CPS311 Lecture: Memory Devices ... Need: Projectables: Dynamic RAM cell, ROM Basic Cell, EPROM Basic...
... on the same chip as the CPU.) c. Static RAM has fairly high power consumption, because one side of each flip flop is always conducting. This means that heat dissipation is a key limiting factor in chip capacity. (In August, 2001, IBM's web site listed SRAM's with capacities up to 8 megabits per chip ...
... on the same chip as the CPU.) c. Static RAM has fairly high power consumption, because one side of each flip flop is always conducting. This means that heat dissipation is a key limiting factor in chip capacity. (In August, 2001, IBM's web site listed SRAM's with capacities up to 8 megabits per chip ...
SRAM Design
... These are memories that require power to maintain the stored information. Randomaccess memory (RAM) is a form of computer data storage. It takes the form of integrated circuits that allow stored data to be accessed in any order. "Random" refers to the idea that any piece of data can be returned in a ...
... These are memories that require power to maintain the stored information. Randomaccess memory (RAM) is a form of computer data storage. It takes the form of integrated circuits that allow stored data to be accessed in any order. "Random" refers to the idea that any piece of data can be returned in a ...
Nonvolatile memory chips
... Because the electric charge tends to leak out, each bit in a DRAM must be refreshed (reloaded) every few msecs to prevent the data from leaking away. o Because external logic must take care of the refreshing, DRAMs require more complex interfacing than static ones, although in many applications this ...
... Because the electric charge tends to leak out, each bit in a DRAM must be refreshed (reloaded) every few msecs to prevent the data from leaking away. o Because external logic must take care of the refreshing, DRAMs require more complex interfacing than static ones, although in many applications this ...
Ultimate Memory Guide
... A logical unit of memory in a computer, the size of which the CPU determines. For example, a 32bit CPU requires memory banks that provide 32 bits of information at a time. A bank can consist of one or more memory modules. Memory Bus The bus that runs from the CPU to the memory expansion slots. Memor ...
... A logical unit of memory in a computer, the size of which the CPU determines. For example, a 32bit CPU requires memory banks that provide 32 bits of information at a time. A bank can consist of one or more memory modules. Memory Bus The bus that runs from the CPU to the memory expansion slots. Memor ...
INTRODUCTION - WordPress.com
... The word "static" indicates that the memory retains its contents as long as power remains applied, unlike dynamic RAM (DRAM) that needs to be periodically refreshed Random access means that locations in the memory can be written to or read from in any order, regardless of the memory location that wa ...
... The word "static" indicates that the memory retains its contents as long as power remains applied, unlike dynamic RAM (DRAM) that needs to be periodically refreshed Random access means that locations in the memory can be written to or read from in any order, regardless of the memory location that wa ...
POST
... After the power supply is stable and it has completed a self test – the power supply changes the voltage on the Power Good (PG) line from 0 to 5 volts. This allows the CPU to stop resetting and begin operation. (C) Richard L. Goldman ...
... After the power supply is stable and it has completed a self test – the power supply changes the voltage on the Power Good (PG) line from 0 to 5 volts. This allows the CPU to stop resetting and begin operation. (C) Richard L. Goldman ...
of embedded systems
... Connect side-by-side to increase width of words Connect top to bottom to increase number of words • added high-order address line selects smaller memory containing desired word using a decoder Combine techniques to increase number and width of words ...
... Connect side-by-side to increase width of words Connect top to bottom to increase number of words • added high-order address line selects smaller memory containing desired word using a decoder Combine techniques to increase number and width of words ...
A “short list” of embedded systems
... Connect side-by-side to increase width of words Connect top to bottom to increase number of words • added high-order address line selects smaller memory containing desired word using a decoder Combine techniques to increase number and width of words ...
... Connect side-by-side to increase width of words Connect top to bottom to increase number of words • added high-order address line selects smaller memory containing desired word using a decoder Combine techniques to increase number and width of words ...
Discriminating Between Soft Errors and Hard
... Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable f ...
... Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable f ...
Computational RAM: Implementing Processors in Memory
... with two well-known apmodes of communication possible. proaches4,11 to issuing SIMD instructions. The first is to have the host microprocessor a primitive cache. The processing elements and support cir- issue native computational RAM instructions directly via a cuitry add 18% to the area of an exist ...
... with two well-known apmodes of communication possible. proaches4,11 to issuing SIMD instructions. The first is to have the host microprocessor a primitive cache. The processing elements and support cir- issue native computational RAM instructions directly via a cuitry add 18% to the area of an exist ...
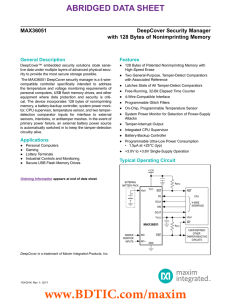
ABRIDGED DATA SHEET MAX36051 DeepCover Security Manager with 128 Bytes of Nonimprinting Memory
... DeepCover Security Manager with 128 Bytes of Nonimprinting Memory ...
... DeepCover Security Manager with 128 Bytes of Nonimprinting Memory ...
chp2 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... programs such as a database, other optimizations would be more worthwhile. There will be more architectural discussion about CPUs in later chapters. The heat produced by the CPU should be dissipated using a heat sink and a fan to avoid damage to the CPU and other components in the computer. Differen ...
... programs such as a database, other optimizations would be more worthwhile. There will be more architectural discussion about CPUs in later chapters. The heat produced by the CPU should be dissipated using a heat sink and a fan to avoid damage to the CPU and other components in the computer. Differen ...
Electronic Components and Materials
... dynamic voltage/frequency scaling architecture. This LSI has an architecture that uses a microprocessor with dedicated accelerator circuit modules and an embedded DRAM, as shown in the figure (top). The audio module is isolated in a separate domain under independent control for voltage and frequency ...
... dynamic voltage/frequency scaling architecture. This LSI has an architecture that uses a microprocessor with dedicated accelerator circuit modules and an embedded DRAM, as shown in the figure (top). The audio module is isolated in a separate domain under independent control for voltage and frequency ...
Intro to PLC
... required for solving the control program, and the I/O update time, or time required to read inputs and update outputs. The program scan time generally depends on the amount of memory taken by the control program and type of instructions used in the program. The time to make a single scan can vary fr ...
... required for solving the control program, and the I/O update time, or time required to read inputs and update outputs. The program scan time generally depends on the amount of memory taken by the control program and type of instructions used in the program. The time to make a single scan can vary fr ...
Emerging Non-volatile Memory Technologies for Reconfigurable
... defects to become an issue. The non-volatile memory technologies described in the previous section all have demonstrated retention times of 10 years or longer and can endure at least 106 write/erase cycles. B. Area, Cost, and Scalability Not only can the alternative memory technologies be fabricated ...
... defects to become an issue. The non-volatile memory technologies described in the previous section all have demonstrated retention times of 10 years or longer and can endure at least 106 write/erase cycles. B. Area, Cost, and Scalability Not only can the alternative memory technologies be fabricated ...
The Memory Hierarchy - Computer Systems: A Programmer`s
... the sensors in digital cameras and camcorders are essentially arrays of DRAM cells. Various sources of leakage current cause a DRAM cell to lose its charge within a time period of around 10 to 100 milliseconds. Fortunately, for computers operating with clock cycles times measured in nanoseconds, thi ...
... the sensors in digital cameras and camcorders are essentially arrays of DRAM cells. Various sources of leakage current cause a DRAM cell to lose its charge within a time period of around 10 to 100 milliseconds. Fortunately, for computers operating with clock cycles times measured in nanoseconds, thi ...
An Introduction to the Bell System`s First Electronic Switching Office
... book." The stored order words thus control the system sequences and decisions for both telephone calls and internal trouble detection and location. The advantages of the use of a stored program are reduced system compleixty, fewer variatioris in manufactured units, reduction in wired options, simpli ...
... book." The stored order words thus control the system sequences and decisions for both telephone calls and internal trouble detection and location. The advantages of the use of a stored program are reduced system compleixty, fewer variatioris in manufactured units, reduction in wired options, simpli ...
ch5
... (a) Negative charges form a channel between source and drain storing a logic 1 (b) Large positive voltage at gate causes negative charges to move out of channel and get trapped in floating gate storing a ...
... (a) Negative charges form a channel between source and drain storing a logic 1 (b) Large positive voltage at gate causes negative charges to move out of channel and get trapped in floating gate storing a ...
Figure 1.4
... Cells = manageable units (typically 8 bits) into which a computer’s main memory is arranged. Byte = a string of 8 bits. High-order end = the left end of the conceptual row in which the contents of a cell are laid out. Low-order end = the right end of the conceptual row in which the contents of a cel ...
... Cells = manageable units (typically 8 bits) into which a computer’s main memory is arranged. Byte = a string of 8 bits. High-order end = the left end of the conceptual row in which the contents of a cell are laid out. Low-order end = the right end of the conceptual row in which the contents of a cel ...
DesignReview1
... this memory will always be operated at room temperature, we are simulating the same in 27C temperature only. We have simulated our sub-threshold memory in PVT of TT_0.5V_27C corner and the functionality we are getting from simulation is what we intended. The supply voltage of 0.5V was chosen by the ...
... this memory will always be operated at room temperature, we are simulating the same in 27C temperature only. We have simulated our sub-threshold memory in PVT of TT_0.5V_27C corner and the functionality we are getting from simulation is what we intended. The supply voltage of 0.5V was chosen by the ...
Contents - Brunswick Bowling
... or CPU. This device is the “brain” of the computer which reads and executes program instructions, performs calculations, and makes decisions. The CPU is responsible for moving information from one part of the computer to another. For this reason, some people compare it to a central switching station ...
... or CPU. This device is the “brain” of the computer which reads and executes program instructions, performs calculations, and makes decisions. The CPU is responsible for moving information from one part of the computer to another. For this reason, some people compare it to a central switching station ...
Chapter5
... Word line capacitor is charged to write a 1 (voltage applied to Word line and to the Bit line) ...
... Word line capacitor is charged to write a 1 (voltage applied to Word line and to the Bit line) ...
THE OAK RIDGE AUTOMATIC COMPUTER
... required voltage levels shift. Figure 7 is the ORACLE memory. There are two operating modes available in the ORACLE memory system. In either case, dot-dash display is used. The dot is used to regenerate a zero, and dot-dash is used to regenerate a one. Mode 1 is the 1024-word mode in which time mult ...
... required voltage levels shift. Figure 7 is the ORACLE memory. There are two operating modes available in the ORACLE memory system. In either case, dot-dash display is used. The dot is used to regenerate a zero, and dot-dash is used to regenerate a one. Mode 1 is the 1024-word mode in which time mult ...
Random-access memory

Random-access memory (RAM /ræm/) is a form of computer data storage. A random-access memory device allows data items to be accessed (read or written) in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory. In contrast, with other direct-access data storage media such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older drum memory, the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement delays.Today, random-access memory takes the form of integrated circuits. RAM is normally associated with volatile types of memory (such as DRAM memory modules), where stored information is lost if power is removed, although many efforts have been made to develop non-volatile RAM chips. Other types of non-volatile memory exist that allow random access for read operations, but either do not allow write operations or have limitations on them. These include most types of ROM and a type of flash memory called NOR-Flash.Integrated-circuit RAM chips came into the market in the late 1960s, with the first commercially available DRAM chip, the Intel 1103, introduced in October 1970.