Word - Changing the Balance
... An Anopheles mosquito takes a blood meal, using proteins in her salvia to keep the blood from coagulating and stopping her meal. Parasites (such as Plasmodium falciparum) that cause malaria also ride along in the saliva. At this stage in their life, these disease carriers are shaped like stretched-o ...
... An Anopheles mosquito takes a blood meal, using proteins in her salvia to keep the blood from coagulating and stopping her meal. Parasites (such as Plasmodium falciparum) that cause malaria also ride along in the saliva. At this stage in their life, these disease carriers are shaped like stretched-o ...
Parasitism: The parasite niche
... The castration barnacle— Anelasma squalicola – this one’s for ...
... The castration barnacle— Anelasma squalicola – this one’s for ...
Viral and cellular microarray-based studies (virogenomics)
... Current antiviral therapeutic strategies are centered on a relatively small number of non-structural protein targets in the viral genome; for instance, there are less than ten such targets in HIV, influenza A, and hepatitis C viruses. Although initially successful, the usefulness of these strategies ...
... Current antiviral therapeutic strategies are centered on a relatively small number of non-structural protein targets in the viral genome; for instance, there are less than ten such targets in HIV, influenza A, and hepatitis C viruses. Although initially successful, the usefulness of these strategies ...
Pathogenesis
... • Pathogenesis refers both to the mechanism of infection and to the mechanism by which disease develops. ...
... • Pathogenesis refers both to the mechanism of infection and to the mechanism by which disease develops. ...
Understanding Our Environment - Mr. Prather`s Environmental
... malaria was slowed with three strategies: Applying massive amounts of pesticides to kill mosquitoes. Treating infected individuals with antimalarial drugs to ...
... malaria was slowed with three strategies: Applying massive amounts of pesticides to kill mosquitoes. Treating infected individuals with antimalarial drugs to ...
Leaky Gut Syndrome - Back In Action Chiropratic
... Leakage of imperfectly digested proteins (peptides) and carbohydrates (sugars), through a compromised intestinal lining, is now known to be a common cause of food and environmental sensitivities. Human physiology tells us that the final stage of protein and carbohydrate digestion occurs in the cells ...
... Leakage of imperfectly digested proteins (peptides) and carbohydrates (sugars), through a compromised intestinal lining, is now known to be a common cause of food and environmental sensitivities. Human physiology tells us that the final stage of protein and carbohydrate digestion occurs in the cells ...
Topics 6&11 Defence against infectious disease cont*d
... • Antibodies are proteins secreted from lymphocytes that destroy pathogen and antigen infections • B-cells make antibodies. • An antibody (also called an immunoglobulin) is a protein molecule that can bind specifically to an antigen. • Antibodies all have a similar structure composed of 4 polypeptid ...
... • Antibodies are proteins secreted from lymphocytes that destroy pathogen and antigen infections • B-cells make antibodies. • An antibody (also called an immunoglobulin) is a protein molecule that can bind specifically to an antigen. • Antibodies all have a similar structure composed of 4 polypeptid ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... Any organism that transmits infections to humans. Broader because it includes organisms that carry parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Frequently, it is an obligate host for a parasite. ...
... Any organism that transmits infections to humans. Broader because it includes organisms that carry parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Frequently, it is an obligate host for a parasite. ...
Disease evolution - Brian O`Meara Lab
... Each host infects Each host infects Each host infects 1 person on 40 people on 100 people on average average average ...
... Each host infects Each host infects Each host infects 1 person on 40 people on 100 people on average average average ...
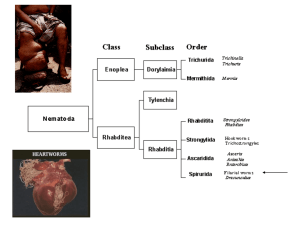
lecture_22_Mar_05_filarial worms
... Onchocerciasis is a major cause of blindness. Rarely life-threatening, the disease causes chronic suffering and severe disability. In Africa, it constitutes a serious obstacle to socioeconomic development. It is often called river blindness because of its most extreme manifestation and because the ...
... Onchocerciasis is a major cause of blindness. Rarely life-threatening, the disease causes chronic suffering and severe disability. In Africa, it constitutes a serious obstacle to socioeconomic development. It is often called river blindness because of its most extreme manifestation and because the ...
Disease Class Notes
... • Animals: Bites. Examples – dogs can spread rabies which can be fatal. Mosquitos can pass Malaria. • Contaminated objects: An uninfected person touches an object an infected person used. Example- glasses, eating utensils, toothbrushes, needles. • The environment: Food, water, soil, and air can cont ...
... • Animals: Bites. Examples – dogs can spread rabies which can be fatal. Mosquitos can pass Malaria. • Contaminated objects: An uninfected person touches an object an infected person used. Example- glasses, eating utensils, toothbrushes, needles. • The environment: Food, water, soil, and air can cont ...
ANIMAL ASSOCIATIONS SYMBIOSIS: • De Bary
... Some parasites induce cell division. Ex: Fasciola hepatica causes the thickcning of bile ducts in the sheep by stimulating cell division. This condition characterised by an increase in the number of cells is known as 'hyperplasia' Some parasites cause an increase in the size of cells. The R B C affe ...
... Some parasites induce cell division. Ex: Fasciola hepatica causes the thickcning of bile ducts in the sheep by stimulating cell division. This condition characterised by an increase in the number of cells is known as 'hyperplasia' Some parasites cause an increase in the size of cells. The R B C affe ...
The Chain of Infection
... • Fungi - Plant-like organisms that live on dead organic matter (yeasts and molds – e.g., thrush) • Rickettsiae (parasitic organisms – fleas, ticks, mites – e.g., Lyme disease) • Viruses - smallest microbes (HIV, Hepatitis B and C) • Helmiths - parasitic worms ...
... • Fungi - Plant-like organisms that live on dead organic matter (yeasts and molds – e.g., thrush) • Rickettsiae (parasitic organisms – fleas, ticks, mites – e.g., Lyme disease) • Viruses - smallest microbes (HIV, Hepatitis B and C) • Helmiths - parasitic worms ...
Parasitology Lecture: 1 Dr. Azhar 4 - 10
... parasitic disease. However, host immunity is decisive in many parasitic infections. Increased susceptibility to many parasitic infections is a consequence of immunodeficiency, as in the HIV infected. Many new parasitic infections have been identified in AIDS patients in the developed countries. ...
... parasitic disease. However, host immunity is decisive in many parasitic infections. Increased susceptibility to many parasitic infections is a consequence of immunodeficiency, as in the HIV infected. Many new parasitic infections have been identified in AIDS patients in the developed countries. ...
Schistosoma mansoni

Schistosoma mansoni is a significant parasite of humans, a trematode that is one of the major agents of the disease schistosomiasis which is one type of helminthiasis, a neglected tropical disease. The schistosomiasis caused by Schistosoma mansoni is intestinal schistosomiasis.Schistosomes are atypical trematodes in that the adult stages have two sexes (dioecious) and are located in blood vessels of the definitive host. Most other trematodes are hermaphroditic and are found in the intestinal tract or in organs, such as the liver. The lifecycle of schistosomes includes two hosts: a definitive host (i.e. human) where the parasite undergoes sexual reproduction, and a single intermediate snail host where there are a number of asexual reproductive stages.S. mansoni is named after Sir Patrick Manson, who first identified it in Formosa (now Taiwan).