The first cool rocky/icy exoplanet
... much later (Einstein 1936) after intense persuasion by Czech engineer and amateur scientist R W Mandl. For those interested in the historical details, there is a delightful article by Renn, Sauer and Stachel (Renn et al. 1997). According to General Relativity (Einstein 1915), a point-like (spherical ...
... much later (Einstein 1936) after intense persuasion by Czech engineer and amateur scientist R W Mandl. For those interested in the historical details, there is a delightful article by Renn, Sauer and Stachel (Renn et al. 1997). According to General Relativity (Einstein 1915), a point-like (spherical ...
ATA2010
... SNII (progenitor M > 8M) produce -elements (O, Mg, Si, Ca,Ti), some Fe-peak elements (V … Zn), and r-process elements (eg Eu) all on timescales ~ 107 years SNIa (lower mass progenitors, probably white dwarf binaries) produce mainly Fe-peak elements but on longer timescales ~ 109 years AGB stars ov ...
... SNII (progenitor M > 8M) produce -elements (O, Mg, Si, Ca,Ti), some Fe-peak elements (V … Zn), and r-process elements (eg Eu) all on timescales ~ 107 years SNIa (lower mass progenitors, probably white dwarf binaries) produce mainly Fe-peak elements but on longer timescales ~ 109 years AGB stars ov ...
The Effect of Stacking Multiple Sub
... = signal rate from the wanted part of the image in ADUs/second = exposure time in seconds = signal rate from sky background in ADUs/second = signal rate from thermal noise in ADUS/second = readout noise in ADUs rms ...
... = signal rate from the wanted part of the image in ADUs/second = exposure time in seconds = signal rate from sky background in ADUs/second = signal rate from thermal noise in ADUS/second = readout noise in ADUs rms ...
Slide 1
... need to get my personal approval in writing. I have put 100’s of hours into the production of these presentations over the years, and I have created them for the students in our classrooms, not for fortune or fame. I hope that you do not take advantage of this work ...
... need to get my personal approval in writing. I have put 100’s of hours into the production of these presentations over the years, and I have created them for the students in our classrooms, not for fortune or fame. I hope that you do not take advantage of this work ...
HOW HIGH ARE PULSAR MOUNTAINS?
... astronomers Jocelyn Bell and Antony Hewish. They are neutron stars, which are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have run out of fuel and gone supernova (up until this discovery they had just been theoretical objects first proposed by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1934). They are very rapi ...
... astronomers Jocelyn Bell and Antony Hewish. They are neutron stars, which are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have run out of fuel and gone supernova (up until this discovery they had just been theoretical objects first proposed by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1934). They are very rapi ...
Effects of Mutual Transits by Extrasolar Planet
... of ω → 0 as a reference. In this case, motion of the two objects is nothing but a translation. Because of the time lag between the first and second transits, a certain plateau appears in light curves. The other is a slow spin case as W = 1, where W denotes the dimensionless spin ratio defined as aω/ ...
... of ω → 0 as a reference. In this case, motion of the two objects is nothing but a translation. Because of the time lag between the first and second transits, a certain plateau appears in light curves. The other is a slow spin case as W = 1, where W denotes the dimensionless spin ratio defined as aω/ ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... angle ∆Ω (see figure 5) per small time interval ∆t in the small frequency range [ν, ν + ∆ν]. Intensity is measured in units of W/m2 /sr/Hz. Here the factor cos θ comes from the fact that energy per solid angle per area is lower by a factor cos θ for an observer making an angle θ with the normal to t ...
... angle ∆Ω (see figure 5) per small time interval ∆t in the small frequency range [ν, ν + ∆ν]. Intensity is measured in units of W/m2 /sr/Hz. Here the factor cos θ comes from the fact that energy per solid angle per area is lower by a factor cos θ for an observer making an angle θ with the normal to t ...
Transiting exoplanets from the CoRoT space mission
... (Valenti & Piskunov 1996), we derived the spectral type and luminosity class of the star and the stellar parameters, which are summarized in Table 3. In short, the star is a G0 V with Teff = 5900 ± 100 K, M⋆ = 1.14 ± 0.08 M⊙ , logg = 4.3 ± 0.2 and features solar type abundances : [Fe/H]: [ 0.05 , 0. ...
... (Valenti & Piskunov 1996), we derived the spectral type and luminosity class of the star and the stellar parameters, which are summarized in Table 3. In short, the star is a G0 V with Teff = 5900 ± 100 K, M⋆ = 1.14 ± 0.08 M⊙ , logg = 4.3 ± 0.2 and features solar type abundances : [Fe/H]: [ 0.05 , 0. ...
"Cosmic furnaces"()
... released, partly as gamma rays (γ). The CNO cycle requires the presence of carbon nuclei 12C, and the cycle starts when these absorb protons. ...
... released, partly as gamma rays (γ). The CNO cycle requires the presence of carbon nuclei 12C, and the cycle starts when these absorb protons. ...
Midterm Exam, AST 203, Spring 2012 Thursday, March 15, 3:00
... 1. White dwarf (50 points) A hot white dwarf star has the same luminosity as does the Sun. It can be seen with a moderate-size telescope; it is 1016 times less bright than is the Sun. From its spectrum, its surface temperature is measured to be a blazing 60,000 K. Scaling from what you know about th ...
... 1. White dwarf (50 points) A hot white dwarf star has the same luminosity as does the Sun. It can be seen with a moderate-size telescope; it is 1016 times less bright than is the Sun. From its spectrum, its surface temperature is measured to be a blazing 60,000 K. Scaling from what you know about th ...
Chapter 8 – Continuous Absorption
... • Independent of wavelength • In hot stars (O and early B) where hydrogen dominates, then Pe~0.5Pg, and (e) is independent of pressure • In cool stars, e- scattering is small compared to other absorbers for main sequence star but is more important for higher luminosity stars ...
... • Independent of wavelength • In hot stars (O and early B) where hydrogen dominates, then Pe~0.5Pg, and (e) is independent of pressure • In cool stars, e- scattering is small compared to other absorbers for main sequence star but is more important for higher luminosity stars ...
Learning goals for Astronomy`s Final 2013
... 6. Explain azimuth and altitude as parts of a celestial coordinate system. Include when are they useful 7. Find objects in the sky by computing altitude and azimuth using your hand o If your fist fits 9 times between the horizon and the zenith, it covers 10o. Explain why o find how many degrees a ha ...
... 6. Explain azimuth and altitude as parts of a celestial coordinate system. Include when are they useful 7. Find objects in the sky by computing altitude and azimuth using your hand o If your fist fits 9 times between the horizon and the zenith, it covers 10o. Explain why o find how many degrees a ha ...
The Case against Copernicus
... kilometers in diameter was clearly huge. What could power such a body around the sun, when it was difficult just to pull a loaded wagon down the street? In contrast, the motion of celestial bodies such as stars and planets was easy to explain—astronomers since the time of Aristotle had postulated th ...
... kilometers in diameter was clearly huge. What could power such a body around the sun, when it was difficult just to pull a loaded wagon down the street? In contrast, the motion of celestial bodies such as stars and planets was easy to explain—astronomers since the time of Aristotle had postulated th ...
Notes 3 - 1 Notes 3: Formation of the solar system 3.1 Starting
... Generally hydrogen, and helium are found in atomic form (as individual atoms), though hydrogen can also be found commonly as H2, it is usually most often observed in the galaxy as H I (neutral atomic form). Hydrogen and helium are thought to be originally from the Big Bang rather than as by-products ...
... Generally hydrogen, and helium are found in atomic form (as individual atoms), though hydrogen can also be found commonly as H2, it is usually most often observed in the galaxy as H I (neutral atomic form). Hydrogen and helium are thought to be originally from the Big Bang rather than as by-products ...
File
... Identify the celestial object in our solar system that has a period of rotation that is most similar to the period of rotation of Earth's Moon. Base your answers to questions 76 through 78 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The data table shows five galaxies, A through E ...
... Identify the celestial object in our solar system that has a period of rotation that is most similar to the period of rotation of Earth's Moon. Base your answers to questions 76 through 78 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The data table shows five galaxies, A through E ...
It`s cosmic! - NSW Department of Education
... Looking back in time Now here is something to make you wonder! When you look at a star, you are seeing light that has travelled all the way from the star to your eyes. Light travels quickly but stars are so far away that it takes a long time for the light to arrive. For example, Rigel is 900 ly away ...
... Looking back in time Now here is something to make you wonder! When you look at a star, you are seeing light that has travelled all the way from the star to your eyes. Light travels quickly but stars are so far away that it takes a long time for the light to arrive. For example, Rigel is 900 ly away ...
$doc.title
... aligned it with the others. In the end, it turned out that all six supernovae are siblings, and that they all have spectra that are very blue—with the brightest wavelengths shining in the ultraviolet ...
... aligned it with the others. In the end, it turned out that all six supernovae are siblings, and that they all have spectra that are very blue—with the brightest wavelengths shining in the ultraviolet ...
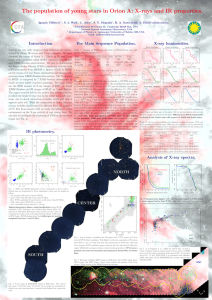
The population of young stars in Orion A: X-rays and... Ignazio Pillitteri , S. J. Wolk , L. Allen
... Through Spitzer and XMM-Newton we identify ∼ 702 PMS stars that emit in X-rays out of 1060 X-ray sources. By assuming the same fraction of X-ray detection of WTT stars and CTT stars we estimate a population of ∼ 1850 PMS stars, for an overall detection efficiency of ∼ 38% among PMS stars and a mean ...
... Through Spitzer and XMM-Newton we identify ∼ 702 PMS stars that emit in X-rays out of 1060 X-ray sources. By assuming the same fraction of X-ray detection of WTT stars and CTT stars we estimate a population of ∼ 1850 PMS stars, for an overall detection efficiency of ∼ 38% among PMS stars and a mean ...
R136a1

RMC 136a1 (usually abbreviated to R136a1) is a Wolf-Rayet star located at the center of R136, the central condensation of stars of the large NGC 2070 open cluster in the Tarantula Nebula. It lies at a distance of about 50 kiloparsecs (163,000 light-years) in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It has the highest mass and luminosity of any known star, at 265 M☉ and 8.7 million L☉, and also one of the hottest at over 50,000 K.