Spinglass
... The scalability of distributed protocols and systems is a major determinant of success in demanding systems. For example, consider the recent field-test of the Navy’s Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC). During the period Sept. 13-27, 2000, this system (which offers an over-the-horizon cooperati ...
... The scalability of distributed protocols and systems is a major determinant of success in demanding systems. For example, consider the recent field-test of the Navy’s Cooperative Engagement Capability (CEC). During the period Sept. 13-27, 2000, this system (which offers an over-the-horizon cooperati ...
Slides
... What other statistics have pan-private algorithms? Pan-private streaming algorithms for: • Stream density / number of distinct elements • t-cropped mean: mean, over users, of min(t,#appearances) • Fraction of users appearing k times exactly • Fraction of heavy-hitters, users appearing at ...
... What other statistics have pan-private algorithms? Pan-private streaming algorithms for: • Stream density / number of distinct elements • t-cropped mean: mean, over users, of min(t,#appearances) • Fraction of users appearing k times exactly • Fraction of heavy-hitters, users appearing at ...
Towards Using Grid Services for Mining Fuzzy Association Rules
... process in a Grid network we shall consider that: • the database DB is stored on K-grid node NodeA. ...
... process in a Grid network we shall consider that: • the database DB is stored on K-grid node NodeA. ...
Quantile Regression for Large-scale Applications
... variable and observed covariates, and it is more appropriate in certain non-Gaussian settings. For these reasons, quantile regression has found applications in many areas (Buchinsky, 1994; Koenker & Hallock, 2001; Buhai, 2005). As with `1 regression, the quantile regression problem can be formulated ...
... variable and observed covariates, and it is more appropriate in certain non-Gaussian settings. For these reasons, quantile regression has found applications in many areas (Buchinsky, 1994; Koenker & Hallock, 2001; Buhai, 2005). As with `1 regression, the quantile regression problem can be formulated ...
Scientific Discovery Learning with Computer Simulations of
... unsupported simulation based discovery learning to some form of expository teaching. These studies show that advantages of simulation based learning are not always met, and suggest that one of the reasons for this is that learners have problems with discovery learning. This conclusion brings us to t ...
... unsupported simulation based discovery learning to some form of expository teaching. These studies show that advantages of simulation based learning are not always met, and suggest that one of the reasons for this is that learners have problems with discovery learning. This conclusion brings us to t ...
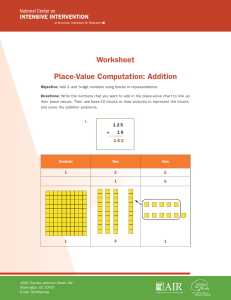
Worksheet Place-Value Computation: Addition
... Worksheet Place-Value Computation: Division Objective: Divide 3-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers, using manipulatives to represent the problem. Directions: 1. Write the problem in the grid with the dividend inside the box and the divisor outside. 2. Represent the dividend with base 10 blocks in the ...
... Worksheet Place-Value Computation: Division Objective: Divide 3-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers, using manipulatives to represent the problem. Directions: 1. Write the problem in the grid with the dividend inside the box and the divisor outside. 2. Represent the dividend with base 10 blocks in the ...
Theoretical computer science

Theoretical computer science is a division or subset of general computer science and mathematics that focuses on more abstract or mathematical aspects of computing and includes the theory of computation.It is not easy to circumscribe the theory areas precisely and the ACM's Special Interest Group on Algorithms and Computation Theory (SIGACT) describes its mission as the promotion of theoretical computer science and notes:Template:""To this list, the ACM's journal Transactions on Computation Theory adds coding theory, computational learning theory and theoretical computer science aspects of areas such as databases, information retrieval, economic models and networks. Despite this broad scope, the ""theory people"" in computer science self-identify as different from the ""applied people."" Some characterize themselves as doing the ""(more fundamental) 'science(s)' underlying the field of computing."" Other ""theory-applied people"" suggest that it is impossible to separate theory and application. This means that the so-called ""theory people"" regularly use experimental science(s) done in less-theoretical areas such as software system research. It also means that there is more cooperation than mutually exclusive competition between theory and application.