7.4. Computations of Invariant factors
... – Steps: (1) Find the nonzero entry with lowest degree. Move to the first column. – (2) Make the first column of form (p,0,..,0). – (3) The first row is of form (p,a,…,b). – (3’) If p divides a,..,b, then we can make the first row (p,0,…,0) and be done. – (4) Do column operations to make the first ...
... – Steps: (1) Find the nonzero entry with lowest degree. Move to the first column. – (2) Make the first column of form (p,0,..,0). – (3) The first row is of form (p,a,…,b). – (3’) If p divides a,..,b, then we can make the first row (p,0,…,0) and be done. – (4) Do column operations to make the first ...
Lectures five and six
... polynomial can be uniquely expressed as a direct sum of homogeneous polynomials, they in fact form a direct sum decomposition into invariant subspaces. Since this is a representation of the general linear group, we can also use it to give rise to representations of subgroups of the general linear gr ...
... polynomial can be uniquely expressed as a direct sum of homogeneous polynomials, they in fact form a direct sum decomposition into invariant subspaces. Since this is a representation of the general linear group, we can also use it to give rise to representations of subgroups of the general linear gr ...
Course 1 - Glencoe
... Apply Properties to Problem Solving MUSEUMS Three friends are going to the science museum. The cost of ...
... Apply Properties to Problem Solving MUSEUMS Three friends are going to the science museum. The cost of ...
7.4. Computations of Invariant factors
... – Steps: (1) Find the nonzero entry with lowest degree. Move to the first column. – (2) Make the first column of form (p,0,..,0). – (3) The first row is of form (p,a,…,b). – (3’) If p divides a,..,b, then we can make the first row (p,0,…,0) and be done. – (4) Do column operations to make the first ...
... – Steps: (1) Find the nonzero entry with lowest degree. Move to the first column. – (2) Make the first column of form (p,0,..,0). – (3) The first row is of form (p,a,…,b). – (3’) If p divides a,..,b, then we can make the first row (p,0,…,0) and be done. – (4) Do column operations to make the first ...
3. Matrices Often if one starts with a coordinate system (x1,x2,x3
... Then the first entry of AB is 4 but the first entry of BA is 1. Finally, it is clear that matrix multiplication does not commute if one thinks about transformations. E.g. if A corresponds to reflection in the y-axis and B to rotation through π/4, then AB represents rotation through π/4 and reflectio ...
... Then the first entry of AB is 4 but the first entry of BA is 1. Finally, it is clear that matrix multiplication does not commute if one thinks about transformations. E.g. if A corresponds to reflection in the y-axis and B to rotation through π/4, then AB represents rotation through π/4 and reflectio ...
Matrices - what is a matrix
... We give these matrices special names. A square matrix, as the name suggests, has the same number of rows as columns. So the matrices A and D above are square. A diagonal matrix is a square matrix with zeros everywhere except possibly on the diagonal which runs from the top left to the bottom right. ...
... We give these matrices special names. A square matrix, as the name suggests, has the same number of rows as columns. So the matrices A and D above are square. A diagonal matrix is a square matrix with zeros everywhere except possibly on the diagonal which runs from the top left to the bottom right. ...
The inverse of a matrix
... This means A · A–1 = I and A–1 · A = I.. There are some square matrices A for which an A–1 does not exist. Such matrices are called singular or non-invertible. To solve: AX = B where A, X, B are matrices. Multiply both sides by A–1 on the left: A–1AX = A–1B I X = A–1B X = A–1B ...
... This means A · A–1 = I and A–1 · A = I.. There are some square matrices A for which an A–1 does not exist. Such matrices are called singular or non-invertible. To solve: AX = B where A, X, B are matrices. Multiply both sides by A–1 on the left: A–1AX = A–1B I X = A–1B X = A–1B ...
HALL-LITTLEWOOD POLYNOMIALS, ALCOVE WALKS, AND
... q, t, which bear his name. These polynomials generalize the spherical functions for a p-adic group, the Jack polynomials, and the zonal polynomials. At q = 0, Macdonald’s integral form polynomials Jλ (X; q, t) specialize to the Hall-Littlewood Q-polynomials, and thus they further specialize to the W ...
... q, t, which bear his name. These polynomials generalize the spherical functions for a p-adic group, the Jack polynomials, and the zonal polynomials. At q = 0, Macdonald’s integral form polynomials Jλ (X; q, t) specialize to the Hall-Littlewood Q-polynomials, and thus they further specialize to the W ...
Week 24 Geometry Assignment
... volume of a cube or rectangular prism. Work to show: #All problems: Write down the formulas, fill in, and work out. #9-14: Leave all answers in simplified radical form. #9: This is a cube, which means each face is a square. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the sides of the top of t ...
... volume of a cube or rectangular prism. Work to show: #All problems: Write down the formulas, fill in, and work out. #9-14: Leave all answers in simplified radical form. #9: This is a cube, which means each face is a square. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the lengths of the sides of the top of t ...
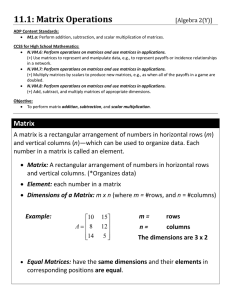
11.1: Matrix Operations - Algebra 1 and Algebra 2
... Matrix: A rectangular arrangement of numbers in horizontal rows and vertical columns. (*Organizes data) Element: each number in a matrix Dimensions of a Matrix: m x n (where m = #rows, and n = #columns) ...
... Matrix: A rectangular arrangement of numbers in horizontal rows and vertical columns. (*Organizes data) Element: each number in a matrix Dimensions of a Matrix: m x n (where m = #rows, and n = #columns) ...