DIOPTRICS OF THE FACET LENSES OF MALE BLOWFLIES
... path profile as a function of the distance from the axis. From these two measurements it is possible to calculate the optical quality of the fly facet lens quite straightforwardly. We have selected for this analysis two blowfly species of which the males are known to have a wide variation in facet s ...
... path profile as a function of the distance from the axis. From these two measurements it is possible to calculate the optical quality of the fly facet lens quite straightforwardly. We have selected for this analysis two blowfly species of which the males are known to have a wide variation in facet s ...
Experiment 24 - School of Physics
... Figure 24-1 shows the layout of the Michelson interferometer used in this experiment. The mirrors, beamsplitter and compensator plate are mounted on a marble slab for stability. The apparatus is housed in a clear plastic box to exclude drafts and to keep the optics clean. Light from the source is sp ...
... Figure 24-1 shows the layout of the Michelson interferometer used in this experiment. The mirrors, beamsplitter and compensator plate are mounted on a marble slab for stability. The apparatus is housed in a clear plastic box to exclude drafts and to keep the optics clean. Light from the source is sp ...
AS Waves and Optics
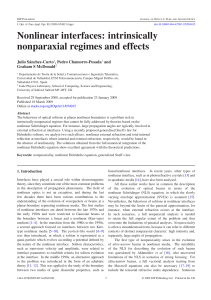
... (a) In an experiment, a narrow beam of white light from a filament lamp is directed at normal incidence at a diffraction grating. Complete the diagram in the figure below to show the light beams transmitted by the grating, showing the zero-order beam and the ...
... (a) In an experiment, a narrow beam of white light from a filament lamp is directed at normal incidence at a diffraction grating. Complete the diagram in the figure below to show the light beams transmitted by the grating, showing the zero-order beam and the ...
Optical Detection Computer Screen Photo-assisted Techniques Ellipsometry Jimmy W.P. Bakker
... e . If the displacement r oscillations in the electric field E as described by equation (2.6), damping of ...
... e . If the displacement r oscillations in the electric field E as described by equation (2.6), damping of ...
EM theory and its application to microwave remote sensing
... giving rise to a non-zero phase relationship between the E and H field components. While a medium’s loss may be due to its conductivity, or the imaginary components of permittivity or permeability, in most microwave remote sensing applications the magnetization loss () is negligible. Exceptions in ...
... giving rise to a non-zero phase relationship between the E and H field components. While a medium’s loss may be due to its conductivity, or the imaginary components of permittivity or permeability, in most microwave remote sensing applications the magnetization loss () is negligible. Exceptions in ...
Principles and Clinical Applications of Ray-Tracing
... of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrometers are currently the most important tools for estimating optical conditions so that a more comp ...
... of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrometers are currently the most important tools for estimating optical conditions so that a more comp ...
Nonlinear interfaces: intrinsically nonparaxial regimes and effects
... in quadratic media [14], have also been analysed. All these earlier works have in common the description of the evolution of optical beams in terms of the nonlinear Schrödinger (NLS) equation, in which the slowly varying envelope approximation (SVEA) is assumed [15]. Nevertheless, the behaviour of ...
... in quadratic media [14], have also been analysed. All these earlier works have in common the description of the evolution of optical beams in terms of the nonlinear Schrödinger (NLS) equation, in which the slowly varying envelope approximation (SVEA) is assumed [15]. Nevertheless, the behaviour of ...
Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence
... roughly 100 beads per field (with Invitrogen FluoSpheres diluted ∼1:10,000). When viewing the sample through the oculars with the field near the critical angle (but prior to entering TIR) the emission from the free beads may appear as an inclined beam, with more beads visible on the side of the samp ...
... roughly 100 beads per field (with Invitrogen FluoSpheres diluted ∼1:10,000). When viewing the sample through the oculars with the field near the critical angle (but prior to entering TIR) the emission from the free beads may appear as an inclined beam, with more beads visible on the side of the samp ...
Phase Mismatch–Free Nonlinear Propagation in Optical Zero
... the refractive index [(B) and (C)] as it propagates. All of these sources add up coherently to generate the net nonlinear emission. In a zero-index medium (C), the radiations from all nonlinear sources acquire no phase as they propagate, guaranteeing a constructive interference and an increase of th ...
... the refractive index [(B) and (C)] as it propagates. All of these sources add up coherently to generate the net nonlinear emission. In a zero-index medium (C), the radiations from all nonlinear sources acquire no phase as they propagate, guaranteeing a constructive interference and an increase of th ...
Experimental observation of speckle instability in Kerr random
... within the nonlinear material. The pump beam is itself scattered by this grating and nonlinearity-driven energy transfer is achieved from the pump to the probe when ∆f = fp − fm 6= 0. This transfer of energy via the Kerr nonlinearity has been interpreted as an amplification process, where the gain r ...
... within the nonlinear material. The pump beam is itself scattered by this grating and nonlinearity-driven energy transfer is achieved from the pump to the probe when ∆f = fp − fm 6= 0. This transfer of energy via the Kerr nonlinearity has been interpreted as an amplification process, where the gain r ...
Chapter 13
... observers so quickly that accurate measurements of the time taken could not be made. 2. The orientation of the mirrors in a Michelson-type experiment has to be very precise in order for the light to be reflected directly toward the observation point. If the rotating mirror is not turning such that t ...
... observers so quickly that accurate measurements of the time taken could not be made. 2. The orientation of the mirrors in a Michelson-type experiment has to be very precise in order for the light to be reflected directly toward the observation point. If the rotating mirror is not turning such that t ...
Quanta and Waves Q` and solutions
... state where this occurs. Calculate the maximum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. State the minimum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. Calculate the potential and kinetic energy of the object when its ...
... state where this occurs. Calculate the maximum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. State the minimum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. Calculate the potential and kinetic energy of the object when its ...
PhysicsQuantaandWaves_tcm4-726389
... state where this occurs. Calculate the maximum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. State the minimum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. Calculate the potential and kinetic energy of the object when its ...
... state where this occurs. Calculate the maximum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. State the minimum value of the potential energy of the object and state where this occurs. Calculate the potential and kinetic energy of the object when its ...
Light scattering properties for spherical and cylindrical particles: a
... represent the radius of the particle and the wavelength in the surrounding medium, respectively, and by m, the ratio of the refractive indices of the particle and surrounding medium. Absorption by the spherical and cylindrical particles can be considered as well in Mie theory. However, it is not tak ...
... represent the radius of the particle and the wavelength in the surrounding medium, respectively, and by m, the ratio of the refractive indices of the particle and surrounding medium. Absorption by the spherical and cylindrical particles can be considered as well in Mie theory. However, it is not tak ...
Notes on optical fibres and fibre bundles
... given length, reach the core material boundary and pass to another medium (glass, air, etc.). Depending on the incident angle, some of the energy will be refracted outward (leaky modes) and some will reflect back into the core material (guided modes). If they are much thicker than ∼1 mm, the fibres ...
... given length, reach the core material boundary and pass to another medium (glass, air, etc.). Depending on the incident angle, some of the energy will be refracted outward (leaky modes) and some will reflect back into the core material (guided modes). If they are much thicker than ∼1 mm, the fibres ...
Metamaterials: a new frontier of science and technology Chem. Soc. Rev 40
... array of copper SRRs and wires was used to measure the refraction of a beam at the exit interface (Fig. 4(a)). Negative refraction was indeed observed in a manner consistent with Snell’s law. Although there were fierce debates on the validity of the experimental results as well as the fundamental pro ...
... array of copper SRRs and wires was used to measure the refraction of a beam at the exit interface (Fig. 4(a)). Negative refraction was indeed observed in a manner consistent with Snell’s law. Although there were fierce debates on the validity of the experimental results as well as the fundamental pro ...
Reflectivity of Nonlinear Apodized Chirped Fiber Bragg Grating Under Water
... crest in the index modulation is in phase with the next one, we have maximum mode coupling or reflection. Then, the Bragg condition is fulfilled. By modulating the quasi-periodic index perturbation in amplitude and (or) phase, we may obtain different optical filter characteristics. The formation of ...
... crest in the index modulation is in phase with the next one, we have maximum mode coupling or reflection. Then, the Bragg condition is fulfilled. By modulating the quasi-periodic index perturbation in amplitude and (or) phase, we may obtain different optical filter characteristics. The formation of ...
Wave Refraction in Negative-Index Media: Always Positive
... we call them NIM (negative-index media) rather than left-handed media (while PIM 苷 positive index media). The electromagnetic properties of NIMs, which do not occur naturally, take us into new territory, where even familiar concepts must be handled carefully. Most importantly, we point out that at a ...
... we call them NIM (negative-index media) rather than left-handed media (while PIM 苷 positive index media). The electromagnetic properties of NIMs, which do not occur naturally, take us into new territory, where even familiar concepts must be handled carefully. Most importantly, we point out that at a ...
Analysis of Tilted Grating Etalon for DWDM Demultiplexer Sommart Sang-Ngern, Non-member
... Fig.7(f), when increasing the incident angle, the center bragg wavelength is up-shifted. For Fig.7(c) the center bragg wavelength at the wavelength of about 1490 nm but for Fig.7(e) the center bragg wavelength at the wavelength of about 1557 nm. Furthermore, the relation between the center bragg wav ...
... Fig.7(f), when increasing the incident angle, the center bragg wavelength is up-shifted. For Fig.7(c) the center bragg wavelength at the wavelength of about 1490 nm but for Fig.7(e) the center bragg wavelength at the wavelength of about 1557 nm. Furthermore, the relation between the center bragg wav ...
POLARIZATION AND CRYSTAL OPTICS
... The state of polarization of the wave is determined by the shapeof the ellipse (the direction of the major axis and the ellipticity, the ratio of the minor to the major axis of the ellipse). The shapeof the ellipse therefore depends on two parameters-the ratio of the magnitudes ~,,/a, and the phased ...
... The state of polarization of the wave is determined by the shapeof the ellipse (the direction of the major axis and the ellipticity, the ratio of the minor to the major axis of the ellipse). The shapeof the ellipse therefore depends on two parameters-the ratio of the magnitudes ~,,/a, and the phased ...