Ming Li Talk about Bioinformatics
... and W(n). What recursion scheme would get us there? The Master theorem Case 1 says if b=4, a=2, then log4 2 =1/2. So if we have something like T(n) = 2T(n/4) + o(√n) we would get O(√n) solution for L(n) and W(n). ...
... and W(n). What recursion scheme would get us there? The Master theorem Case 1 says if b=4, a=2, then log4 2 =1/2. So if we have something like T(n) = 2T(n/4) + o(√n) we would get O(√n) solution for L(n) and W(n). ...
Problem Set #1: Basic Data Structures
... at right give a level-order traversal. Give a (short) algorithm for performing a level-order traversal. ...
... at right give a level-order traversal. Give a (short) algorithm for performing a level-order traversal. ...
Trees Informal Definition: Tree Formal Definition: Tree
... Tree: set of nodes storing elements in a parent-child relationship with the following properties: – T has a special node r, called the root of T, with no parent node; – Each node v of T, such that v ≠ r, has a unique parent node u Note a tree cannot be empty (must have root) – Just a convention ...
... Tree: set of nodes storing elements in a parent-child relationship with the following properties: – T has a special node r, called the root of T, with no parent node; – Each node v of T, such that v ≠ r, has a unique parent node u Note a tree cannot be empty (must have root) – Just a convention ...
red-black tree
... ”symmetric binary B-trees”, but acquired its modern name in a paper in 1978 by Leo J. Guibas and Robert Sedgewick. It is complex, but has good worst-case running time for its operations and is efficient in practice: it can search, insert, and delete in O(log n) time, where n is the number of element ...
... ”symmetric binary B-trees”, but acquired its modern name in a paper in 1978 by Leo J. Guibas and Robert Sedgewick. It is complex, but has good worst-case running time for its operations and is efficient in practice: it can search, insert, and delete in O(log n) time, where n is the number of element ...
New_Laboratory_2
... Wikipedia1 defines a tree as: In graph theory, a tree is a graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. Alternatively, any connected graph with no cycles is a tree. A forest is a disjoint union of trees. Trees are widely used in computer science data structures such as binary s ...
... Wikipedia1 defines a tree as: In graph theory, a tree is a graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. Alternatively, any connected graph with no cycles is a tree. A forest is a disjoint union of trees. Trees are widely used in computer science data structures such as binary s ...
Part Seven
... Initially push Null onto STACK and then set PTR = ROOT. Then repeat the following step (1) and (2) until NULL is popped from STACK. (1) Proceed down the left-most path rooted at PTR, pushing each node N onto STACK and stopping when a node N with no left child is pushed onto STACK. (2) Pop and proces ...
... Initially push Null onto STACK and then set PTR = ROOT. Then repeat the following step (1) and (2) until NULL is popped from STACK. (1) Proceed down the left-most path rooted at PTR, pushing each node N onto STACK and stopping when a node N with no left child is pushed onto STACK. (2) Pop and proces ...
Trees
... A rooted tree has one vertex designated as the root and every other edge is directed away from the root The above tree is a binary tree We put the root at the top by convention ...
... A rooted tree has one vertex designated as the root and every other edge is directed away from the root The above tree is a binary tree We put the root at the top by convention ...
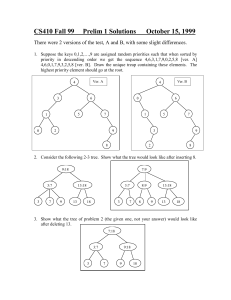
Prelim 1 solutions - Cornell Computer Science
... structures we have discussed in class without saying how they work, but describe in detail any modifications you need to do to achieve the desired time bounds, and describe in detail your implementation of count. Use any balanced tree scheme for dictionaries such as 2-3 trees or red-black trees. Aug ...
... structures we have discussed in class without saying how they work, but describe in detail any modifications you need to do to achieve the desired time bounds, and describe in detail your implementation of count. Use any balanced tree scheme for dictionaries such as 2-3 trees or red-black trees. Aug ...
Quadtree
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are most often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants or regions. The regions may be square or rectangular, or may have arbitrary shapes. This data structure was named a quadtree by Raphael Finkel and J.L. Bentley in 1974. A similar partitioning is also known as a Q-tree. All forms of quadtrees share some common features: They decompose space into adaptable cells Each cell (or bucket) has a maximum capacity. When maximum capacity is reached, the bucket splits The tree directory follows the spatial decomposition of the quadtree.