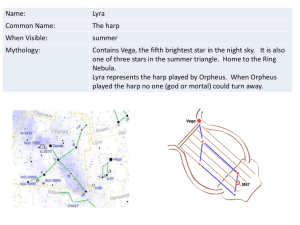
ASTR1010_HW06
... around the star. If they move around the star over time following Kepler’s Third Law, then they are planets. The trick, of course, is to get rid of most of the star’s light, otherwise you couldn’t see the faint planets. See Figures 6-16 and 6-17 for actual images. There is a fifth method, not mentio ...
... around the star. If they move around the star over time following Kepler’s Third Law, then they are planets. The trick, of course, is to get rid of most of the star’s light, otherwise you couldn’t see the faint planets. See Figures 6-16 and 6-17 for actual images. There is a fifth method, not mentio ...
1. Base your answer to the following question
... the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? (1) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. (2) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the infrared end of the spectrum and the star is moving ...
... the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? (1) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. (2) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the infrared end of the spectrum and the star is moving ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... Since a star’s brightness varies as√ the inverse square of the distance, the distance would have to decrease by a factor of 15.85 = 3.981. (I.e., 3.9812 = 15.85.) Since Barnard’s star is now at 5.9 ly, we would have to move it to 5.9/3.981 = 1.48 ly. Barnard’s star is actually moving towards us at 1 ...
... Since a star’s brightness varies as√ the inverse square of the distance, the distance would have to decrease by a factor of 15.85 = 3.981. (I.e., 3.9812 = 15.85.) Since Barnard’s star is now at 5.9 ly, we would have to move it to 5.9/3.981 = 1.48 ly. Barnard’s star is actually moving towards us at 1 ...
Our Sun - Stephen W. Ramsden
... hydrogen fuel, it either stops burning (becoming a dwarf star) or, if it is large enough (so that gravity compresses the helium strongly) it begins burning the helium into heavier elements. Because fusion reactions cease to release energy once elements heavier than iron are involved, the larger star ...
... hydrogen fuel, it either stops burning (becoming a dwarf star) or, if it is large enough (so that gravity compresses the helium strongly) it begins burning the helium into heavier elements. Because fusion reactions cease to release energy once elements heavier than iron are involved, the larger star ...
May 2014
... contains two remarkable deep sky objects. Largest of globular star clusters, Omega Centauri (originally classified as a star), and Centaurus A, a powerfully radiating disturbed galaxy. They are both visible from Southern California. But farther south are Alpha and Beta Centauri, two first magnitude ...
... contains two remarkable deep sky objects. Largest of globular star clusters, Omega Centauri (originally classified as a star), and Centaurus A, a powerfully radiating disturbed galaxy. They are both visible from Southern California. But farther south are Alpha and Beta Centauri, two first magnitude ...
Stars Take Center Stage in
... Sunspots Spotlighted in Star “Journey” Matthias Rempel , a researcher at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, provided visualizations of sunspots for the “Journey to the Stars,” after developing some of the most comprehensive numerical models of sunspots ever created. Sunspots encompass int ...
... Sunspots Spotlighted in Star “Journey” Matthias Rempel , a researcher at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, provided visualizations of sunspots for the “Journey to the Stars,” after developing some of the most comprehensive numerical models of sunspots ever created. Sunspots encompass int ...
Chapter14- Our Galaxy - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... One of these novae, however, turned out to be a Cepheid variable, a star that changes predictably in brightness ...
... One of these novae, however, turned out to be a Cepheid variable, a star that changes predictably in brightness ...
Star - AUSD Blogs
... magnetic tape and the thousands of photographs we are carrying back to earth. Other scientists can interpret them as easily as I can, and I am not one who would condone that tampering with the truth which often gave my order a bad name in the olden days. The crew are already sufficiently depressed: ...
... magnetic tape and the thousands of photographs we are carrying back to earth. Other scientists can interpret them as easily as I can, and I am not one who would condone that tampering with the truth which often gave my order a bad name in the olden days. The crew are already sufficiently depressed: ...
Unit 5 - Stars
... Then- spectrum analysis… strength of Hydrogen, starts at A, goes through the alphabet ...
... Then- spectrum analysis… strength of Hydrogen, starts at A, goes through the alphabet ...
PPT - UBC
... (e) Masses and radii of stars from binary systems, Kepler's Laws, Mass-radius relationship. Pre-reading pages 23 - 33, 48 - 49, 180 - 198. (f) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, dwarf, giant and supergiant stars, white dwarfs, first clues to stellar evolution. Pre-reading Chapter 8. ...
... (e) Masses and radii of stars from binary systems, Kepler's Laws, Mass-radius relationship. Pre-reading pages 23 - 33, 48 - 49, 180 - 198. (f) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, dwarf, giant and supergiant stars, white dwarfs, first clues to stellar evolution. Pre-reading Chapter 8. ...
Exploring the Universe
... 1. H-R diagrams are used to estimate the sizes of stars and their distances, and to infer how stars change over time a. Horizontal axis=surface temperature b. Vertical axis=absolute brightness ...
... 1. H-R diagrams are used to estimate the sizes of stars and their distances, and to infer how stars change over time a. Horizontal axis=surface temperature b. Vertical axis=absolute brightness ...
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: Astronomy 1
... Orion Nebula. Can you spot the star Betelgeuse, which shows up as a blue/white dot in the upper centre? The ring to the right of Betelgeuse is the remnant of a supernova (the dying explosion of a giant star). ...
... Orion Nebula. Can you spot the star Betelgeuse, which shows up as a blue/white dot in the upper centre? The ring to the right of Betelgeuse is the remnant of a supernova (the dying explosion of a giant star). ...
Document
... Orion Nebula. Can you spot the star Betelgeuse, which shows up as a blue/white dot in the upper centre? The ring to the right of Betelgeuse is the remnant of a supernova (the dying explosion of a giant star). ...
... Orion Nebula. Can you spot the star Betelgeuse, which shows up as a blue/white dot in the upper centre? The ring to the right of Betelgeuse is the remnant of a supernova (the dying explosion of a giant star). ...
Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... 96. The Stephan-Boltzmann law is given by Energy = σ T4. If a star's temperature doubles, how much more energy will it be giving off? 97. Compare and contrast emission lines and absorption lines. Give an example of an object that produces each. 98. Give an acronym that successfully describes the st ...
... 96. The Stephan-Boltzmann law is given by Energy = σ T4. If a star's temperature doubles, how much more energy will it be giving off? 97. Compare and contrast emission lines and absorption lines. Give an example of an object that produces each. 98. Give an acronym that successfully describes the st ...
Physics 2028: Great Ideas in Science II: The Changing Earth Module
... planetary systems have yet to be discovered using this technique. For instance, the center-of-mass of the Sun and Jupiter is just outside the surface of the Sun some 4.6 × 107 m (0.066 R ) above the Sun’s photosphere. From the distance of the nearest star α Cen, this corresponds to a total wobble d ...
... planetary systems have yet to be discovered using this technique. For instance, the center-of-mass of the Sun and Jupiter is just outside the surface of the Sun some 4.6 × 107 m (0.066 R ) above the Sun’s photosphere. From the distance of the nearest star α Cen, this corresponds to a total wobble d ...
Ch2a
... The Elevation of the North Pole Star The north pole star is always at an elevation, or altitude, a, above the northern horizon, that is equal to the latitude, of the observer. Circumpolar stars are stars which are always in view. They never set below the horizon. All stars with declinations ...
... The Elevation of the North Pole Star The north pole star is always at an elevation, or altitude, a, above the northern horizon, that is equal to the latitude, of the observer. Circumpolar stars are stars which are always in view. They never set below the horizon. All stars with declinations ...
REVIEW FOR TEST ON THURSDAY!!!! 1. Scientist can use for
... REVIEW FOR TEST ON THURSDAY!!!! 1. Scientist can use ______________________ for satellites, solar panels, telescopes, and many other instruments, to study space, or make our lives easier. A. gravity ...
... REVIEW FOR TEST ON THURSDAY!!!! 1. Scientist can use ______________________ for satellites, solar panels, telescopes, and many other instruments, to study space, or make our lives easier. A. gravity ...
Benchmark lesson
... Most people living in Florida know that the Sun constantly gives off a lot of energy. Its energy comes from reaction between the hydrogen gas and the helium gas that makes up the Sun. During the reaction, called nuclear fusion, large amounts of energy are given off in the form of light and heat. Man ...
... Most people living in Florida know that the Sun constantly gives off a lot of energy. Its energy comes from reaction between the hydrogen gas and the helium gas that makes up the Sun. During the reaction, called nuclear fusion, large amounts of energy are given off in the form of light and heat. Man ...
Schedule for Spring 2013 SCI 103 Introductory Astronomy
... Relationship between the radius, temperature and luminosity of the Sun ...
... Relationship between the radius, temperature and luminosity of the Sun ...
R136a1

RMC 136a1 (usually abbreviated to R136a1) is a Wolf-Rayet star located at the center of R136, the central condensation of stars of the large NGC 2070 open cluster in the Tarantula Nebula. It lies at a distance of about 50 kiloparsecs (163,000 light-years) in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It has the highest mass and luminosity of any known star, at 265 M☉ and 8.7 million L☉, and also one of the hottest at over 50,000 K.