Separation of the hydrogen atom Schrödinger equation
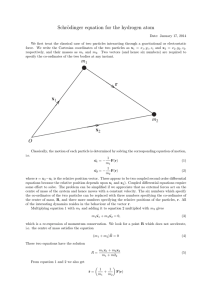
... is called the reduced mass. This way of writing the equation of motion makes explicit the fact that the motion of this two body system is mathematically equivalent to the motion of a single particle of mass µ under the action of the force F. That is, the problem reduces to one whose mathematical ana ...
... is called the reduced mass. This way of writing the equation of motion makes explicit the fact that the motion of this two body system is mathematically equivalent to the motion of a single particle of mass µ under the action of the force F. That is, the problem reduces to one whose mathematical ana ...