Pediatric Mental Health - Idaho School Counselors
... Stays out later than approved by parents Has run away from home two times Truant from school, beginning before age 13 ...
... Stays out later than approved by parents Has run away from home two times Truant from school, beginning before age 13 ...
Chapter 13 PowerPoint
... • Age of the father--incidence of schizophrenia increases with the age of the father ...
... • Age of the father--incidence of schizophrenia increases with the age of the father ...
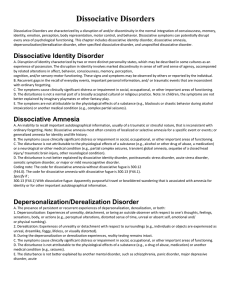
Dissociative Disorders
... D. The disturbance is not a normal part of a broadly accepted cultural or religious practice. Note: In children, the symptoms are not better explained by imaginary playmates or other fantasy play. E. The symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., blackouts or ch ...
... D. The disturbance is not a normal part of a broadly accepted cultural or religious practice. Note: In children, the symptoms are not better explained by imaginary playmates or other fantasy play. E. The symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., blackouts or ch ...
Managing “The Why & When”
... Use only if patients exhibit symptoms that impair functioning or cause danger to themselves or others, and/or interfere with provision of care Agitated behavior is an insufficient reason to use an antipsychotic medication (i.e. must be psychotic or ...
... Use only if patients exhibit symptoms that impair functioning or cause danger to themselves or others, and/or interfere with provision of care Agitated behavior is an insufficient reason to use an antipsychotic medication (i.e. must be psychotic or ...
Personality Disorders - Cornwall Partnership NHS Foundation Trust
... distress and improving wellbeing is from individual or group psychotherapeutic work. This could include dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT), cognitive analytic therapy (CAT) or mindfulness. Some people with personality disorder also have depression, anxiety or para ...
... distress and improving wellbeing is from individual or group psychotherapeutic work. This could include dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT), cognitive analytic therapy (CAT) or mindfulness. Some people with personality disorder also have depression, anxiety or para ...
Quick Guide
... Coma or loss of consciousness. These can be dissociative when they are not due to a general medical condition. Conditions similar to Dissociative Identify Disorder. Some clients may not fully meet the criteria for DID. For example, they may not have two fully formed personality states, or they do no ...
... Coma or loss of consciousness. These can be dissociative when they are not due to a general medical condition. Conditions similar to Dissociative Identify Disorder. Some clients may not fully meet the criteria for DID. For example, they may not have two fully formed personality states, or they do no ...
Borderline personality disorder
... A diagnosis of BPD is usually made in adults, not children or adolescents. That's because what appear to be signs and symptoms of BPD may go away with maturity. Complications ...
... A diagnosis of BPD is usually made in adults, not children or adolescents. That's because what appear to be signs and symptoms of BPD may go away with maturity. Complications ...
2- obsessive compulsive disorders DSM 5
... • The obsessions or compulsion are time consuming (take more than 1 hour per day) or cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning • The OCD symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (drug abuse or ...
... • The obsessions or compulsion are time consuming (take more than 1 hour per day) or cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational or other important areas of functioning • The OCD symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (drug abuse or ...
Impulse Control Disorders Not Elsewhere Classified
... out the hair or when attempting to resist the behavior C. Pleasure, gratification, or relief when pulling out the hair D. The disturbance is not better accounted for by another mental disorder and is not due to a general medical condition (e.g., dermatological condition) E. The disturbance causes cl ...
... out the hair or when attempting to resist the behavior C. Pleasure, gratification, or relief when pulling out the hair D. The disturbance is not better accounted for by another mental disorder and is not due to a general medical condition (e.g., dermatological condition) E. The disturbance causes cl ...
Document
... (1) often loses temper (2) often argues with adults (3) often actively defies or refuses to comply with adults' requests or rules (4) often deliberately annoys people (5) often blames others for his or her mistakes or misbehavior (6) is often touchy or easily annoyed by others (7) is often angry and ...
... (1) often loses temper (2) often argues with adults (3) often actively defies or refuses to comply with adults' requests or rules (4) often deliberately annoys people (5) often blames others for his or her mistakes or misbehavior (6) is often touchy or easily annoyed by others (7) is often angry and ...
Bipolar Disorder (manic–depressive Illness)
... that alternate from periods of severe highs (mania) to extreme lows (depression). These mood swings, which are out of proportion or totally unrelated to events in a person’s life, affect thoughts, feelings, physical health, behavior, and functioning. Bipolar disorder is a neurobiological brain disor ...
... that alternate from periods of severe highs (mania) to extreme lows (depression). These mood swings, which are out of proportion or totally unrelated to events in a person’s life, affect thoughts, feelings, physical health, behavior, and functioning. Bipolar disorder is a neurobiological brain disor ...
presentation ( format)
... • MDD is a chronic and recurrent illness. • Using objective measurements of symptoms and side effects a can help with treatment decisions. • Remission can take time (at least 8, but up to 14 weeks). • Many steps may be needed to reach remission. – Remission rate of 50% was reached after 2 steps. – R ...
... • MDD is a chronic and recurrent illness. • Using objective measurements of symptoms and side effects a can help with treatment decisions. • Remission can take time (at least 8, but up to 14 weeks). • Many steps may be needed to reach remission. – Remission rate of 50% was reached after 2 steps. – R ...
Abnormal Psychology - Rutgers Psychology
... Age of onset and Gender features - What is the average age when symptoms appear that lead to a diagnosis? For Gender features: ex. Bipolar is equally common among men and women, major depression diagnosed 2X more in women than in men. ...
... Age of onset and Gender features - What is the average age when symptoms appear that lead to a diagnosis? For Gender features: ex. Bipolar is equally common among men and women, major depression diagnosed 2X more in women than in men. ...
Adjustment disorders
... a pet is devastating for some people, whereas other people may not be affected at all. ...
... a pet is devastating for some people, whereas other people may not be affected at all. ...
a severe mood disorder characterized by major depressive
... It’s often accompanied by disturbances in appetite and sleep, low self-esteem, and difficulties in maintaining concentration or attention. Interestingly, it begins before birth in about 50% of women who develop it. Both nature and nurture contribute to its development, such as genetic predisposition ...
... It’s often accompanied by disturbances in appetite and sleep, low self-esteem, and difficulties in maintaining concentration or attention. Interestingly, it begins before birth in about 50% of women who develop it. Both nature and nurture contribute to its development, such as genetic predisposition ...
Dissociative Disorders
... B. At least two of these identities or personality states recurrently take control of the person’s behavior C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary ...
... B. At least two of these identities or personality states recurrently take control of the person’s behavior C. Inability to recall important personal information that is too extensive to be explained by ordinary ...
ho-2301-chap14powerpoint
... who has schizophrenia, the greater the risk that she will be diagnosed with schizophrenia at some point in her lifetime – If either biological parent of an adopted individual has schizophrenia, the adopted individual is at greater risk to develop ...
... who has schizophrenia, the greater the risk that she will be diagnosed with schizophrenia at some point in her lifetime – If either biological parent of an adopted individual has schizophrenia, the adopted individual is at greater risk to develop ...
Review Questions Psychosomatic, Somatoform, Dissociative Disorders
... – The number of people diagnosed with the disorder has been increasing – Although the disorder is still uncommon, thousands of cases have been documented in the U.S. and Canada alone • Two factors may account for this increase: – Clinicians are more willing to make such a diagnosis – Diagnostic proc ...
... – The number of people diagnosed with the disorder has been increasing – Although the disorder is still uncommon, thousands of cases have been documented in the U.S. and Canada alone • Two factors may account for this increase: – Clinicians are more willing to make such a diagnosis – Diagnostic proc ...
4468 ANXIETY DISORDERS - PANIC DISORDER
... a. responsiveness to medication b. intensity and sudden, episodic nature c. co-occurrence with substance abuse 11. Typically, an early age of onset of panic disorder carries greater risks that it will: a. develop into a personality disorder b. become chronic and cause more impairment c. evolve into ...
... a. responsiveness to medication b. intensity and sudden, episodic nature c. co-occurrence with substance abuse 11. Typically, an early age of onset of panic disorder carries greater risks that it will: a. develop into a personality disorder b. become chronic and cause more impairment c. evolve into ...
Learners with Emotional or Behavioral Disorders
... • a need to count or a need for things to be symmetrical, it is just as common for individuals with OCD to suffer most from symptoms that are less well-known, none of which is more common than indecision. • And indecision is always at its worst when the patient is presented with two options that are ...
... • a need to count or a need for things to be symmetrical, it is just as common for individuals with OCD to suffer most from symptoms that are less well-known, none of which is more common than indecision. • And indecision is always at its worst when the patient is presented with two options that are ...
Psychological Disorders
... attacks) marked by a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensation are the main symptom of panic disorder. It is also characterized by ...
... attacks) marked by a minutes-long episode of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensation are the main symptom of panic disorder. It is also characterized by ...
Excoriation disorder
Excoriation disorder (also known as dermatillomania, skin-picking disorder, neurotic excoriation, acne excoriee, pathologic skin picking (PSP), compulsive skin picking (CSP) or psychogenic excoriation) is an impulse control disorder characterized by the repeated urge to pick at one's own skin, often to the extent that damage is caused. Research has suggested that the urge to pick is similar to a Body-focused repetitive behavior but others have argued that for some the condition is more akin to a substance abuse disorder. The two main strategies for treating this condition are pharmacological and behavioral intervention.