Name Date ______ Mrs. Geithner-Marron (Bio 200) Period ______
... 19. When a trait is sex-linked it is carried on only which type of chromosome (body or sex)? 20. _____(Males/Females)_____ will have only 1 allele for traits carried on the X chromosome. 21. When making a Punnett Square for ______________ traits (such as hemophilia), you must consider the sex chromo ...
... 19. When a trait is sex-linked it is carried on only which type of chromosome (body or sex)? 20. _____(Males/Females)_____ will have only 1 allele for traits carried on the X chromosome. 21. When making a Punnett Square for ______________ traits (such as hemophilia), you must consider the sex chromo ...
11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution
... – less likely to have some individuals that can adapt to a changing environment due to loss of genetic variation – harmful alleles can become more common due to chance Example of Genetic Drift Cheetahs exhibit much lower levels of variation than other mammals. In most species, related individuals sh ...
... – less likely to have some individuals that can adapt to a changing environment due to loss of genetic variation – harmful alleles can become more common due to chance Example of Genetic Drift Cheetahs exhibit much lower levels of variation than other mammals. In most species, related individuals sh ...
Adaptation and Evolution
... What happens? If we repeat this for many generations, we find that the system reaches equilibrium: a point at which allele frequencies no longer change. This is called Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. In other words, allele frequencies will not change unless something happens. ...
... What happens? If we repeat this for many generations, we find that the system reaches equilibrium: a point at which allele frequencies no longer change. This is called Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. In other words, allele frequencies will not change unless something happens. ...
Evolution and symbiogenesis
... • A given characteristic is variably distributed throughout a population of a single species. • This characteristic is heritable from parent to offspring via reproduction. • Those organisms with the greatest positive aspect of this characteristic survive to reproduce in greater numbers than those or ...
... • A given characteristic is variably distributed throughout a population of a single species. • This characteristic is heritable from parent to offspring via reproduction. • Those organisms with the greatest positive aspect of this characteristic survive to reproduce in greater numbers than those or ...
Molecular Evidence for Evolution
... Chimpanzees and humans turn out to be very similar—if you look at their DNA. When scientists determined the entire genetic code of both humans and chimpanzees, they found that we have over 98% identical DNA. Molecular Evidence ...
... Chimpanzees and humans turn out to be very similar—if you look at their DNA. When scientists determined the entire genetic code of both humans and chimpanzees, they found that we have over 98% identical DNA. Molecular Evidence ...
GenomicVariation_11-22
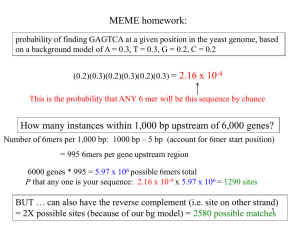
... probability of finding GAGTCA at a given position in the yeast genome, based on a background model of A = 0.3, T = 0.3, G = 0.2, C = 0.2 (0.2)(0.3)(0.2)(0.3)(0.2)(0.3) = 2.16 x 10-4 This is the probability that ANY 6 mer will be this sequence by chance ...
... probability of finding GAGTCA at a given position in the yeast genome, based on a background model of A = 0.3, T = 0.3, G = 0.2, C = 0.2 (0.2)(0.3)(0.2)(0.3)(0.2)(0.3) = 2.16 x 10-4 This is the probability that ANY 6 mer will be this sequence by chance ...
Chp 15, 16, 17 Homework Handouts
... What are the 2 main sources of genetic variation? 1.______________________________________ Explain:______________________________________________________ ...
... What are the 2 main sources of genetic variation? 1.______________________________________ Explain:______________________________________________________ ...
C. Brandon Ogbunu 2_23_17 - The UCLA Institute for Society and
... relationship between genotype and phenotype. The age of genomics has offered much in the way of this disentanglement, having identified thousands of individual gene networks, genes, and single nucleotide polymorphisms that are associated with a range of phenotypes across different species. Along wit ...
... relationship between genotype and phenotype. The age of genomics has offered much in the way of this disentanglement, having identified thousands of individual gene networks, genes, and single nucleotide polymorphisms that are associated with a range of phenotypes across different species. Along wit ...
L567 19 October 2006
... Step 1: Population of interbreeding organisms becomes broken into 2, or more, smaller populations (in space or time). The break may occur by i) the erection of geographical barriers within the population’s range, or ii) by the migration by some individuals across barriers. Step 2: Genetic divergence ...
... Step 1: Population of interbreeding organisms becomes broken into 2, or more, smaller populations (in space or time). The break may occur by i) the erection of geographical barriers within the population’s range, or ii) by the migration by some individuals across barriers. Step 2: Genetic divergence ...
Good Evening Ladies and Gentlemen. Evolution is one of those
... Evolution is one of those funny ideas that many people, while they may have a rough idea about what it is about, often hold incorrect assumptions and beliefs as to what really goes on. It’s our role tonight, to clear up these misconceptions, and guide you through the various theories that make up th ...
... Evolution is one of those funny ideas that many people, while they may have a rough idea about what it is about, often hold incorrect assumptions and beliefs as to what really goes on. It’s our role tonight, to clear up these misconceptions, and guide you through the various theories that make up th ...
AP_SG_Chap15_mech_modified evolution
... selection as a mechanism for evolutionary change. Explain how an essay by the Rev. Thomas Malthus influenced Charles Darwin. Distinguish between artificial selection and natural selection. Explain why an individual organism cannot evolve. Explain how evidence from biogeography, paleontology, ...
... selection as a mechanism for evolutionary change. Explain how an essay by the Rev. Thomas Malthus influenced Charles Darwin. Distinguish between artificial selection and natural selection. Explain why an individual organism cannot evolve. Explain how evidence from biogeography, paleontology, ...
Natural selection works directly on the expression or appearance of
... By the 1800's a number of scientists came to the realization that species could change, and that this change had occurred throughout earth's history. But the fossil record did not indicate how or why one species could evolve into one or a number of other species (adaptive radiation). Jean Baptiste d ...
... By the 1800's a number of scientists came to the realization that species could change, and that this change had occurred throughout earth's history. But the fossil record did not indicate how or why one species could evolve into one or a number of other species (adaptive radiation). Jean Baptiste d ...
are we still evolving?
... All of these findings mesh beautifully with the notion that cultural and demographic shifts sparked our transformation. Our exodus out of Africa, for example, paved the way for one of the most obvious markers of race, skin hue. As scientists widely recognize, paler complexions are a genetic adjustme ...
... All of these findings mesh beautifully with the notion that cultural and demographic shifts sparked our transformation. Our exodus out of Africa, for example, paved the way for one of the most obvious markers of race, skin hue. As scientists widely recognize, paler complexions are a genetic adjustme ...
SBI3U - Evolution - OISE-IS-BIOLOGY-2011-2012
... C3.1. explain the fundamental theory of evolution, using the evolutionary mechanism of natural selection to illustrate the process of biological change over time 2. Environment Stresses and Change C1.2 Evaluate the possible impact of an environmental change on natural selection and on the vulnerabil ...
... C3.1. explain the fundamental theory of evolution, using the evolutionary mechanism of natural selection to illustrate the process of biological change over time 2. Environment Stresses and Change C1.2 Evaluate the possible impact of an environmental change on natural selection and on the vulnerabil ...
Populations evolution
... 11-4: Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 and p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele q = frequency of the recessive allele p2 = % of homozygous dominant individuals q2 = % of homozygous recessive individuals 2pq = % of heterozygous individuals ...
... 11-4: Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 and p + q = 1 p = frequency of the dominant allele q = frequency of the recessive allele p2 = % of homozygous dominant individuals q2 = % of homozygous recessive individuals 2pq = % of heterozygous individuals ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... But for all this to work, the population must remain in equilibrium so… These calculations are not always what we see in nature in fact, populations are rarely in perfect equilibrium as frequencies change from generation to generation Therefore, HW is not maintained evolution is ...
... But for all this to work, the population must remain in equilibrium so… These calculations are not always what we see in nature in fact, populations are rarely in perfect equilibrium as frequencies change from generation to generation Therefore, HW is not maintained evolution is ...
Development and Evolutionary Change Chapter 21
... Evolution and Development • homeobox genes guide segmentation in insects and mammals – Drosophila ems, tll & otd and mammalian homologs guide anterior brain development – mutations in homeobox genes result in misassignment of segment identities many diverse developmental programs are initiated by ...
... Evolution and Development • homeobox genes guide segmentation in insects and mammals – Drosophila ems, tll & otd and mammalian homologs guide anterior brain development – mutations in homeobox genes result in misassignment of segment identities many diverse developmental programs are initiated by ...
evolution_2010
... are selected. The limiting factor acts as a selection pressure. • Adaptation over time: Environments change over time. Heritable characteristics that suit a particular environment will be selected. Populations diverge over time and become adapted to new conditions. • Chance effects: In small populat ...
... are selected. The limiting factor acts as a selection pressure. • Adaptation over time: Environments change over time. Heritable characteristics that suit a particular environment will be selected. Populations diverge over time and become adapted to new conditions. • Chance effects: In small populat ...
Analysis of genetic systems using experimental evolution and whole
... The comparative study of extant genomes has revolutionized biology, shedding light not only on evolution but also on physiology, genetics and medicine. But the utility of comparisons among naturally evolved isolates is lessened by incomplete knowledge of the environment to which the organisms adapte ...
... The comparative study of extant genomes has revolutionized biology, shedding light not only on evolution but also on physiology, genetics and medicine. But the utility of comparisons among naturally evolved isolates is lessened by incomplete knowledge of the environment to which the organisms adapte ...
Evidences of evolution File
... – Darwin hypothesized that different beak shapes were related to food gathering – Darwin wrote “…one might really fancy that…one species has been taken and modified for different ends.” ...
... – Darwin hypothesized that different beak shapes were related to food gathering – Darwin wrote “…one might really fancy that…one species has been taken and modified for different ends.” ...
mutations - Université d`Ottawa
... At molecular level, most evolutionary changes occur by random genetic drift of alleles which are selectively neutral (or nearly so) “Survival of the luckiest” BUT …. presence of different neutral alleles in population important eg. if environment changes, certain alleles may be advantageous & select ...
... At molecular level, most evolutionary changes occur by random genetic drift of alleles which are selectively neutral (or nearly so) “Survival of the luckiest” BUT …. presence of different neutral alleles in population important eg. if environment changes, certain alleles may be advantageous & select ...
UNIT PLAN- DNA and MITOSIS
... The frequency of an allele in a gene pool of a population depends on many factors and may be stable or unstable over time. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1. Students know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. 2. Students know why alleles tha ...
... The frequency of an allele in a gene pool of a population depends on many factors and may be stable or unstable over time. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1. Students know why natural selection acts on the phenotype rather than the genotype of an organism. 2. Students know why alleles tha ...
Study Guide
... of DNA. Because mutations in somatic cells disappear when the individual dies, only mutations in somatic cells disappear when the individual dies, only mutations in cell lines that produce gametes can be passed to offspring. Mutation has two roles. It is a H-W factor and can contribute to changes ...
... of DNA. Because mutations in somatic cells disappear when the individual dies, only mutations in somatic cells disappear when the individual dies, only mutations in cell lines that produce gametes can be passed to offspring. Mutation has two roles. It is a H-W factor and can contribute to changes ...