299-112-1
... sliding velocity. This is the case for bulk viscous materials and fluids. The asymptotic transition from a 3D bulk viscous material to a 2D interface between two such materials results in an indefinite (“zero over zero”) value of sliding velocity and in shear force proportional to the normal load, i ...
... sliding velocity. This is the case for bulk viscous materials and fluids. The asymptotic transition from a 3D bulk viscous material to a 2D interface between two such materials results in an indefinite (“zero over zero”) value of sliding velocity and in shear force proportional to the normal load, i ...
Friction
... between objects that are sliding with respect to one another. • Once enough force has been applied to the object to overcome static friction and get the object to move, the friction changes to sliding (or kinetic) friction. • Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction. • If the componen ...
... between objects that are sliding with respect to one another. • Once enough force has been applied to the object to overcome static friction and get the object to move, the friction changes to sliding (or kinetic) friction. • Sliding (kinetic) friction is less than static friction. • If the componen ...
Net External Force
... Free body diagram - sketch that shows a defined system in isolation with all the force vectors acting on the system » defined system: the body of interest » vector: arrow to represent a force – length: size of the force ...
... Free body diagram - sketch that shows a defined system in isolation with all the force vectors acting on the system » defined system: the body of interest » vector: arrow to represent a force – length: size of the force ...
Problems on Friction
... Problem 2: A 1000-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 300 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure a. (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (b) If the 300-N force is instead pulling the ...
... Problem 2: A 1000-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 300 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure a. (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (b) If the 300-N force is instead pulling the ...
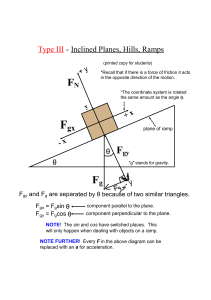
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... This is an example of a system where there are multiple masses, the Atwood machine. We will apply the concept of forces to determine the resulting acceleration. ...
... This is an example of a system where there are multiple masses, the Atwood machine. We will apply the concept of forces to determine the resulting acceleration. ...
Physics 20 - Structured Independent Learning
... The greater the normal force, the greater the interaction between the atoms and electrons of the object and the surface and, therefore, the greater the frictional force. The second factor is the nature of the interaction between object and the surface. If the surface and object are rough in texture, ...
... The greater the normal force, the greater the interaction between the atoms and electrons of the object and the surface and, therefore, the greater the frictional force. The second factor is the nature of the interaction between object and the surface. If the surface and object are rough in texture, ...
Fulltext PDF
... application of the net force exerted by the surface on the body, the weight of the body produces a torque, which is directed opposite to the angular velocity of the rolling body. Both the translational as well as the rotational speed of the body decrease under the action of the force N exerted by th ...
... application of the net force exerted by the surface on the body, the weight of the body produces a torque, which is directed opposite to the angular velocity of the rolling body. Both the translational as well as the rotational speed of the body decrease under the action of the force N exerted by th ...
Inclined Plane Problems
... 6. An incline has an angle of inclination that is adjustable. A 20 kg block is put on the incline and the angle is increased until the block begins to slide. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.6 between the block and the incline, find the angle that causes the block to slide. 7. A 70 kg ski ...
... 6. An incline has an angle of inclination that is adjustable. A 20 kg block is put on the incline and the angle is increased until the block begins to slide. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.6 between the block and the incline, find the angle that causes the block to slide. 7. A 70 kg ski ...
How is friction useful?
... object (m2) by a string. If a pulling force F of 20 N is applied to the 5.0 kg object as shown, A) what is the acceleration of the system? (Assume no friction; draw the figure and proceed). ...
... object (m2) by a string. If a pulling force F of 20 N is applied to the 5.0 kg object as shown, A) what is the acceleration of the system? (Assume no friction; draw the figure and proceed). ...
Frictional contact mechanics

Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. This can be divided into compressive and adhesive forces in the direction perpendicular to the interface, and frictional forces in the tangential direction. Frictional contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of bodies in the presence of frictional effects, whereas frictionless contact mechanics assumes the absence of such effects.Frictional contact mechanics is concerned with a large range of different scales. At the macroscopic scale, it is applied for the investigation of the motion of contacting bodies (see Contact dynamics). For instance the bouncing of a rubber ball on a surface depends on the frictional interaction at the contact interface. Here the total force versus indentation and lateral displacement are of main concern. At the intermediate scale, one is interested in the local stresses, strains and deformations of the contacting bodies in and near the contact area. For instance to derive or validate contact models at the macroscopic scale, or to investigate wear and damage of the contacting bodies’ surfaces. Application areas of this scale are tire-pavement interaction, railway wheel-rail interaction, roller bearing analysis, etc. Finally, at the microscopic and nano-scales, contact mechanics is used to increase our understanding of tribological systems, e.g. investigate the origin of friction, and for the engineering of advanced devices like atomic force microscopes and MEMS devices.This page is mainly concerned with the second scale: getting basic insight in the stresses and deformations in and near the contact patch, without paying too much attention to the detailed mechanisms by which they come about.