History of Horticulture: Lectures 6–8 1
... They gather in the fruits of the earth with less labor than any other people, … for they have not the toil of breaking up the furrow with the plough, nor of hoeing, nor of any other work which all other men must labor at to obtain a crop of corn; but when the river has come of its own accord and irr ...
... They gather in the fruits of the earth with less labor than any other people, … for they have not the toil of breaking up the furrow with the plough, nor of hoeing, nor of any other work which all other men must labor at to obtain a crop of corn; but when the river has come of its own accord and irr ...
The Crown of Lower Egypt The Crown of Upper Egypt
... be short-lived, should it get into the hand of unauthorized people, he believed. After Teti’s obelisk many other pharaohs built their own obelisks. It seems as if most pharaohs had understood some parts of the secret document with its symbolic addition of an obelisk. Neither had the construction of ...
... be short-lived, should it get into the hand of unauthorized people, he believed. After Teti’s obelisk many other pharaohs built their own obelisks. It seems as if most pharaohs had understood some parts of the secret document with its symbolic addition of an obelisk. Neither had the construction of ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt and Kush
... part of the Sahara (suh • HAR • uh), the largest desert in the world. To the east, stretching to the Red Sea, is the Eastern Desert. In some places, the change from green land to barren sand is so abrupt that a person can stand with one foot in each. The ancient Egyptians called the deserts “the Red ...
... part of the Sahara (suh • HAR • uh), the largest desert in the world. To the east, stretching to the Red Sea, is the Eastern Desert. In some places, the change from green land to barren sand is so abrupt that a person can stand with one foot in each. The ancient Egyptians called the deserts “the Red ...
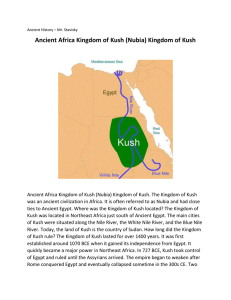
Ancient Egypt and Nubia.
... The Nile River Valley (pgs. 144 & 145) At about 3,500 miles, the is the world’s longest river. Its sources are the Blue Nile and White Nile. The Nile divides Egypt into Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. separate the two parts. ...
... The Nile River Valley (pgs. 144 & 145) At about 3,500 miles, the is the world’s longest river. Its sources are the Blue Nile and White Nile. The Nile divides Egypt into Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. separate the two parts. ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt and Kush
... part of the Sahara (suh • HAR • uh), the largest desert in the world. To the east, stretching to the Red Sea, is the Eastern Desert. In some places, the change from green land to barren sand is so abrupt that a person can stand with one foot in each. The ancient Egyptians called the deserts “the Red ...
... part of the Sahara (suh • HAR • uh), the largest desert in the world. To the east, stretching to the Red Sea, is the Eastern Desert. In some places, the change from green land to barren sand is so abrupt that a person can stand with one foot in each. The ancient Egyptians called the deserts “the Red ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt and Kush
... part of the Sahara (suh • HAR • uh), the largest desert in the world. To the east, stretching to the Red Sea, is the Eastern Desert. In some places, the change from green land to barren sand is so abrupt that a person can stand with one foot in each. The ancient Egyptians called the deserts “the Red ...
... part of the Sahara (suh • HAR • uh), the largest desert in the world. To the east, stretching to the Red Sea, is the Eastern Desert. In some places, the change from green land to barren sand is so abrupt that a person can stand with one foot in each. The ancient Egyptians called the deserts “the Red ...
Chapter 3
... are not sure exactly how the unification came about, but ancient Egyptian legends say that a ruler named Menes (mee-neez) from Upper Egypt conquered the north. Menes is also said to have founded the city of Memphis, the capital of unified Egypt. As the ruler of both kingdoms, Menes adopted the symbo ...
... are not sure exactly how the unification came about, but ancient Egyptian legends say that a ruler named Menes (mee-neez) from Upper Egypt conquered the north. Menes is also said to have founded the city of Memphis, the capital of unified Egypt. As the ruler of both kingdoms, Menes adopted the symbo ...
In what ways did location influence the history of Kush?
... Egypt once more invaded Kush and was able to destroy its capital city, Napata (NAP-uh-tuh). The Kushites decided to make Meroë their new capital. Meroë was 300 miles south of Napata, safely out of Egypt’s reach. Meroë’s location helped Kush remain an important center of trade. Traders used the Nile, ...
... Egypt once more invaded Kush and was able to destroy its capital city, Napata (NAP-uh-tuh). The Kushites decided to make Meroë their new capital. Meroë was 300 miles south of Napata, safely out of Egypt’s reach. Meroë’s location helped Kush remain an important center of trade. Traders used the Nile, ...
Chapter 10 - The Kingdom of Kush In what ways did Kush`s location
... Meroë was a large and wealthy city. It became the center of a Kushite civilization that lasted for nearly 1,000 years. At its height, the city thrived as a great center of industry as well as culture. It became especially well known for producing iron. Because of their superior knowledge of iron tec ...
... Meroë was a large and wealthy city. It became the center of a Kushite civilization that lasted for nearly 1,000 years. At its height, the city thrived as a great center of industry as well as culture. It became especially well known for producing iron. Because of their superior knowledge of iron tec ...
thutmose iii - The University of Michigan Press
... and central Nubia. This empire, delivering annual tribute and services, greatly increased the wealth of Egypt’s kings and was the basis for an imperial system that persisted, to varying degrees, well into the Twentieth Dynasty. Thutmose’s contacts beyond the empire included not only other parts of t ...
... and central Nubia. This empire, delivering annual tribute and services, greatly increased the wealth of Egypt’s kings and was the basis for an imperial system that persisted, to varying degrees, well into the Twentieth Dynasty. Thutmose’s contacts beyond the empire included not only other parts of t ...
Lesson 10 - The Kingdom of Kush Section 1
... 590 B.C.E., Egypt once more invaded Kush and was able to destroy its capital city, Napata (NAP-uh-tuh). The Kushites decided to make Meroë their new capital. Meroë was 300 miles south of Napata, safely out of Egypt’s reach. Meroë’s location helped Kush remain an important center of trade. Traders us ...
... 590 B.C.E., Egypt once more invaded Kush and was able to destroy its capital city, Napata (NAP-uh-tuh). The Kushites decided to make Meroë their new capital. Meroë was 300 miles south of Napata, safely out of Egypt’s reach. Meroë’s location helped Kush remain an important center of trade. Traders us ...
6th Grade Social Studies Curriculum Guide
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
chapter-5-social-studies-curriculum
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
Rhonda K. Hageman Brenda L. Lowe Book Review The
... (and who is also often identified as Narmer) in the first cartouche Despite the lack of explicitly written game instructions, in the Kings’ List at Abydos (Fig. 2). The meaning of the biliteral researchers have gleaned enough information from inscriptions hieroglyph mn is variously translated as “en ...
... (and who is also often identified as Narmer) in the first cartouche Despite the lack of explicitly written game instructions, in the Kings’ List at Abydos (Fig. 2). The meaning of the biliteral researchers have gleaned enough information from inscriptions hieroglyph mn is variously translated as “en ...
COMPACT MATERIAL
... 2. Pharaohs and the world of the gods Tutankhamun married Ankhesenamun, the third daughter of Akhenaten and Nefertiti, in other words his older sister or half-sister. They probably had no children. Tutankhamun reigned for nine years. Under him, Memphis became the capital of the kingdom. He went back ...
... 2. Pharaohs and the world of the gods Tutankhamun married Ankhesenamun, the third daughter of Akhenaten and Nefertiti, in other words his older sister or half-sister. They probably had no children. Tutankhamun reigned for nine years. Under him, Memphis became the capital of the kingdom. He went back ...
History_Alive-The_Ancient_World_Chapter_10
... Kingdom. In this chapter, you will learn about Egypt's neighbor to the south, the African kingdom of Kush. The civilization of Kush thrived from about 2000 H.C.K. to 350 c.i-:. Kush and Hgypt had a close relationship throughout much of Kush's long history. Signs of their close ties can be found in p ...
... Kingdom. In this chapter, you will learn about Egypt's neighbor to the south, the African kingdom of Kush. The civilization of Kush thrived from about 2000 H.C.K. to 350 c.i-:. Kush and Hgypt had a close relationship throughout much of Kush's long history. Signs of their close ties can be found in p ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt
... Narmer wore a double crown: the helmetlike white crown represented Upper Egypt, and the open red crown represented Lower Egypt. ...
... Narmer wore a double crown: the helmetlike white crown represented Upper Egypt, and the open red crown represented Lower Egypt. ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt
... Narmer wore a double crown: the helmetlike white crown represented Upper Egypt, and the open red crown represented Lower Egypt. ...
... Narmer wore a double crown: the helmetlike white crown represented Upper Egypt, and the open red crown represented Lower Egypt. ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt
... Narmer wore a double crown: the helmetlike white crown represented Upper Egypt, and the open red crown represented Lower Egypt. ...
... Narmer wore a double crown: the helmetlike white crown represented Upper Egypt, and the open red crown represented Lower Egypt. ...
R: Quiz 1 Answers - Tapestry of Grace
... The availability of the Nile for transportation encouraged Egyptians to develop boats and boating skills. Egyptians could use the Nile’s current to travel downhill and north to the Nile delta, and then could use the prevailing winds, which blew from the Mediterranean Sea, to sail south (upstream) ag ...
... The availability of the Nile for transportation encouraged Egyptians to develop boats and boating skills. Egyptians could use the Nile’s current to travel downhill and north to the Nile delta, and then could use the prevailing winds, which blew from the Mediterranean Sea, to sail south (upstream) ag ...
No Slide Title
... Behind these kings and queens were pawns; behind these temples, palaces and pyramids were the workers of the cities and peasants of the fields. The population of Egypt in the fourth century before Christ is estimated at some 7,000,000 souls. Herodotus describes them optimistically as he found them a ...
... Behind these kings and queens were pawns; behind these temples, palaces and pyramids were the workers of the cities and peasants of the fields. The population of Egypt in the fourth century before Christ is estimated at some 7,000,000 souls. Herodotus describes them optimistically as he found them a ...
The First Colonial Empire: Egypt in Nubia, 3200
... dominionup the Nile as far as the FourthCataract,far in the Africaninterior. However, the effort of maintainingan overseas empire in the face of Hittite, Assyrian, and other Asiatic powers eventuallyplaced an impossible strainon the pharaonicstate and economy, and afterthe TwentiethDynastythe foreig ...
... dominionup the Nile as far as the FourthCataract,far in the Africaninterior. However, the effort of maintainingan overseas empire in the face of Hittite, Assyrian, and other Asiatic powers eventuallyplaced an impossible strainon the pharaonicstate and economy, and afterthe TwentiethDynastythe foreig ...
File
... Capitals. The Kingdom of Kush had two different capital cities. The first capital was Napata. Napata was located along the Nile River in Northern Kush. Napata served as the capital during the height of Kush's power. Sometime around 590 BCE, the capital moved to the city of Meroe. Meroe was further ...
... Capitals. The Kingdom of Kush had two different capital cities. The first capital was Napata. Napata was located along the Nile River in Northern Kush. Napata served as the capital during the height of Kush's power. Sometime around 590 BCE, the capital moved to the city of Meroe. Meroe was further ...
Living in Ancient Egypt
... wheat, and dates, are the same as those that fed the ancient Egyptians and many of their farming methods are pretty much the same as well, for a lot of work is still done by hand or with the help of domesticated animals that have been trained to plow the fields and bring water to the crops Three tho ...
... wheat, and dates, are the same as those that fed the ancient Egyptians and many of their farming methods are pretty much the same as well, for a lot of work is still done by hand or with the help of domesticated animals that have been trained to plow the fields and bring water to the crops Three tho ...
Ancient Egypt
... 6.2.1-locate and describe the major river systems and discuss the physical settings that supported permanent settlement and early civilizations 6.2.2-trace the development of agricultural techniques that permitted the production of economic surplus and the emergence of cities as centers of culture a ...
... 6.2.1-locate and describe the major river systems and discuss the physical settings that supported permanent settlement and early civilizations 6.2.2-trace the development of agricultural techniques that permitted the production of economic surplus and the emergence of cities as centers of culture a ...
Thebes, Egypt

Thebes (Ancient Greek: Θῆβαι, Thēbai), known to the ancient Egyptians as Waset, was an ancient Egyptian city located east of the Nile about 800 kilometers (500 mi) south of the Mediterranean. Its ruins lie within the modern Egyptian city of Luxor. Karnak and the necropolis of ancient Thebes lie nearby on the Nile's west bank.