Ancient Egypt Test
... The Nile River allowed for the development of Ancient Egypt in the Sahara Desert. 2. What caused the soil in the Nile River Valley to become more fertile? The silt from the Nile River caused the soil to become fertile. 3. In what ways did the ancient Egyptians utilize the Nile River? The Ancient Egy ...
... The Nile River allowed for the development of Ancient Egypt in the Sahara Desert. 2. What caused the soil in the Nile River Valley to become more fertile? The silt from the Nile River caused the soil to become fertile. 3. In what ways did the ancient Egyptians utilize the Nile River? The Ancient Egy ...
Egypt - Teacher Pages
... • Egyptians found a way to measure land, or survey. • Papyrus is a reed plant that grew along the shores of the Nile. They used it to make baskets, sandals, river rafts, and later, paper. ...
... • Egyptians found a way to measure land, or survey. • Papyrus is a reed plant that grew along the shores of the Nile. They used it to make baskets, sandals, river rafts, and later, paper. ...
EGYPTIANS - Mr. Ray`s Website
... Fearing future invasions, the Egyptians took control of all possible invasion routes into the ...
... Fearing future invasions, the Egyptians took control of all possible invasion routes into the ...
IV. ANCIENT EGYPT A. Geography 1. The Nile River – the
... 1. The Nile River – the longest river in the world (4,187 miles) i. Source – Lake Victoria and the mountains of East Africa ii. Flooding – each year the river overflows when the snow melts in mountains. The river picks up bits of soil and plant life called silt, which is rich in nutrients. The silt ...
... 1. The Nile River – the longest river in the world (4,187 miles) i. Source – Lake Victoria and the mountains of East Africa ii. Flooding – each year the river overflows when the snow melts in mountains. The river picks up bits of soil and plant life called silt, which is rich in nutrients. The silt ...
Lower Egypt.
... • The Nile flowed through rocky, hilly land to the south of Egypt. At several points, this rough terrain caused cataracts, or rapids, to form. • The first cataract was located 720 miles south of the Mediterranean Sea. It marked the southern border of Upper Egypt. Five more cataracts lay farther sou ...
... • The Nile flowed through rocky, hilly land to the south of Egypt. At several points, this rough terrain caused cataracts, or rapids, to form. • The first cataract was located 720 miles south of the Mediterranean Sea. It marked the southern border of Upper Egypt. Five more cataracts lay farther sou ...
Unit Test on Ancient Egypt Study Guide Answers
... 8. It was built from more than 2 million stone blocks. It had tunnels inside. What was it? ...
... 8. It was built from more than 2 million stone blocks. It had tunnels inside. What was it? ...
Ancient Egypt Test (Part A) 30 Marks Name Multiple Choice (One
... 15. __________________and his wife Queen Nefertiti, tried to make Egypt worship only one God. 16. _________________, the hill people from Western Asia, invaded Lower Egypt using bronze weapons, ________________ and bows. ...
... 15. __________________and his wife Queen Nefertiti, tried to make Egypt worship only one God. 16. _________________, the hill people from Western Asia, invaded Lower Egypt using bronze weapons, ________________ and bows. ...
Ancient Egypt
... • The New Kingdom was a period from 1550 to 1100 BCE. • Strong pharaohs such as Ramses (?) expelled the Hyksos. • It was during this time that the Hebrews were enslaved. • The divinity of the pharaohs was reduced to a symbolic divinity. ...
... • The New Kingdom was a period from 1550 to 1100 BCE. • Strong pharaohs such as Ramses (?) expelled the Hyksos. • It was during this time that the Hebrews were enslaved. • The divinity of the pharaohs was reduced to a symbolic divinity. ...
Ancient Egypt - geostuff.net
... • Agriculture made up most of Egypt’s wealth – grain, vegetables, fruit, cattle, goats, pigs and fowl • Abundance and management of food supplies (not royal treasury) was the measure of Egypt’s wealth = full granaries, plenty of wildlife and fish, and thriving herds were the signs of prosperity. The ...
... • Agriculture made up most of Egypt’s wealth – grain, vegetables, fruit, cattle, goats, pigs and fowl • Abundance and management of food supplies (not royal treasury) was the measure of Egypt’s wealth = full granaries, plenty of wildlife and fish, and thriving herds were the signs of prosperity. The ...
Ancient Egypt Close Read
... including perch, catfish and tilapia. What's more, during the summer flood, huge numbers of water birds would flock to the Nile. These were often trapped or snared to provide a little seasonal variety on the dinner table. Ancient flood technology The Egyptians made the most of the flood season in ot ...
... including perch, catfish and tilapia. What's more, during the summer flood, huge numbers of water birds would flock to the Nile. These were often trapped or snared to provide a little seasonal variety on the dinner table. Ancient flood technology The Egyptians made the most of the flood season in ot ...
скачати - ua
... Though they were close geographically, the differences in their customs put Mesopotamia and Egypt worlds apart. These two Empires were in some ways radically different, yet in others, amazingly similar. Both built temples, farmed, had social classes, had government, and praised many gods. Under thei ...
... Though they were close geographically, the differences in their customs put Mesopotamia and Egypt worlds apart. These two Empires were in some ways radically different, yet in others, amazingly similar. Both built temples, farmed, had social classes, had government, and praised many gods. Under thei ...
Chapter 3 Egypt
... have destroyed much – Tomb of Tutankhamen – Statues have graceful lines, great dignity – Had only primitive tools to do this work ...
... have destroyed much – Tomb of Tutankhamen – Statues have graceful lines, great dignity – Had only primitive tools to do this work ...
Ancient Egypt
... 1. What is located in the burial chamber? 2. What is the name of the steps closest to the Sarcophagus? 3. What passage is not a set of steps? 4. Why would the burial chamber need to be so large? ...
... 1. What is located in the burial chamber? 2. What is the name of the steps closest to the Sarcophagus? 3. What passage is not a set of steps? 4. Why would the burial chamber need to be so large? ...
Ancient Egypt and Kush
... The _________________ found on his mummy is one of the most valuable discoveries ever made ...
... The _________________ found on his mummy is one of the most valuable discoveries ever made ...
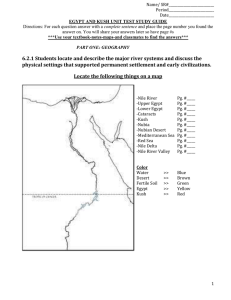
egypt and kush unit test study guide
... 6.2.6 Describe the role of Egyptian trade in the eastern Mediterranean and Nile Valley 1) What made it possible for the Assyrians to kick the Kushites out of Egypt? What did the Kushites do in response? Pg. #_____ 2) Explain the history of wars in Egypt. Who conquered who and explain the history in ...
... 6.2.6 Describe the role of Egyptian trade in the eastern Mediterranean and Nile Valley 1) What made it possible for the Assyrians to kick the Kushites out of Egypt? What did the Kushites do in response? Pg. #_____ 2) Explain the history of wars in Egypt. Who conquered who and explain the history in ...
Part 2: Archaic Egypt, Mesopotamia and Persia I. Archaic Egypt No
... 1. The Tombs of the Pharaohs a) As is now well known, the pyramids were tombs for “pharaohs” (kings of Egypt) and a few other important people (such as their queens). b) The tombs held the “mummies” of the pharaohs. c) The Egyptians believed that if a pharaoh’s body was properly cared for and preser ...
... 1. The Tombs of the Pharaohs a) As is now well known, the pyramids were tombs for “pharaohs” (kings of Egypt) and a few other important people (such as their queens). b) The tombs held the “mummies” of the pharaohs. c) The Egyptians believed that if a pharaoh’s body was properly cared for and preser ...
Book of the Dead
... Farming communities formed along the Nile during the Neolithic period - before 7000 B.C. ...
... Farming communities formed along the Nile during the Neolithic period - before 7000 B.C. ...
Egyptian Vocabulary Worksheet
... a ram-headed _________________. He was also seen as a creator-god who molded people on a potter’s w_________ from the mud of the Nile River. Slide #9 Papyrus: Long, thin ____________ that grew wild along the riverbanks of the Nile. We get our word _______________ from papyrus. Pharaoh: The term mean ...
... a ram-headed _________________. He was also seen as a creator-god who molded people on a potter’s w_________ from the mud of the Nile River. Slide #9 Papyrus: Long, thin ____________ that grew wild along the riverbanks of the Nile. We get our word _______________ from papyrus. Pharaoh: The term mean ...
YearsPeriods / DynastiesMain events and
... sculptures.xxWhen the common Egyptian died, he/she would be buried in a simple grave in a desert. They used their great art in things concerning death, also in deserts. Space was valuable, therefore, no house was left to rot. Their pyramids were made of stone and domesticated houses were made of sun ...
... sculptures.xxWhen the common Egyptian died, he/she would be buried in a simple grave in a desert. They used their great art in things concerning death, also in deserts. Space was valuable, therefore, no house was left to rot. Their pyramids were made of stone and domesticated houses were made of sun ...
test alert - TeacherWeb
... 1. A line of rulers that passes power from father to son is a _______________. 2. Egypt’s decline and fall was due in part to_________________________. 3. The reliance of Egyptians on the Nile River for farming led to ______________________. 4. Who was the chief god of the Egyptians? 5. Why did the ...
... 1. A line of rulers that passes power from father to son is a _______________. 2. Egypt’s decline and fall was due in part to_________________________. 3. The reliance of Egyptians on the Nile River for farming led to ______________________. 4. Who was the chief god of the Egyptians? 5. Why did the ...
ancient river valley civilizations
... • Ancient Egyptian society developed around the Nile River, which was geographically different from the Tigris and Euphrates — it was a much more navigable and predictable river. The Nile flooded regularly but predictably, as opposed to the Tigris and Euphrates, which had more erratic schedules and ...
... • Ancient Egyptian society developed around the Nile River, which was geographically different from the Tigris and Euphrates — it was a much more navigable and predictable river. The Nile flooded regularly but predictably, as opposed to the Tigris and Euphrates, which had more erratic schedules and ...
Family Life in Egypt
... 3. By the 1400s BC the Egyptian empire extended from the Euphrates River to southern Nubia. 4. Military conquests made Egypt rich as well as powerful. The conquered kingdoms sent gifts and treasure to the Egyptians. Growth and Effects of Trade As Egypt’s empire expanded, conquest brought Egyptian ...
... 3. By the 1400s BC the Egyptian empire extended from the Euphrates River to southern Nubia. 4. Military conquests made Egypt rich as well as powerful. The conquered kingdoms sent gifts and treasure to the Egyptians. Growth and Effects of Trade As Egypt’s empire expanded, conquest brought Egyptian ...