AN OVERVIEW OF FRAGMENTATION DESIGN FOR DISTRIBUTED
... The emerging of smart phone and tablet market has generated big volume of data and it grown exponentially in every minute. This gigantic volume of data also has been named as Big Data. The cohesiveness between these data is low as data might or might not be related to each other. Thus, XML is a good ...
... The emerging of smart phone and tablet market has generated big volume of data and it grown exponentially in every minute. This gigantic volume of data also has been named as Big Data. The cohesiveness between these data is low as data might or might not be related to each other. Thus, XML is a good ...
Hash Tables
... expensive. Range queries, proximity queries, selection, and sorted traversals are possible only if the keys are copied into a sorted data structure. There are hash table implementations that keep the keys in order, but they are far from efficient. ...
... expensive. Range queries, proximity queries, selection, and sorted traversals are possible only if the keys are copied into a sorted data structure. There are hash table implementations that keep the keys in order, but they are far from efficient. ...
Hashing 1
... expensive. Range queries, proximity queries, selection, and sorted traversals are possible only if the keys are copied into a sorted data structure. There are hash table implementations that keep the keys in order, but they are far from efficient. ...
... expensive. Range queries, proximity queries, selection, and sorted traversals are possible only if the keys are copied into a sorted data structure. There are hash table implementations that keep the keys in order, but they are far from efficient. ...
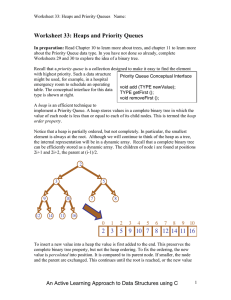
Worksheet 33: Heaps and Priority Queues
... value of each node is less than or equal to each of its child nodes. This is termed the heap order property. Notice that a heap is partially ordered, but not completely. In particular, the smallest element is always at the root. Although we will continue to think of the heap as a tree, the internal ...
... value of each node is less than or equal to each of its child nodes. This is termed the heap order property. Notice that a heap is partially ordered, but not completely. In particular, the smallest element is always at the root. Although we will continue to think of the heap as a tree, the internal ...
pptx - UTA.edu
... • You need to support as efficiently as possible: – insert(my_list, val) – create a new node with value val and insert it in the correct place in the list. If it is a duplicate (there is at least one other node with value val) it can be inserted before or after the node with the ...
... • You need to support as efficiently as possible: – insert(my_list, val) – create a new node with value val and insert it in the correct place in the list. If it is a duplicate (there is at least one other node with value val) it can be inserted before or after the node with the ...
Cse 373
... • When the tree is at its widest – how many nodes is that? • N/2: half the nodes of a tree are leaves ...
... • When the tree is at its widest – how many nodes is that? • N/2: half the nodes of a tree are leaves ...
Analysis of Approximate Nearest Neighbor Searching
... In this section we describe how kd-trees are used for performing exact and approximate nearest neighbor searching. Bentley introduced the kd-tree as a generalization of the binary search tree in higher dimensions [Ben75]. Each node of the tree is implicitly associated with a d-dimensional rectangle, ...
... In this section we describe how kd-trees are used for performing exact and approximate nearest neighbor searching. Bentley introduced the kd-tree as a generalization of the binary search tree in higher dimensions [Ben75]. Each node of the tree is implicitly associated with a d-dimensional rectangle, ...
Document
... paths from the root to all nodes in the tree. Prove by structural induction Base case. 0 is needed to get the proper value for a tree with a single node. Assume (ipl (left BT)) and (ipl (right BT)) compute the sum of the lengths of paths in the left and right subtrees The length of each path ...
... paths from the root to all nodes in the tree. Prove by structural induction Base case. 0 is needed to get the proper value for a tree with a single node. Assume (ipl (left BT)) and (ipl (right BT)) compute the sum of the lengths of paths in the left and right subtrees The length of each path ...
heap sorting - WordPress.com
... time and in-place. We then recursively sort the lesser and greater sublists. Efficient implementations of quicksort (with in-place partitioning) are typically unstable sorts and somewhat complex, but are among the fastest sorting algorithms in practice. Together with its modest O(log n) space usage, ...
... time and in-place. We then recursively sort the lesser and greater sublists. Efficient implementations of quicksort (with in-place partitioning) are typically unstable sorts and somewhat complex, but are among the fastest sorting algorithms in practice. Together with its modest O(log n) space usage, ...
Chapter 11
... Identifier – unique tag (number) identifies file within file system Type – needed for systems that support different types Location – pointer to file location on device Size – current file size Protection – controls who can do reading, writing, executing Time, date, and user identificati ...
... Identifier – unique tag (number) identifies file within file system Type – needed for systems that support different types Location – pointer to file location on device Size – current file size Protection – controls who can do reading, writing, executing Time, date, and user identificati ...
Chapter 19 Implementing Trees and Priority Queues
... General trees: Trees with no restrictions on number of children Binary trees: Each node has at most two children: left child and right child. ...
... General trees: Trees with no restrictions on number of children Binary trees: Each node has at most two children: left child and right child. ...
Slider: Incremental Sliding Window Analytics
... sub-computations, and then a dependence graph is constructed to track control and data dependencies between all sub-computations. Thereafter, a change propagation algorithm is used to update the output by propagating the changes through the graph. The idea behind change propagation is to initially i ...
... sub-computations, and then a dependence graph is constructed to track control and data dependencies between all sub-computations. Thereafter, a change propagation algorithm is used to update the output by propagating the changes through the graph. The idea behind change propagation is to initially i ...
Algorithms for on-the-fly generalization of point data using quadtrees
... structure until an empty leaf node is found or otherwise subdividing the tree further. The order of insertion does not define the shape of the tree, rather it is highly dependent on the spatial distribution of the inserted point set. For two close points many levels of partioning may be needed. This ...
... structure until an empty leaf node is found or otherwise subdividing the tree further. The order of insertion does not define the shape of the tree, rather it is highly dependent on the spatial distribution of the inserted point set. For two close points many levels of partioning may be needed. This ...
Suffix Trees and their Applications in String Algorithms
... In many applications, the text (e.g., the Oxford English Dictionary or a DNA sequence) is fixed and static, with the above string matching query being repeated on-line for different patterns many times. Thus it is better to build the suffix tree T on x$ as shown next [101]. Assume that y occurs at l ...
... In many applications, the text (e.g., the Oxford English Dictionary or a DNA sequence) is fixed and static, with the above string matching query being repeated on-line for different patterns many times. Thus it is better to build the suffix tree T on x$ as shown next [101]. Assume that y occurs at l ...
Shape Analysis for Composite Data Structures
... The new predicates can be defined using instances of the inductive predicate in combination with previously synthesized predicates, thus allowing our abstract domain to express a variety of complex data structures. We have tested our approach on set of small (i.e. <100 LOC) examples representative o ...
... The new predicates can be defined using instances of the inductive predicate in combination with previously synthesized predicates, thus allowing our abstract domain to express a variety of complex data structures. We have tested our approach on set of small (i.e. <100 LOC) examples representative o ...
ch13hashing
... • A hash function should be extremely easy to compute and should scatter the search keys evenly throughout the hash table • A collision occurs when two different search keys hash into the same array location • Hashing does not efficiently support operations that require the table items to be ordered ...
... • A hash function should be extremely easy to compute and should scatter the search keys evenly throughout the hash table • A collision occurs when two different search keys hash into the same array location • Hashing does not efficiently support operations that require the table items to be ordered ...
B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. B-trees are a good example of a data structure for external memory. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.