Lesson 2 - Society
... Describe the class divisions of Egyptian society Identify the following people: Menes, Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, Memphis, Kush, Napata, and Meroe ...
... Describe the class divisions of Egyptian society Identify the following people: Menes, Hatshepsut, Thutmose III, Memphis, Kush, Napata, and Meroe ...
IV. Egyptian Mathematics
... They also had less observational astronomy, though they had a 365 day year by 2776 B.C.E. Their new year was measured by the heliacal (rises at dawn and disappears in the sunlight) rising of the star we call Sirius, the dog star. To them it was the soul of Isis. Isis is the sister and wife of Osiris ...
... They also had less observational astronomy, though they had a 365 day year by 2776 B.C.E. Their new year was measured by the heliacal (rises at dawn and disappears in the sunlight) rising of the star we call Sirius, the dog star. To them it was the soul of Isis. Isis is the sister and wife of Osiris ...
File
... As a young child Akhenaten was raised in a traditional Ancient Egyptian manner and observed religious rituals to the god Amon. Ancient Egyptians were polytheistic, meaning they believed in many gods. In Thebes, Amon was the god that was elevated to the highest position above the other gods. One of t ...
... As a young child Akhenaten was raised in a traditional Ancient Egyptian manner and observed religious rituals to the god Amon. Ancient Egyptians were polytheistic, meaning they believed in many gods. In Thebes, Amon was the god that was elevated to the highest position above the other gods. One of t ...
Egypt Notes - Dublin City Schools
... Built 2 major temples, one for him, one for main wife Nefertari (hers is smaller). Declaration of his diplomatic & military success - Last great “warrior pharaoh”. His has 4 colossal seated statues more than 65 feel tall. SIZE - Usomg art to show power. Youthful, vibrant, energetic. Virile, had arou ...
... Built 2 major temples, one for him, one for main wife Nefertari (hers is smaller). Declaration of his diplomatic & military success - Last great “warrior pharaoh”. His has 4 colossal seated statues more than 65 feel tall. SIZE - Usomg art to show power. Youthful, vibrant, energetic. Virile, had arou ...
The Old Kingdom, spanning the Third to Eighth Dynasties of Egypt
... animals, plants, and even landscapes, thereby recording the essential elements of their world for eternity in scenes painted and carved on the walls of temples and tombs. These images and structures had two principal functions: to ensure an ordered existence and to defeat death by preserving life in ...
... animals, plants, and even landscapes, thereby recording the essential elements of their world for eternity in scenes painted and carved on the walls of temples and tombs. These images and structures had two principal functions: to ensure an ordered existence and to defeat death by preserving life in ...
AnEgypt - River Grove School
... the continuing existence and activity of the gods on earth by means of religious acts and to maintain the natural order such as the flow of the Nile an the fertility of the soil. He did not rule by the consent of the governed but by the decision of the gods. (Nagle, 25) ...
... the continuing existence and activity of the gods on earth by means of religious acts and to maintain the natural order such as the flow of the Nile an the fertility of the soil. He did not rule by the consent of the governed but by the decision of the gods. (Nagle, 25) ...
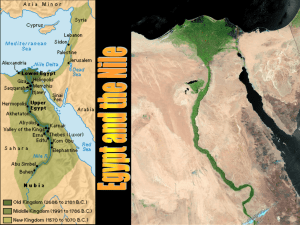
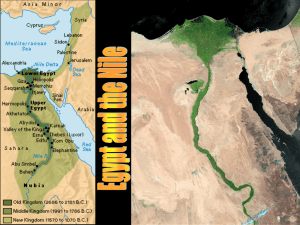
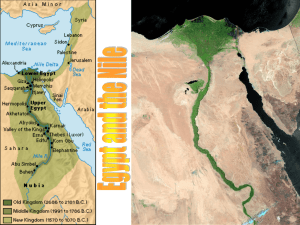
Egypt and the Nile
... the continuing existence and activity of the gods on earth by means of religious acts and to maintain the natural order such as the flow of the Nile an the fertility of the soil. He did not rule by the consent of the governed but by the decision of the gods. (Nagle, 25) ...
... the continuing existence and activity of the gods on earth by means of religious acts and to maintain the natural order such as the flow of the Nile an the fertility of the soil. He did not rule by the consent of the governed but by the decision of the gods. (Nagle, 25) ...
EGYPTIAN CHRONOLOGY
... Intermediate Period, although by the 9th Dynasty the town of Herakleopolis Magna was producing rulers. They came into conflict with a family line from Thebes in the early part of the 11th Dynasty which Egyptologists often include in this period. MIDDLE KINGDOM: 2040-1640 BC; Dynasties XI/XII The mid ...
... Intermediate Period, although by the 9th Dynasty the town of Herakleopolis Magna was producing rulers. They came into conflict with a family line from Thebes in the early part of the 11th Dynasty which Egyptologists often include in this period. MIDDLE KINGDOM: 2040-1640 BC; Dynasties XI/XII The mid ...
Queen Hatshepsut
... Seven Egyptian queens were known as Cleopatra, but the most famous was the last; Cleopatra VII. Cleopatra was also known as Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator. She was about 17 years old when she became queen. She was born in 69 BC and lived for 69 years. Cleopatra and her family were not Egyptian, but f ...
... Seven Egyptian queens were known as Cleopatra, but the most famous was the last; Cleopatra VII. Cleopatra was also known as Cleopatra VII Thea Philopator. She was about 17 years old when she became queen. She was born in 69 BC and lived for 69 years. Cleopatra and her family were not Egyptian, but f ...
File - 7th Grade Global Studies
... They often DEPICTED THEMSELVES AS WARRIORS who singlehandedly killed scores of enemies and slaughtered a whole pride of lions. ...
... They often DEPICTED THEMSELVES AS WARRIORS who singlehandedly killed scores of enemies and slaughtered a whole pride of lions. ...
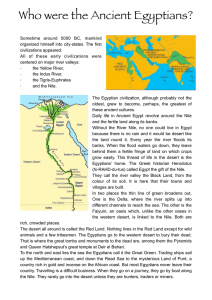
Who were the Ancient Egyptians?
... Lower Egypt ruled from a town called Pe. He wore a red crown to symbolize his authority. Nekhen was the capital city of Upper Egypt. In this kingdom, the king wore a cone-shaped white crown. ...
... Lower Egypt ruled from a town called Pe. He wore a red crown to symbolize his authority. Nekhen was the capital city of Upper Egypt. In this kingdom, the king wore a cone-shaped white crown. ...
IV. ANCIENT EGYPT A. Geography 1. The Nile River – the
... i. Menes (ca. 3100 B.C.) – He united Upper and Lower Egypt under double crown and founded Egypt 1st dynasty. He set up his capital at Memphis, between Upper and Lower Egypt. ii. Pharaohs – rulers, believed to be living gods, who had unlimited power. The pharaoh wore two crowns, a sign of his rule ov ...
... i. Menes (ca. 3100 B.C.) – He united Upper and Lower Egypt under double crown and founded Egypt 1st dynasty. He set up his capital at Memphis, between Upper and Lower Egypt. ii. Pharaohs – rulers, believed to be living gods, who had unlimited power. The pharaoh wore two crowns, a sign of his rule ov ...
Egyptian Society
... River, similar to city-states in Mesopotamia – Because of the food production, cities and towns along the Nile River began to grow in size ...
... River, similar to city-states in Mesopotamia – Because of the food production, cities and towns along the Nile River began to grow in size ...
Blue Nile and White Nile 2) How
... 12) What are the three time periods, or kingdoms, into which these dynasties are divided? The Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. 13) If you looked at a timeline of the dynasties in Ancient Egypt and saw gaps or breaks between the kingdoms, what would this tell you? Gaps meant ther ...
... 12) What are the three time periods, or kingdoms, into which these dynasties are divided? The Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom. 13) If you looked at a timeline of the dynasties in Ancient Egypt and saw gaps or breaks between the kingdoms, what would this tell you? Gaps meant ther ...
Ancient Egypt
... • The New Kingdom was a period from 1550 to 1100 BCE. • Strong pharaohs such as Ramses (?) expelled the Hyksos. • It was during this time that the Hebrews were enslaved. • The divinity of the pharaohs was reduced to a symbolic divinity. ...
... • The New Kingdom was a period from 1550 to 1100 BCE. • Strong pharaohs such as Ramses (?) expelled the Hyksos. • It was during this time that the Hebrews were enslaved. • The divinity of the pharaohs was reduced to a symbolic divinity. ...
Egypt
... the continuing existence and activity of the gods on earth by means of religious acts and to maintain the natural order such as the flow of the Nile an the fertility of the soil. He did not rule by the consent of the governed but by the decision of the gods. (Nagle, 25) ...
... the continuing existence and activity of the gods on earth by means of religious acts and to maintain the natural order such as the flow of the Nile an the fertility of the soil. He did not rule by the consent of the governed but by the decision of the gods. (Nagle, 25) ...
Early Egyptian Civilization
... • When young Amenhotep IV (1367-1350 B.C.) came to the throne he was apparently determined to resist the priesthood of Amon. • He moved his capital from Thebes (the center of Amon worship) to a city three hundred miles to the north at a place now called El Amarna. • Its god was Aton, the physical di ...
... • When young Amenhotep IV (1367-1350 B.C.) came to the throne he was apparently determined to resist the priesthood of Amon. • He moved his capital from Thebes (the center of Amon worship) to a city three hundred miles to the north at a place now called El Amarna. • Its god was Aton, the physical di ...
Ch. 3 Reading Questions
... 3. How did the institution of the pharaoh evolve, and what was the nature of the pharaoh's power through the Old Kingdom period? After 3100 B.C.E. Egyptian rulers forged all the territory between the Nile delta and the first cataract into one unified kingdom that was larger and more powerful than an ...
... 3. How did the institution of the pharaoh evolve, and what was the nature of the pharaoh's power through the Old Kingdom period? After 3100 B.C.E. Egyptian rulers forged all the territory between the Nile delta and the first cataract into one unified kingdom that was larger and more powerful than an ...
Egypt Fall 2014
... and then the body is placed in natron [a type of salt], covered entirely for 70 days... the body is washed and then wrapped from the head to the feet in linen which has been cut into strips and smeared on the underside with gum [similar to glue]. -Herodotus, Greek Historian 450 BCE ...
... and then the body is placed in natron [a type of salt], covered entirely for 70 days... the body is washed and then wrapped from the head to the feet in linen which has been cut into strips and smeared on the underside with gum [similar to glue]. -Herodotus, Greek Historian 450 BCE ...
site in Egypt - Africa Smart Grid Forum 2016
... It is known as Al-Muallaka (the hanging) because it was built on the ruins of two old towers that remained from an old fortress called the Fortress of Babylon. It was dedicated to The Virgin Mary and St. Dimiana. It dates back to the end of the 3rd Century A.D and the beginning of the 4th Century A. ...
... It is known as Al-Muallaka (the hanging) because it was built on the ruins of two old towers that remained from an old fortress called the Fortress of Babylon. It was dedicated to The Virgin Mary and St. Dimiana. It dates back to the end of the 3rd Century A.D and the beginning of the 4th Century A. ...
Study Guide: Egypt and Kush
... • Egypt controls when Thumose invades • Kush then controls Egypt – but reestablishes much of Egyptian culture • Kush defeated by Assyrians in Egypt ...
... • Egypt controls when Thumose invades • Kush then controls Egypt – but reestablishes much of Egyptian culture • Kush defeated by Assyrians in Egypt ...
3.4 Ancient Egypt Outline
... 2. c. 3100 BCE: Narmer, king of Upper Egypt, conquered Lower Egypt: united Egypt 1) Combined the two crowns to make the Double Crown 2) Established the capital at Memphis, on the boundary between Upper and Lower Egypt 3) Important artifact: Slate Palette of Narmer a) Depicts Narmer defeating the kin ...
... 2. c. 3100 BCE: Narmer, king of Upper Egypt, conquered Lower Egypt: united Egypt 1) Combined the two crowns to make the Double Crown 2) Established the capital at Memphis, on the boundary between Upper and Lower Egypt 3) Important artifact: Slate Palette of Narmer a) Depicts Narmer defeating the kin ...
Pharaoh
... A series of rulers from a single family is called a dynasty; Menes starts the 1st dynasty of Egypt. Ancient Egypt would consist of 31 dynasties, spanning 2,800 years. ...
... A series of rulers from a single family is called a dynasty; Menes starts the 1st dynasty of Egypt. Ancient Egypt would consist of 31 dynasties, spanning 2,800 years. ...
Nile
... Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death. He had an eternal spirit, or ka, that continued to take part in the governing of Egypt. Egyptians also believed that the ka remained much like a living pharaoh in its needs and pleasures. Pharaoh’s Tomb needed the following: Eternal c ...
... Egyptians believed that their pharaoh ruled even after his death. He had an eternal spirit, or ka, that continued to take part in the governing of Egypt. Egyptians also believed that the ka remained much like a living pharaoh in its needs and pleasures. Pharaoh’s Tomb needed the following: Eternal c ...
The Pyramid Builders
... their lives would be happy. If Egypt suffered hard times for a long period, the people blamed the pharaoh for angering the gods. In such a case, a rival might drive him from power and start a new dynasty. Because the pharaoh was thought to be a god, government and religion were not separate in ancie ...
... their lives would be happy. If Egypt suffered hard times for a long period, the people blamed the pharaoh for angering the gods. In such a case, a rival might drive him from power and start a new dynasty. Because the pharaoh was thought to be a god, government and religion were not separate in ancie ...
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis (Arabic: منف Manf pronounced [mænf]; Greek: Μέμφις) was the ancient capital of Aneb-Hetch, the first nome of Lower Egypt. Its ruins are located near the town of Mit Rahina, 20 km (12 mi) south of Giza.According to legend related by Manetho, the city was founded by the pharaoh Menes. Capital of Egypt during the Old Kingdom, it remained an important city throughout ancient Mediterranean history. It occupied a strategic position at the mouth of the Nile delta, and was home to feverish activity. Its principal port, Peru-nefer, harboured a high density of workshops, factories, and warehouses that distributed food and merchandise throughout the ancient kingdom. During its golden age, Memphis thrived as a regional centre for commerce, trade, and religion.Memphis was believed to be under the protection of the god Ptah, the patron of craftsmen. Its great temple, Hut-ka-Ptah (meaning ""Enclosure of the ka of Ptah""), was one of the most prominent structures in the city. The name of this temple, rendered in Greek as Aί γυ πτoς (Ai-gy-ptos) by the historian Manetho, is believed to be the etymological origin of the modern English name Egypt.The history of Memphis is closely linked to that of the country itself. Its eventual downfall is believed to be due to the loss of its economic significance in late antiquity, following the rise of coastal Alexandria. Its religious significance also diminished after the abandonment of the ancient religion following the Edict of Thessalonica.The ruins of the former capital today offer fragmented evidence of its past. They have been preserved, along with the pyramid complex at Giza, as a World Heritage Site since 1979. The site is open to the public as an open-air museum.