Precision Labs Print - Lecture v1.0
... 1. Which is not a noise source used in intrinsic noise calculations. a.! Op Amp voltage noise sources b.! Op amp current noise sources c.! Inductor noise sources d.! Resistor noise sources 2. (T/F) Noise gain is the same as signal gain. a.! True b.! False 3. Where is the noise voltage source located ...
... 1. Which is not a noise source used in intrinsic noise calculations. a.! Op Amp voltage noise sources b.! Op amp current noise sources c.! Inductor noise sources d.! Resistor noise sources 2. (T/F) Noise gain is the same as signal gain. a.! True b.! False 3. Where is the noise voltage source located ...
EE20 RC_RJIT Conference
... widely applicable in large number of applications. This paper proposed a new multilevel inverter structure with low output harmonics. In this paper the number of switching device is less as compare to the conventional multilevel inverter. It consists of an H-bridge inverter which produces multilevel ...
... widely applicable in large number of applications. This paper proposed a new multilevel inverter structure with low output harmonics. In this paper the number of switching device is less as compare to the conventional multilevel inverter. It consists of an H-bridge inverter which produces multilevel ...
Design of CMOS Inverter Using Different Aspect Ratios
... Student, B. Tech. 4th Year, Shanti Institute Of Technology Kurali, Meerut ...
... Student, B. Tech. 4th Year, Shanti Institute Of Technology Kurali, Meerut ...
Chapter 1 Power Electronic Devices (Part I)
... Reverse recovery time and charge specified. trr is usually less than 1μs, for many less than 100 ns —— ultra-fast recovery diode. ...
... Reverse recovery time and charge specified. trr is usually less than 1μs, for many less than 100 ns —— ultra-fast recovery diode. ...
access to he diploma approved units: engineering
... 4.3. Deduce constant current and constant voltage equivalent circuits for practical sources and convert them from on type of equivalent circuit to the other. 4.4. Solve problems using Theremin’s and Norton’s Theorems. 4.5. Apply the maximum power transfer theorem for resistive loads. 4.6. Derive the ...
... 4.3. Deduce constant current and constant voltage equivalent circuits for practical sources and convert them from on type of equivalent circuit to the other. 4.4. Solve problems using Theremin’s and Norton’s Theorems. 4.5. Apply the maximum power transfer theorem for resistive loads. 4.6. Derive the ...
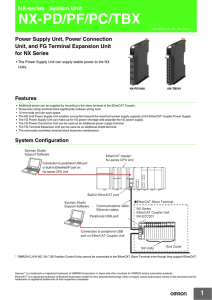
NX-PD/PF/PC/TBX
... The terminal number indications are the same regardless of the number of terminals on the terminal block. ...
... The terminal number indications are the same regardless of the number of terminals on the terminal block. ...
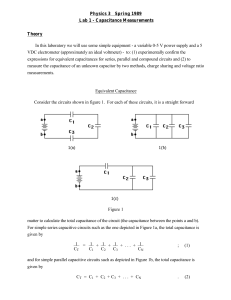
Physics 3 Spring 1989 Lab 1 - Capacitance Measurements Theory
... and for simple parallel capacitive circuits such as depicted in Figure 1b, the total capacitance is given by CT = C1 + C2 + C3 + . . . + CN ...
... and for simple parallel capacitive circuits such as depicted in Figure 1b, the total capacitance is given by CT = C1 + C2 + C3 + . . . + CN ...
PMP1563 ATCA Board Power Reference Design Developer's Guide
... The 4mΩ sense resistor sets the TPS2393A overcurrent level at a nominal 10A. Over temperature and tolerance, the overcurrent level can range from 8.1A to 11.9A. This operating range ensures that the board can get a full 200W without going into current limit mode even if the input voltage magnitude i ...
... The 4mΩ sense resistor sets the TPS2393A overcurrent level at a nominal 10A. Over temperature and tolerance, the overcurrent level can range from 8.1A to 11.9A. This operating range ensures that the board can get a full 200W without going into current limit mode even if the input voltage magnitude i ...