Predicting Individual Response with Aggregate Data
... In practice, group-level conditional means can be obtained from the group-level joint distributions of individual variables. The challenge however is that group-level joint distributions are not available directly. For example, census data are mostly reported as contingency tables of individual var ...
... In practice, group-level conditional means can be obtained from the group-level joint distributions of individual variables. The challenge however is that group-level joint distributions are not available directly. For example, census data are mostly reported as contingency tables of individual var ...
Chapter 4 - City University of Hong Kong
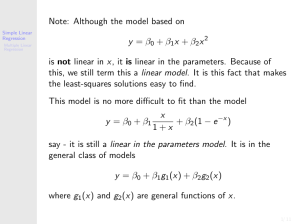
... Represent the part of the variability of the response variable Y that can be explained by the explanatory variable X or the regression model Random component (e): Represent the part of the variability of the response variable that cannot be explained by the regression model 3. Data form for simple ...
... Represent the part of the variability of the response variable Y that can be explained by the explanatory variable X or the regression model Random component (e): Represent the part of the variability of the response variable that cannot be explained by the regression model 3. Data form for simple ...
Slide 1 - UNDP Climate Change Adaptation
... In Stata, pie and bar charts are drawn using the sum of the variables specified. Therefore, any zero values will not appear in the chart, as they sum to zero and make no difference to the sum of any other values. If you have a categorical variable that contains labeled integers (for example, 0 or 1, ...
... In Stata, pie and bar charts are drawn using the sum of the variables specified. Therefore, any zero values will not appear in the chart, as they sum to zero and make no difference to the sum of any other values. If you have a categorical variable that contains labeled integers (for example, 0 or 1, ...