LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 12. What is meant by lactose intolerance? How it can be overcome? 13. How the viscosity of starch solution is related to its structure? 14. Give a brief account of cyclodextrins and their use. 15. Explain the biological role of NAD+. 16. What are (i) oxidoreductases (ii) transferases. Give two examp ...
... 12. What is meant by lactose intolerance? How it can be overcome? 13. How the viscosity of starch solution is related to its structure? 14. Give a brief account of cyclodextrins and their use. 15. Explain the biological role of NAD+. 16. What are (i) oxidoreductases (ii) transferases. Give two examp ...
Chapter 2 Notes ch._2_lecture_notes_2005
... Carbohydrates serve as the major source of energy for most living organisms. When simple sugars combine to form polymers they can function as long term food storage molecules, as protective coverings for cells and organisms, as the main structural support for land plants (cellulose) and constituents ...
... Carbohydrates serve as the major source of energy for most living organisms. When simple sugars combine to form polymers they can function as long term food storage molecules, as protective coverings for cells and organisms, as the main structural support for land plants (cellulose) and constituents ...
Publications de l`équipe
... found that axonal microtubules were preferentially stained by the anti-GTP-tubulin antibody hMB11. Super-resolution microscopy combined with EM immunocytochemistry revealed that hMB11 was localized at KIF5 attachment sites. In addition, EB1, which binds preferentially to guanylyl-methylene-diphospha ...
... found that axonal microtubules were preferentially stained by the anti-GTP-tubulin antibody hMB11. Super-resolution microscopy combined with EM immunocytochemistry revealed that hMB11 was localized at KIF5 attachment sites. In addition, EB1, which binds preferentially to guanylyl-methylene-diphospha ...
Probabilistic Approaches to Predicting the Secondary Structure of Proteins
... X-ray crystallography has been the traditional method for determining the structure of a protein. Protein samples are crystallized, and a fine beam of x-rays is targeted at them. The x-ray diffraction detected is then used to generate a model of the electron density of the protein. Several disadvant ...
... X-ray crystallography has been the traditional method for determining the structure of a protein. Protein samples are crystallized, and a fine beam of x-rays is targeted at them. The x-ray diffraction detected is then used to generate a model of the electron density of the protein. Several disadvant ...
Instructions for Mem-mEN Web-server
... Membrane proteins, which interact with the membranes of a cell or an organelle, play essential roles in a variety of vital biological processes. Because membrane proteins mediate many interactions between cells and extracellular surroundings as well as between the cytosol and membrane-bound organell ...
... Membrane proteins, which interact with the membranes of a cell or an organelle, play essential roles in a variety of vital biological processes. Because membrane proteins mediate many interactions between cells and extracellular surroundings as well as between the cytosol and membrane-bound organell ...
B-PERfusions
... B-PER and fusion proteins time the pellets were uniformly dispersed in the lysis solution. From this point, the IPIII-His and MBP fusion lysates were processed differently, as detailed in the next two paragraphs. Purification of His-tagged fusion proteins To each IPIII-His fusion lysate was added 1 ...
... B-PER and fusion proteins time the pellets were uniformly dispersed in the lysis solution. From this point, the IPIII-His and MBP fusion lysates were processed differently, as detailed in the next two paragraphs. Purification of His-tagged fusion proteins To each IPIII-His fusion lysate was added 1 ...
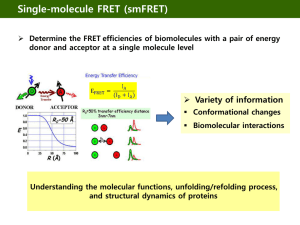
Single molecule analysis - Biomolecular Engineering Laboratory
... Large spectral separation between donor and acceptor emissions Similar quantum yields and detection efficiencies cf) Fluorescent proteins : low stability, photoinduced blinking Quantum dots : large size (>20 nm), lack of a monovalent ...
... Large spectral separation between donor and acceptor emissions Similar quantum yields and detection efficiencies cf) Fluorescent proteins : low stability, photoinduced blinking Quantum dots : large size (>20 nm), lack of a monovalent ...
Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic: prokaryotic – no internal
... Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic: prokaryotic – no internal membranes therefore no membranebound organelles (they only have ribosomes) and no nucleus; their chromosomes are circular and do not have histone proteins; bacteria and archeae are the only examples. Eukaryotic – have organelles; DNA in linear chr ...
... Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic: prokaryotic – no internal membranes therefore no membranebound organelles (they only have ribosomes) and no nucleus; their chromosomes are circular and do not have histone proteins; bacteria and archeae are the only examples. Eukaryotic – have organelles; DNA in linear chr ...
DNA elements: Shaping up transcription factor binding
... structural features had a particularly important role in determining which Hox proteins bound. Crucially, these analyses confirmed a key role for minor-groove width at the same positions as were identified in the crystal structure, indicating that such computational modelling could be used to identi ...
... structural features had a particularly important role in determining which Hox proteins bound. Crucially, these analyses confirmed a key role for minor-groove width at the same positions as were identified in the crystal structure, indicating that such computational modelling could be used to identi ...
Mass Spectrometry
... A potential application of MS is for the early detection of certain cancers. MALDITOF-MS offers the opportunity to rapidly detect and monitor oncoprotein expression against a background of normal protein activity An promising application of MS is the analysis of tissue samples for molecular distribu ...
... A potential application of MS is for the early detection of certain cancers. MALDITOF-MS offers the opportunity to rapidly detect and monitor oncoprotein expression against a background of normal protein activity An promising application of MS is the analysis of tissue samples for molecular distribu ...
(Affinity and SRM) assays for detection of potential biomarkers for
... rather than scanning all the peptides and then identifying the target. AFFIRM is a platform that combines antibody and mass spectrometry technologies to detect and quantify proteins. We produced antibodies that would bind specifically to the target proteins and the antibodies were bound to magnetic ...
... rather than scanning all the peptides and then identifying the target. AFFIRM is a platform that combines antibody and mass spectrometry technologies to detect and quantify proteins. We produced antibodies that would bind specifically to the target proteins and the antibodies were bound to magnetic ...
Detailed characterization of the interactions between hepatitis C virus and host proteins.
... processes in details, several novel viral-host interactions have been identified through yeast-twohybrid screen, proteomic and bioinformatic approaches. For the first part of the project, we aim to determine the mechanism of binding for each pair of viral-host proteins. By using deletion and substit ...
... processes in details, several novel viral-host interactions have been identified through yeast-twohybrid screen, proteomic and bioinformatic approaches. For the first part of the project, we aim to determine the mechanism of binding for each pair of viral-host proteins. By using deletion and substit ...
Organic Chemistry Notes
... m. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon bonded covalently to four other partners. n. Three of those partners are common to all amino acids: a carboxyl group (COOH), an amino group (-NH2) and a hydrogen atom. o. The fourth spot is called the side group and varies between amino acids; the side ...
... m. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon bonded covalently to four other partners. n. Three of those partners are common to all amino acids: a carboxyl group (COOH), an amino group (-NH2) and a hydrogen atom. o. The fourth spot is called the side group and varies between amino acids; the side ...
Protein Story-telling S. Krishnaswamy, The Institute of Mathematical
... S. Krishnaswamy, The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai Proteins are molecules that are needed by humans and insects and all the other living things. Without these molecules, we will not live or function. They are the machines of the cells. . Proteins such as synthetases help make other pro ...
... S. Krishnaswamy, The Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai Proteins are molecules that are needed by humans and insects and all the other living things. Without these molecules, we will not live or function. They are the machines of the cells. . Proteins such as synthetases help make other pro ...
Illustrating Protein Synthesis
... Illustrating Protein Synthesis The Central dogma states that DNA is transcribed into RNA and RNA is then translated into Proteins. For this assignment, you (and 1 partner if you would like) will illustrate this process being sure to include the components below. This illustration must show the proce ...
... Illustrating Protein Synthesis The Central dogma states that DNA is transcribed into RNA and RNA is then translated into Proteins. For this assignment, you (and 1 partner if you would like) will illustrate this process being sure to include the components below. This illustration must show the proce ...
Slides #5B (Green)
... modifications e.g. hydroxylation, etc) Sequence evolution/MSA MS for identifying proteins in a mixture Protein interactions Important types of proteins ...
... modifications e.g. hydroxylation, etc) Sequence evolution/MSA MS for identifying proteins in a mixture Protein interactions Important types of proteins ...
L10 Protein-carbo and protein-lipids interactions - e
... The texture and organoleptic properties of many foods arise as a consequence of their multiphase nature. Emulsion - a liquid and an oil phase – found in sauces, gravies, and spreads. The two phases are naturally immiscible and the successful stabilization of the dispersed phase within the continuum ...
... The texture and organoleptic properties of many foods arise as a consequence of their multiphase nature. Emulsion - a liquid and an oil phase – found in sauces, gravies, and spreads. The two phases are naturally immiscible and the successful stabilization of the dispersed phase within the continuum ...
Document
... For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino acid preferences for different structural environments p ...
... For each alignment, the probability that that each amino acid residue would occur in such an environment is calculated based on observed preferences in determined structures. § Rationale: • Limited number of basic folds found in nature • Amino acid preferences for different structural environments p ...
Name - KS Blogs
... 5. Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a golgi apparatus. How would this affect how the cell works? Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a smooth E.R. What would happen? Organelle ___ Ribosome ___ Endoplasmic reticulum ___ Golgi apparatus ___ Lysosome ___ Vacuole ___ Chloroplast ___ Mitochondrion ...
... 5. Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a golgi apparatus. How would this affect how the cell works? Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a smooth E.R. What would happen? Organelle ___ Ribosome ___ Endoplasmic reticulum ___ Golgi apparatus ___ Lysosome ___ Vacuole ___ Chloroplast ___ Mitochondrion ...
Catalog# 786-842 PROTOCOL - G
... of proteins. The resin consists of 6% cross-linked agarose covalently coupled to heparin through amide bonds. The coupling chemistry used generates a highly stable purification resin that is stable most commonly used buffers and denaturants. Heparin is a linear glycosaminoglycan composed of equimola ...
... of proteins. The resin consists of 6% cross-linked agarose covalently coupled to heparin through amide bonds. The coupling chemistry used generates a highly stable purification resin that is stable most commonly used buffers and denaturants. Heparin is a linear glycosaminoglycan composed of equimola ...
Structural domains of P450-containing monooxygenase
... [email protected] All known P450-containing monooxygenase systems share common structural and functional domain architecture. Apart from P450 itself, these systems can comprise several fundamentally different protein components or domains, all of which are shared by other multicomponent/multido ...
... [email protected] All known P450-containing monooxygenase systems share common structural and functional domain architecture. Apart from P450 itself, these systems can comprise several fundamentally different protein components or domains, all of which are shared by other multicomponent/multido ...
Prokaryotic Cells, Eukaryotic cells and HIV: Structures, Transcription
... RNA will fold onto itself due to self-complementarity. This will create a hairpin structure that will help the newly synthesized RNA ‘push’ off RNA polymerase from the RNA/DNA hybrid. This is not always how it happens, but the example for you to remember. Eukaryotic transcription: Promoters – You ca ...
... RNA will fold onto itself due to self-complementarity. This will create a hairpin structure that will help the newly synthesized RNA ‘push’ off RNA polymerase from the RNA/DNA hybrid. This is not always how it happens, but the example for you to remember. Eukaryotic transcription: Promoters – You ca ...
BRIEF REVISION OF CHEMISTRY TERMS Atom The building block
... Proteins are macromolecules that consist of long, unbranched chains of amino acids. These chains may contain about 20 up to hundreds of amino acids. An example of the size of proteins is the red pigment in red blood cells called haemoglobin with the chemical formula – C3032 H4816 O872 N780 S8 Fe4 Ea ...
... Proteins are macromolecules that consist of long, unbranched chains of amino acids. These chains may contain about 20 up to hundreds of amino acids. An example of the size of proteins is the red pigment in red blood cells called haemoglobin with the chemical formula – C3032 H4816 O872 N780 S8 Fe4 Ea ...
Intrinsically disordered proteins

An intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure. IDPs cover a spectrum of states from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coils, (pre-)molten globules, and large multi-domain proteins connected by flexible linkers. They constitute one of the main types of protein (alongside globular, fibrous and membrane proteins).The discovery of IDPs has challenged the traditional protein structure paradigm, that protein function depends on a fixed three-dimensional structure. This dogma has been challenged over the last decades by increasing evidence from various branches of structural biology, suggesting that protein dynamics may be highly relevant for such systems. Despite their lack of stable structure, IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins. In some cases, IDPs can adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after binding to other macromolecules.