Checking Data Structure Properties Orders of Magnitude Faster
... Intuitively, we memoize whatever the program’s formal contracts need, and use the data structure itself as the storage space. A function is eligible to be memoized, if 1) it is called (directly or indirectly) from a formal contract (otherwise its value is not needed for runtime checks), 2) it has a ...
... Intuitively, we memoize whatever the program’s formal contracts need, and use the data structure itself as the storage space. A function is eligible to be memoized, if 1) it is called (directly or indirectly) from a formal contract (otherwise its value is not needed for runtime checks), 2) it has a ...
Data Structures Question Bank Multiple Choice Section 1
... 1. Each BinaryTreeNode object maintains a reference to the element stored at that node as well as references to each of the nodes (a) ...
... 1. Each BinaryTreeNode object maintains a reference to the element stored at that node as well as references to each of the nodes (a) ...
Document
... The tree is a type of Graph. Generally speaking, when you imeplement a tree, you can inherit the Graph Class and go from there, but there is a simpler way to implement trees in general. ...
... The tree is a type of Graph. Generally speaking, when you imeplement a tree, you can inherit the Graph Class and go from there, but there is a simpler way to implement trees in general. ...
Recurrence Relations
... probability on EVERY input instance but may perform poorly with low probablity on EVERY input instance – Probabilistic analysis of static hash function h says h will work well on most input instances every time but may perform poorly on some input instances every time ...
... probability on EVERY input instance but may perform poorly with low probablity on EVERY input instance – Probabilistic analysis of static hash function h says h will work well on most input instances every time but may perform poorly on some input instances every time ...
BtrFS
... Copy-on-write (COW): data is copied when it is written to add redundancy; also called shadowing Inode: data structure used to store basic information about a file system component Extent: a contiguous block of allocated storage Checksum: a hash value used to check the integrity of stored data Snapsh ...
... Copy-on-write (COW): data is copied when it is written to add redundancy; also called shadowing Inode: data structure used to store basic information about a file system component Extent: a contiguous block of allocated storage Checksum: a hash value used to check the integrity of stored data Snapsh ...
Ch 12 Collections
... list; it is most efficient if the references point from the front toward the rear of the queue • A queue can be represented by an array, using the remainder operator (%) to “wrap around” when the end of the array is reached and space is available at the front of the array ...
... list; it is most efficient if the references point from the front toward the rear of the queue • A queue can be represented by an array, using the remainder operator (%) to “wrap around” when the end of the array is reached and space is available at the front of the array ...
BSP Trees
... the visible regions • Cell-based: Preprocess to identify the potentially visible set (PVS) for each cell – Set may contain whole cells or individual objects • Point-based: Traverse the graph at runtime – Granularity can be whole cells, regions, or objects • Trend is toward point-based, but cell-base ...
... the visible regions • Cell-based: Preprocess to identify the potentially visible set (PVS) for each cell – Set may contain whole cells or individual objects • Point-based: Traverse the graph at runtime – Granularity can be whole cells, regions, or objects • Trend is toward point-based, but cell-base ...
Quadtree
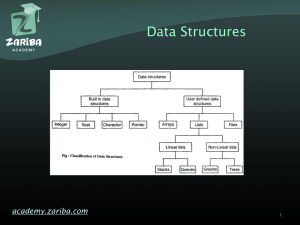
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are most often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four quadrants or regions. The regions may be square or rectangular, or may have arbitrary shapes. This data structure was named a quadtree by Raphael Finkel and J.L. Bentley in 1974. A similar partitioning is also known as a Q-tree. All forms of quadtrees share some common features: They decompose space into adaptable cells Each cell (or bucket) has a maximum capacity. When maximum capacity is reached, the bucket splits The tree directory follows the spatial decomposition of the quadtree.