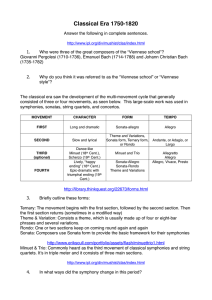
Identify, the choice that best completes the statement
... 96. Brahms was considered by some 19th century musicians to be out of date because he c. often used the same forms as composers of the Classical period 97. How many symphonies did Brahms compose? c. four 98. Brahms's German Requiem is so titled because b. it uses phrases from the Bible that are in G ...
... 96. Brahms was considered by some 19th century musicians to be out of date because he c. often used the same forms as composers of the Classical period 97. How many symphonies did Brahms compose? c. four 98. Brahms's German Requiem is so titled because b. it uses phrases from the Bible that are in G ...
Program Notes
... Skryabin, Schoenberg and Stravinsky. The last three had developed new scales (different combinations of half, whole and augmented intervals) on which their harmony was constructed: Skryabin devised several different modes; Schoenberg worked with the entire chromatic scale – as did Liszt in some of h ...
... Skryabin, Schoenberg and Stravinsky. The last three had developed new scales (different combinations of half, whole and augmented intervals) on which their harmony was constructed: Skryabin devised several different modes; Schoenberg worked with the entire chromatic scale – as did Liszt in some of h ...
Here - Abu Dhabi Festival
... Franz Liszt’s life and work virtually defined the Romantic era. He pushed the bounds of what pianos – and pianists – could do. As music director for the city of Weimar, Germany, he created the genre of the symphonic poem and championed the radical music of Wagner – who became his son-in-law – and Be ...
... Franz Liszt’s life and work virtually defined the Romantic era. He pushed the bounds of what pianos – and pianists – could do. As music director for the city of Weimar, Germany, he created the genre of the symphonic poem and championed the radical music of Wagner – who became his son-in-law – and Be ...
Music Strand 01: Western Classical Tradition
... Music for Voices Works for Choir Choral works include the mass, oratorio, cantata and anthem. These pieces are often set to religious texts and performed in a church or cathedral. Large scale choral works often include a number of choruses for the whole choir and arias for the soloist. ...
... Music for Voices Works for Choir Choral works include the mass, oratorio, cantata and anthem. These pieces are often set to religious texts and performed in a church or cathedral. Large scale choral works often include a number of choruses for the whole choir and arias for the soloist. ...
Notes on Rondo Form
... A sections are generally closed (firmly), and have a clear melodic profile and generally unambiguous formal organization. They provide the primary material for the movement. A sections generally return with no change or only minimal change. If they originally had repeats, the repeats may be omitted ...
... A sections are generally closed (firmly), and have a clear melodic profile and generally unambiguous formal organization. They provide the primary material for the movement. A sections generally return with no change or only minimal change. If they originally had repeats, the repeats may be omitted ...
Music in the Classical Period
... important visitors, dinner music and chamber music for the Prince’s rooms. As a result he wrote over 100 symphonies, 70 string quartets, 50+ keyboard sonatas, and numerous choral and solo voice pieces. Last 12 symphonies written in London. ...
... important visitors, dinner music and chamber music for the Prince’s rooms. As a result he wrote over 100 symphonies, 70 string quartets, 50+ keyboard sonatas, and numerous choral and solo voice pieces. Last 12 symphonies written in London. ...
Piano Sonata In The Classical Era Essay, Research Paper The
... The Piano Sonata in the Classical Period The piano sonata was an important part of music during the Classical period . It characterizes the Classical era’s new trend of musical form. Originally, the sonata was made up of several dance movements, but then in the Classical era, it changed to a fast-sl ...
... The Piano Sonata in the Classical Period The piano sonata was an important part of music during the Classical period . It characterizes the Classical era’s new trend of musical form. Originally, the sonata was made up of several dance movements, but then in the Classical era, it changed to a fast-sl ...
“Americanism” In Music: Piano Sonatas From 1939–1949
... Traditional elements are found in the forms, motivic connections, and counterpoint and fugue American influences found largely in the finale: jazz syncopations, and “blues” ...
... Traditional elements are found in the forms, motivic connections, and counterpoint and fugue American influences found largely in the finale: jazz syncopations, and “blues” ...
Classical period (music)
... was replaced by the piano (or fortepiano). Early piano music was light in texture, often with Alberti bass accompaniment, but it later became richer, more sonorous and more powerful. Importance was given to instrumental music — the main kinds were sonata, trio, string quartet, symphony, concerto and ...
... was replaced by the piano (or fortepiano). Early piano music was light in texture, often with Alberti bass accompaniment, but it later became richer, more sonorous and more powerful. Importance was given to instrumental music — the main kinds were sonata, trio, string quartet, symphony, concerto and ...
Jack Liebeck – violin Kotaro Fukuma – piano
... destroyed it and several others before finally producing the intensely lyrical G major sonata in 1879, which, like all his published violin sonatas, was crafted for his friend, the great virtuoso Joseph Joachim. The same lyricism pervades the second sonata in A major composed in 1886. However, the D ...
... destroyed it and several others before finally producing the intensely lyrical G major sonata in 1879, which, like all his published violin sonatas, was crafted for his friend, the great virtuoso Joseph Joachim. The same lyricism pervades the second sonata in A major composed in 1886. However, the D ...
Camille Saint-Saëns - Rachel M. Kauffman
... The clarinet seems to have fluidity throughout the movement, somber and reflective. The piano connects with the clarinet until the B-section where SaintSaëns begins moving to various keys; the clarinet and piano do not agree on same key at certain points, tension, until Saint-Saëns returns to origin ...
... The clarinet seems to have fluidity throughout the movement, somber and reflective. The piano connects with the clarinet until the B-section where SaintSaëns begins moving to various keys; the clarinet and piano do not agree on same key at certain points, tension, until Saint-Saëns returns to origin ...
Classical Period
... Ludwig van Beethoven, who began as a Classical composer, broke the mold with his revolutionary “Eroica” in 1804 and dominated the musical scene until 1827. European music would never be the same again. Precise forms became less important than the expression of powerful feelings, and Romantic compose ...
... Ludwig van Beethoven, who began as a Classical composer, broke the mold with his revolutionary “Eroica” in 1804 and dominated the musical scene until 1827. European music would never be the same again. Precise forms became less important than the expression of powerful feelings, and Romantic compose ...
Download Article Abstract
... Teaching eighteenth-century music effectively, particularly at a conservatory where the students are quite familiar with the music of Bach, Handel, Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven, can prove challenging when you introduce less familiar material—the early works of Haydn and Mozart, for example, or the w ...
... Teaching eighteenth-century music effectively, particularly at a conservatory where the students are quite familiar with the music of Bach, Handel, Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven, can prove challenging when you introduce less familiar material—the early works of Haydn and Mozart, for example, or the w ...
Major Genres and other Terms Aleatoric Music: a 20th century
... Sonata Form: an esthetic as much as a form, sonata form is made up of an exposition (often repeated) followed by a development section and concluding with a recapitulation. The exposition sets a mood and tonal center (usually with a specific theme or melody) and a departure from that tonal center (o ...
... Sonata Form: an esthetic as much as a form, sonata form is made up of an exposition (often repeated) followed by a development section and concluding with a recapitulation. The exposition sets a mood and tonal center (usually with a specific theme or melody) and a departure from that tonal center (o ...
Introduction - guentersberg.de
... Lively, quick sections alternate with calm passages over a constant meter. As a rule, new themes are first introduced by each player individually before a synthesis is arrived at. The compass of the six-string bass viol is exploited quite well by the two melody parts. Chords are dispensed with. Our ...
... Lively, quick sections alternate with calm passages over a constant meter. As a rule, new themes are first introduced by each player individually before a synthesis is arrived at. The compass of the six-string bass viol is exploited quite well by the two melody parts. Chords are dispensed with. Our ...
Chapter 5: The Classical Era 1750 - 1825
... Works often showed vibrancy; he would ask string players to mistune one of their strings to always play the wrong note His last 12 symphonies, known collectively as the London symphonies, are considered perfect expressions of the Classical style He died during the French occupation of Vienna in 1809 ...
... Works often showed vibrancy; he would ask string players to mistune one of their strings to always play the wrong note His last 12 symphonies, known collectively as the London symphonies, are considered perfect expressions of the Classical style He died during the French occupation of Vienna in 1809 ...
Program Notes
... Classical sonata allegro form, pairing a three-chord tolling motive with a related but more melodic second theme. The second movement Vivace serves as a scherzo with a very short contrasting middle section that could be interpreted as a trio. The final movement, based on another bell-tolling motive ...
... Classical sonata allegro form, pairing a three-chord tolling motive with a related but more melodic second theme. The second movement Vivace serves as a scherzo with a very short contrasting middle section that could be interpreted as a trio. The final movement, based on another bell-tolling motive ...
programme_notes_fina..
... Intermezzo is movement or section that within larger works. The intermezzi for piano solo are usually lyrical and melodic in character. No.2 Intermezzo in A major builds in simple three-part song form (ABA). The A section consists of a graceful melody showing the composer’s introspective depression. ...
... Intermezzo is movement or section that within larger works. The intermezzi for piano solo are usually lyrical and melodic in character. No.2 Intermezzo in A major builds in simple three-part song form (ABA). The A section consists of a graceful melody showing the composer’s introspective depression. ...
worksheet - Boise State University
... Bach Page: 1. What instrument do you hear playing Bach’s “Toccata and Fugue in D minor”? ...
... Bach Page: 1. What instrument do you hear playing Bach’s “Toccata and Fugue in D minor”? ...
The Classical Era - CDNIS Community Sites
... Minuet & Trio: Commonly heard as the third movement of classical symphonies and string quartets. It’s in triple meter and it consists of three main sections. http://www.ipl.org/div/mushist/clas/index.html ...
... Minuet & Trio: Commonly heard as the third movement of classical symphonies and string quartets. It’s in triple meter and it consists of three main sections. http://www.ipl.org/div/mushist/clas/index.html ...
Week 12 Notes p.1 Ludwig van Beethoven (1770
... Fourth Movement; sonata-allegro, brings back first movement material, making the 5th an early example of cyclical form. ...
... Fourth Movement; sonata-allegro, brings back first movement material, making the 5th an early example of cyclical form. ...
Unit 4: Classical music! - Music Second Grade
... The Classical symphony: the word symphony means "sounding together" and it applies to the full orchestra all playing at the same time. Symphonies had three movements (fast-slowfast), but some added an extra, dance-like movement before the last one. Franz Joseph Haydn wrote 104 symphonies during his ...
... The Classical symphony: the word symphony means "sounding together" and it applies to the full orchestra all playing at the same time. Symphonies had three movements (fast-slowfast), but some added an extra, dance-like movement before the last one. Franz Joseph Haydn wrote 104 symphonies during his ...
Special Special tthank hanks tos to Siebe Siebe Henstra and Wilbert
... elegance surely would have appealed to the public. His brother Wilhelm Friedemann, however, was less successful in his musical publications. The sonata in D major was printed in 1745 while Friedemann lived in Dresden, but didn't receive much attention. Probably the piece's scale, contrapuntal outloo ...
... elegance surely would have appealed to the public. His brother Wilhelm Friedemann, however, was less successful in his musical publications. The sonata in D major was printed in 1745 while Friedemann lived in Dresden, but didn't receive much attention. Probably the piece's scale, contrapuntal outloo ...
senior recital program.
... Achille-Claude Debussy (22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. Along with Maurice Ravel, he was one of the most prominent figures associated with Impressionist music, though he himself intensely disliked the term when applied to his compositions. In France, he was made Chevalier of t ...
... Achille-Claude Debussy (22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. Along with Maurice Ravel, he was one of the most prominent figures associated with Impressionist music, though he himself intensely disliked the term when applied to his compositions. In France, he was made Chevalier of t ...