with respect to time. – A plot of signal amplitude versus frequency is referred to as frequency-domain display. – A spectrum analyzer is used to di ...
... the Frequency Domain Frequency-Domain Representation of AM – Observing an AM signal on an oscilloscope, you see only amplitude variations of the carrier with respect to time. – A plot of signal amplitude versus frequency is referred to as frequency-domain display. – A spectrum analyzer is used to di ...
Elements of AC Circuits - The Series RLC circuit
... 2. Connect one DMM to the DVM Output of the function generator. Set this DMM to measure 20VDC. Note that the frequency measured is the product of the reading on this meter and the multiplier setting on the function generator. Connect the other DMM between A and D initially and set it to measure 20 ...
... 2. Connect one DMM to the DVM Output of the function generator. Set this DMM to measure 20VDC. Note that the frequency measured is the product of the reading on this meter and the multiplier setting on the function generator. Connect the other DMM between A and D initially and set it to measure 20 ...