
MATH36001 Background Material 2016
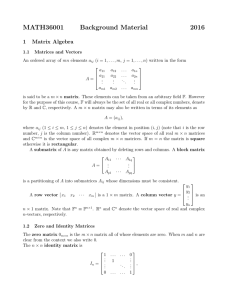
... am1 am2 . . . amn is said to be a m × n matrix. These elements can be taken from an arbitrary field F. However for the purpose of this course, F will always be the set of all real or all complex numbers, denote by R and C, respectively. A m × n matrix may also be written in terms of its elements as ...
... am1 am2 . . . amn is said to be a m × n matrix. These elements can be taken from an arbitrary field F. However for the purpose of this course, F will always be the set of all real or all complex numbers, denote by R and C, respectively. A m × n matrix may also be written in terms of its elements as ...
perA= ]TY[aMi)` « P^X = ^ = xW - American Mathematical Society
... It seems that the representation (4) is important in understanding certain properties of the multinomial distribution. The purpose of this paper is to exploit (4) to settle a conjecture due to Karlin and Rinott [4]. 2. The problem. ...
... It seems that the representation (4) is important in understanding certain properties of the multinomial distribution. The purpose of this paper is to exploit (4) to settle a conjecture due to Karlin and Rinott [4]. 2. The problem. ...
Finding the Inverse of a Matrix
... To see this, note that if A is of dimension m n and B is of dimension n m (where m n ), then the products AB and BA are of different dimensions and so cannot be equal to each other. Not all square matrices have inverses, as you will see later in this section. When a matrix does have an inverse ...
... To see this, note that if A is of dimension m n and B is of dimension n m (where m n ), then the products AB and BA are of different dimensions and so cannot be equal to each other. Not all square matrices have inverses, as you will see later in this section. When a matrix does have an inverse ...
O I A
... triangular matrices is just the incidence algebra of the linear order 1 ≤ ... ≤ n (respectively of its dual n ≤* ... ≤* 1 ). Recall that for any nxn matrix M and non-singular nxn matrix P , the incidence matrix M ' = PMP −1 is called the conjugate of M by P . We are interested in the case where P is ...
... triangular matrices is just the incidence algebra of the linear order 1 ≤ ... ≤ n (respectively of its dual n ≤* ... ≤* 1 ). Recall that for any nxn matrix M and non-singular nxn matrix P , the incidence matrix M ' = PMP −1 is called the conjugate of M by P . We are interested in the case where P is ...
Compact Course on Linear Algebra Introduction to Mobile Robotics
... § Can be defined through § the dot product of row and column vectors § the linear combination of the columns of A scaled by the coefficients of the columns of B ...
... § Can be defined through § the dot product of row and column vectors § the linear combination of the columns of A scaled by the coefficients of the columns of B ...
matrices and systems of equations
... c. This matrix has two rows and two columns. The order of the matrix is 2 2. d. This matrix has three rows and two columns. The order of the matrix is 3 2. ...
... c. This matrix has two rows and two columns. The order of the matrix is 2 2. d. This matrix has three rows and two columns. The order of the matrix is 3 2. ...
![perA= ]TY[aMi)` « P^X = ^ = xW - American Mathematical Society](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014142501_1-23faff90adae754bbfcc6088c2128850-300x300.png)




















