Data Sheet (current)
... Low Power CMOS Dual Operational Amplifier General Description The LPC662 CMOS Dual operational amplifier is ideal for operation from a single supply. It features a wide range of operating voltage from +5V to +15V, rail-to-rail output swing in addition to an input common-mode range that includes grou ...
... Low Power CMOS Dual Operational Amplifier General Description The LPC662 CMOS Dual operational amplifier is ideal for operation from a single supply. It features a wide range of operating voltage from +5V to +15V, rail-to-rail output swing in addition to an input common-mode range that includes grou ...
MAX8510/MAX8511/MAX8512 Ultra-Low-Noise, High PSRR, Low-Dropout, 120mA Linear Regulators General Description
... better noise rejection and line-transient response. Reduce output noise and improve load-transient response, stability, and power-supply rejection by using large output capacitors. Note that some ceramic dielectrics exhibit large capacitance and ESR variation with temperature. With dielectrics such ...
... better noise rejection and line-transient response. Reduce output noise and improve load-transient response, stability, and power-supply rejection by using large output capacitors. Note that some ceramic dielectrics exhibit large capacitance and ESR variation with temperature. With dielectrics such ...
FET
... Usually the semiconductor of choice is silicon, but some chip manufacturers, most notably IBM and Intel, recently started using a chemical compound of silicon and germanium (SiGe) in MOSFET. many semiconductors with better electrical properties than silicon, such as gallium arsenide, do not form goo ...
... Usually the semiconductor of choice is silicon, but some chip manufacturers, most notably IBM and Intel, recently started using a chemical compound of silicon and germanium (SiGe) in MOSFET. many semiconductors with better electrical properties than silicon, such as gallium arsenide, do not form goo ...
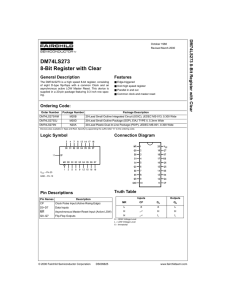
DM74LS273 8-Bit Register with Clear
... Functional Description The DM74LS273 is an 8-bit parallel register with a common Clock and common Master Reset. When the MR input is LOW, the Q outputs are LOW, independent of the other inputs. Information meeting the setup and hold time requirements of the D inputs is transferred to the Q outputs o ...
... Functional Description The DM74LS273 is an 8-bit parallel register with a common Clock and common Master Reset. When the MR input is LOW, the Q outputs are LOW, independent of the other inputs. Information meeting the setup and hold time requirements of the D inputs is transferred to the Q outputs o ...
Sevcon Controller Diagnostic Chart - Electric
... a) Low resistance or short circuit between M1 and B- producing a low voltage across the Mosfets, or b) Contactor coil short circuit. Contactor welded or wiring fault giving a high voltage between M1 and B- before closing the contactor No high voltage (approximately equal to battery voltage) between ...
... a) Low resistance or short circuit between M1 and B- producing a low voltage across the Mosfets, or b) Contactor coil short circuit. Contactor welded or wiring fault giving a high voltage between M1 and B- before closing the contactor No high voltage (approximately equal to battery voltage) between ...
8. Source transformation & Resistor combinations
... • An ideal current source has the voltage necessary to provide its rated current. • An ideal voltage source supplies the current necessary to provide its rated voltage. • A real voltage source cannot supply arbitrarily large amounts of current. • A real current source cannot have an arbitrarily larg ...
... • An ideal current source has the voltage necessary to provide its rated current. • An ideal voltage source supplies the current necessary to provide its rated voltage. • A real voltage source cannot supply arbitrarily large amounts of current. • A real current source cannot have an arbitrarily larg ...
Alternating Current - Happy Physics With Mineesh Gulati
... current. The voltage across an inductor L leads the current by 90°(Φ=+90°), while the voltage across capacitor C lags the current by 90°(Φ=-90°) . The voltage amplitude across each type of device is proportional to the current amplitude I. An inductor has inductive reactance XL=ωL and a capacitor ha ...
... current. The voltage across an inductor L leads the current by 90°(Φ=+90°), while the voltage across capacitor C lags the current by 90°(Φ=-90°) . The voltage amplitude across each type of device is proportional to the current amplitude I. An inductor has inductive reactance XL=ωL and a capacitor ha ...
Note-A-Rific: Voltmeters and Ammeters
... the two points. If the voltmeter was wired in series, it would have a voltage drop of its own, but would not be able to measure the potential difference between two points in the circuit. Since the voltmeter is in parallel, we need to minimize how much of the current will branch off into it. o For t ...
... the two points. If the voltmeter was wired in series, it would have a voltage drop of its own, but would not be able to measure the potential difference between two points in the circuit. Since the voltmeter is in parallel, we need to minimize how much of the current will branch off into it. o For t ...
Section G8: Non-Inverting Amplifier
... Section G8: Non-Inverting Amplifier The schematic for a single input non-inverting amplifier is shown below and to the left, with the equivalent circuit given below and to the right. Again, note that we are neglecting any input offset voltage and using the bias balance constraint (R1≈RA||RF) discuss ...
... Section G8: Non-Inverting Amplifier The schematic for a single input non-inverting amplifier is shown below and to the left, with the equivalent circuit given below and to the right. Again, note that we are neglecting any input offset voltage and using the bias balance constraint (R1≈RA||RF) discuss ...
300 - B. 10 3 i C. 12 5 i D. 3 10 i - + ? + - - - - + - - - A. 7 14i + - +
... B. 7 3i C. 5 3i D. 3 7i 9. What is the product of 5 2i and i ? A. 5 2i B. 7 C. 2 5i D. 2 5i ...
... B. 7 3i C. 5 3i D. 3 7i 9. What is the product of 5 2i and i ? A. 5 2i B. 7 C. 2 5i D. 2 5i ...
Resistor Inductor Capacitor Series Circuits
... icon below channel A. Click on the rescale icon and a graph of the resistor voltage versus time is shown. Click on the Input selection box at the lower left of the graph window (second row, second icon), click on Analog B and click on Voltage to display the inductor voltage graph. Repeat this to se ...
... icon below channel A. Click on the rescale icon and a graph of the resistor voltage versus time is shown. Click on the Input selection box at the lower left of the graph window (second row, second icon), click on Analog B and click on Voltage to display the inductor voltage graph. Repeat this to se ...
Ans: Analogue Electronics
... Ans: Fixed Bias Circuit: Fixed bias circuits get their bias voltages from independently designed reference voltage sources (or even something as simple as a voltage divider). Often is the case that the bias may be left for the end-user to give some control over the operation point of the circuit. Se ...
... Ans: Fixed Bias Circuit: Fixed bias circuits get their bias voltages from independently designed reference voltage sources (or even something as simple as a voltage divider). Often is the case that the bias may be left for the end-user to give some control over the operation point of the circuit. Se ...
Chapter 11 - UNT College of Engineering
... • Low-voltage CMOS families, such as 74LVX and 74LCX, can interface directly with TTL outputs using 3.0-V to 3.3-V power supplies. • TTL outputs using a 5.0-V power supply must be buffered to translate the TTL level down to an appropriate value. ...
... • Low-voltage CMOS families, such as 74LVX and 74LCX, can interface directly with TTL outputs using 3.0-V to 3.3-V power supplies. • TTL outputs using a 5.0-V power supply must be buffered to translate the TTL level down to an appropriate value. ...
Node-Voltage Analysis
... RECALL: Types of connections Resistors connected in series… When JUST two elements connect at a SINGLE node, they are said to be in series and series-connected elements carry the SAME CURRENT (why? KCL) ...
... RECALL: Types of connections Resistors connected in series… When JUST two elements connect at a SINGLE node, they are said to be in series and series-connected elements carry the SAME CURRENT (why? KCL) ...
lecture4
... of the circuit cannot tell whether there are separate resistors in series (or parallel) or just one equivalent resistor. All voltages and currents outside the group are the same whether resistors are separate or combined. Thus, when you want to find currents and voltages outside the group of resisto ...
... of the circuit cannot tell whether there are separate resistors in series (or parallel) or just one equivalent resistor. All voltages and currents outside the group are the same whether resistors are separate or combined. Thus, when you want to find currents and voltages outside the group of resisto ...